15 years one-stop China custom CNC machining parts factory
 380 |
Published by VMT at Sep 10 2023
380 |
Published by VMT at Sep 10 2023
What is Color Anodizing? Advantages and Disadvantages of Color Anodizing
Color Anodizing is a surface treatment process that enhances the appearance and performance of metals, typically aluminum. This method shares similarities with traditional anodizing but introduces vibrant colors to the metal's surface. Let's delve into what Color Anodizing is and explore its advantages and disadvantages.
What is Color Anodizing?
Color Anodizing is a specialized variation of the anodizing process, primarily used to add color to aluminum and other metals. It involves the creation of an oxide layer on the metal's surface through an electrochemical process. What sets it apart is the inclusion of dyes or special electrolytes during this process, which infuse color into the oxide layer.

Advantages of Color Anodizing:
Aesthetic Appeal: The most significant advantage of Color Anodizing is its ability to provide a wide range of colors. This makes it a popular choice for products where aesthetics matter, such as consumer electronics, architectural components, and jewelry.
Corrosion Resistance: Color Anodized surfaces maintain the corrosion resistance properties of traditional anodized surfaces. This makes them suitable for applications exposed to harsh environmental conditions.
Customization: Color Anodizing allows for custom color selection, giving manufacturers the flexibility to match their products' design requirements.
Durability: The coloration becomes an integral part of the oxide layer, ensuring that it doesn't peel or chip easily. This results in long-lasting color vibrancy.
Environmentally Friendly: Color Anodizing is relatively eco-friendly, as the dyes used are usually non-toxic and can be disposed of responsibly.
Disadvantages of Color Anodizing:
Cost: One of the primary drawbacks of Color Anodizing is its cost. The additional steps and materials required for coloring make it more expensive than traditional anodizing.
Thickness Variation: Achieving consistent color across a large surface area can be challenging. Variations in oxide layer thickness can lead to slight color variations.
Limited to Certain Metals: Color Anodizing is most commonly applied to aluminum and its alloys. It may not be suitable for all types of metals.
Complex Process: The addition of colorants and special electrolytes makes the Color Anodizing process more complex compared to traditional anodizing.
In conclusion, Color Anodizing is a versatile surface treatment method that brings a burst of colors to metals while retaining their corrosion resistance. It's an excellent choice for products where aesthetics are a priority. However, it comes at a higher cost and may have slight variations in color due to the intricacies of the process. Manufacturers should carefully consider their project's requirements and budget before opting for Color Anodizing.
Variations in Color Anodizing and Anodizing Processes
Both Color Anodizing and Anodizing are versatile surface treatment methods, but they can be further categorized into various process variations. Let's explore the different ways these methods can be employed:
Color Anodizing Process Variations
1. Standard Color Anodizing:
This is the most common form of Color Anodizing, where various colors are achieved by introducing dyes or pigments during the anodizing process. It's widely used for consumer products, architectural elements, and decorative components.
2. Two-Step Color Anodizing:
In this method, two different colors are applied to the same surface, creating a dual-tone or gradient effect. It requires precise control of the anodizing parameters to achieve the desired result.
3. Hardcoat Color Anodizing:
Hardcoat Color Anodizing is a specialized variation known for its enhanced durability and wear resistance. It's often used in applications where the treated metal needs to withstand harsh conditions.
Anodizing Process Variations
1. Type I - Chromic Acid Anodizing:
This process uses chromic acid and is known for its thin and non-porous oxide layer. It's primarily used for corrosion resistance and is common in the aerospace industry.
2. Type II - Sulfuric Acid Anodizing:
Sulfuric Acid Anodizing is the most widely used anodizing method. It provides a thicker and more porous oxide layer than Type I, making it suitable for coloring and dyeing.
3. Type III - Hard Anodizing:
Hard Anodizing, also known as Type III Anodizing, produces a very thick and hard oxide layer. It's valued for its exceptional wear resistance and is often used in the automotive and defense industries.
4. Type IV - Boric-Sulfuric Acid Anodizing:
This relatively new variation of anodizing is gaining attention for its improved corrosion resistance and adhesion properties, making it suitable for aerospace and automotive applications.
5. Type V - Phosphoric Acid Anodizing:
Phosphoric Acid Anodizing is used for specific applications where a non-chromated, low electrical resistance surface is required. It's commonly seen in the electronics industry.
6. Mixed Acid Anodizing:
This process involves a combination of different acids, offering a unique set of properties tailored to specific needs, such as enhanced corrosion resistance or improved adhesion.
In summary, both Color Anodizing and Anodizing processes come in various forms, each with its own set of advantages and applications. The choice of a particular method depends on factors such as the type of metal, desired finish, and the specific requirements of the project. Manufacturers can select the most suitable process variation to achieve the desired outcome.
What is Anodizing? Advantages and Disadvantages of Anodizing
Anodizing is a surface treatment process widely used to enhance the properties of metals, particularly aluminum. This method involves the controlled oxidation of a metal's surface to create a protective layer of oxide. Let's delve into what anodizing is and explore its pros and cons.
What is Anodizing?
Anodizing is an electrochemical process that transforms the surface of metals, primarily aluminum, into a durable and corrosion-resistant oxide layer. This process involves immersing the metal in an electrolytic bath and applying an electrical current, which causes the metal's surface to oxidize. The result is the formation of a stable oxide layer that adheres tightly to the metal.
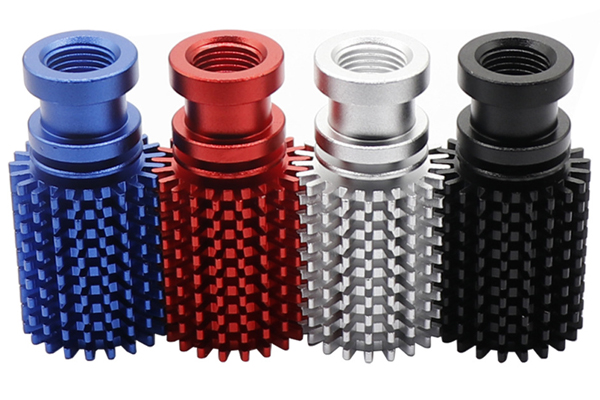

Advantages of Anodizing:
Enhanced Corrosion Resistance: Anodizing significantly improves the metal's resistance to corrosion, making it ideal for applications exposed to harsh environmental conditions.
Improved Durability: The oxide layer created through anodizing is hard and wear-resistant, increasing the overall durability of the treated metal.
Decorative Finish: Anodizing can produce a variety of finishes, including a natural silver color or more colorful options through dyeing. This versatility makes it suitable for both functional and aesthetic purposes.
Electrical Insulation: The oxide layer acts as an electrical insulator, making anodized aluminum suitable for electronic and electrical applications.
Paint Adhesion: Anodized surfaces provide excellent adhesion for paints and adhesives, enhancing their longevity.
Environmental Friendliness: Anodizing is a relatively eco-friendly process, with minimal waste production compared to some other surface treatment methods.
Disadvantages of Anodizing:
Cost: Anodizing can be more expensive than some other surface treatment methods due to the need for specialized equipment and processes.
Color Limitations: While anodizing can offer various colors through dyeing, it may have limitations in achieving specific custom colors compared to alternative coloring methods.
Thickness Variations: Achieving consistent oxide layer thickness across large surfaces can be challenging, leading to slight variations in appearance.
Limited to Certain Metals: Anodizing is primarily used for aluminum and its alloys. It may not be suitable for all types of metals.
In conclusion, anodizing is a valuable surface treatment method that offers significant advantages such as enhanced corrosion resistance, improved durability, and a range of finish options. However, it comes at a cost and may have limitations in terms of color customization. Manufacturers should carefully consider their project's requirements and budget when opting for anodizing as a surface treatment.
Color Anodizing vs. Anodizing: A Detailed Comparison
Surface treatment plays a crucial role in improving the appearance and functionality of metals, especially aluminum. Two common methods for achieving this are Color Anodizing and Anodizing. Let's delve into a detailed comparison of these two processes to understand their differences.
Chemical Process:
Color Anodizing: Color Anodizing is a specialized variation of anodizing. It involves introducing dyes or special electrolytes during the anodizing process to infuse colors into the oxide layer. This additional step in the chemical process distinguishes it from traditional anodizing.
Anodizing: Anodizing, in its standard form, relies on the natural oxidation of the metal's surface when immersed in an electrolytic bath. It creates a protective oxide layer without introducing colorants.
Appearance and Color:
Color Anodizing: As the name suggests, Color Anodizing offers a wide range of vibrant colors, making it ideal for applications where aesthetics are essential. The color possibilities are virtually limitless, allowing for creative and customized finishes.

Anodizing: Traditional anodizing typically results in a silver or grayish finish, which is the natural color of the oxide layer. While it provides a clean and uniform appearance, it lacks the diverse color options of Color Anodizing.
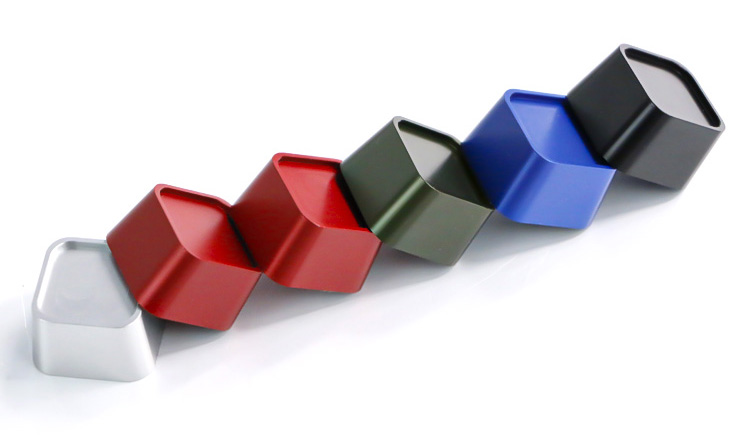
Corrosion Resistance:
Color Anodizing: Color Anodized surfaces maintain corrosion resistance properties similar to traditional anodized surfaces. However, there might be a slight reduction in corrosion resistance due to the introduction of colorants.
Anodizing: Anodizing, in general, enhances the corrosion resistance of metals significantly, making it a preferred choice in industries where protection against environmental factors is critical.
Applications:
Color Anodizing: Color Anodizing finds its niche in consumer products, architectural elements, jewelry, and anywhere visual appeal is crucial. It's perfect for applications where aesthetics play a dominant role.
Anodizing: Traditional anodizing is prevalent in industries like aerospace, automotive manufacturing, and construction, where the focus is primarily on durability and corrosion resistance.
Cost Comparison:
Color Anodizing: Color Anodizing is often more expensive than traditional anodizing due to the additional steps and materials required for coloration.
Anodizing: Traditional anodizing tends to be more cost-effective, making it a practical choice for projects with budget constraints.
Sustainability Considerations:
Color Anodizing: Color Anodizing may involve the use of dyes and chemicals for coloration, which requires proper disposal and management. However, it's relatively eco-friendly compared to some alternative surface treatment methods.
Anodizing: Traditional anodizing is generally more environmentally friendly as it relies on the natural oxidation process without the need for additional colorants or chemicals.
In summary, Color Anodizing and Anodizing are both valuable surface treatment methods, each with its own set of advantages and applications. The choice between them depends on specific project requirements, with Color Anodizing excelling in aesthetics and customization, while traditional Anodizing focuses on durability and corrosion resistance. Manufacturers should carefully consider their project's needs and budget when deciding which method to employ.
Color Anodizing vs. Anodizing: Surface Effects and Cost Comparison
Color Anodizing and Anodizing are surface treatment processes that offer distinct visual effects and cost differences. Let's compare the surface effects and pricing of these two methods to help you understand their unique characteristics.
Surface Effects:
Color Anodizing:
Visual Appeal: Color Anodizing is renowned for its vibrant and customizable color options. It allows for a broad spectrum of colors, making it ideal for applications where aesthetics are paramount.
Customization: You can achieve a wide range of custom colors, gradients, and even two-tone effects using Color Anodizing.
Decorative Finish: It provides an eye-catching, decorative finish that enhances the overall appearance of the treated material.
Anodizing:
Natural Finish: Traditional Anodizing typically results in a natural silver or grayish finish. It offers a clean and uniform appearance.
Limited Color Options: Anodizing, in its standard form, does not introduce color to the oxide layer, so it lacks the diverse color possibilities of Color Anodizing.
Functional Durability: While it may lack colorful aesthetics, traditional Anodizing excels in providing functional benefits such as corrosion resistance and durability.
Cost Comparison:
Color Anodizing:
Costlier: Color Anodizing is generally more expensive than traditional Anodizing.
Additional Steps: The higher cost is due to the added complexity of introducing dyes or colorants during the anodizing process. These additional steps and materials contribute to the increased pricing.
Customization Costs: Achieving custom colors or intricate designs can further raise the overall cost.
Anodizing:
More Economical: Traditional Anodizing is often more cost-effective compared to Color Anodizing.
Simplified Process: The straightforward process of creating a protective oxide layer through anodizing makes it more budget-friendly.
Budget-Friendly Option: Anodizing is a practical choice for projects with budget constraints where the primary focus is on functionality rather than colorful aesthetics.
In summary, the choice between Color Anodizing and Anodizing primarily depends on your project's specific requirements. Color Anodizing offers stunning and customizable visual effects but comes at a higher cost due to added complexity. Traditional Anodizing provides functional benefits at a more budget-friendly price point, making it ideal for applications where aesthetics take a back seat to durability and corrosion resistance.
Color Anodizing vs. Anodizing: Which is Right for You?
The choice between Color Anodizing and Anodizing depends on your specific project requirements and priorities. Let's consider which one might be the most suitable option for your needs.
Choose Color Anodizing if:
Aesthetics Matter: If your project places a high emphasis on visual appeal and you require a wide range of vibrant and customizable colors, Color Anodizing is the preferred choice.
Customization is Key: When you need custom colors, gradients, or intricate designs to match your product's unique style or branding, Color Anodizing offers the flexibility you need.
Decorative Finish Required: For applications where the surface finish needs to be not only protective but also decorative, Color Anodizing excels in providing an eye-catching appearance.
Budget is Not a Primary Concern: If budget constraints are not a limiting factor for your project, and you're willing to invest more for the desired colorful aesthetics, Color Anodizing is a great option.
Choose Anodizing if:
Durability is Paramount: When the primary focus of your project is on functional durability and corrosion resistance, traditional Anodizing is a solid choice.
Cost-Efficiency Matters: If your project has budget constraints and you need a cost-effective surface treatment that still provides excellent protective properties, Anodizing is the more economical option.
Natural Finish is Acceptable: When the natural silver or grayish finish of anodized surfaces aligns with your project's requirements, traditional Anodizing provides a clean and uniform appearance.
Functional Benefits Outweigh Aesthetics: If your project's success relies more on functional benefits like corrosion resistance, electrical insulation, and wear resistance rather than colorful aesthetics, Anodizing is the practical choice.
In conclusion, the decision between Color Anodizing and Anodizing hinges on your project's unique needs. If aesthetics, customization, and a decorative finish are paramount and budget is not a concern, Color Anodizing is the way to go. On the other hand, if cost-efficiency, durability, and functional benefits take precedence, traditional Anodizing is the more suitable option. Carefully evaluating your project's requirements will guide you towards the right choice for your surface treatment needs.
Color Anodizing and Anodizing Applications
Both Color Anodizing and Anodizing are valuable surface treatment processes with distinct applications. Let's explore where each of these methods finds its place in various industries and projects.
Applications of Color Anodizing:
Consumer Electronics: Color Anodizing is commonly used to enhance the visual appeal of electronic devices, such as smartphones, tablets, and laptops. It allows manufacturers to offer products in a range of stylish colors.

Architectural Components: Color Anodized aluminum is popular in architecture for applications like window frames, facades, and decorative elements. It provides both aesthetics and corrosion resistance.
Jewelry: Jewelry designers use Color Anodizing to create vibrant and customized pieces. It offers a durable finish that resists tarnishing and wear.
Aerospace: While functionality is critical in aerospace applications, Color Anodizing can be used for labeling and color-coding components, making it easier for maintenance and identification.
Automotive Accessories: Color Anodizing is employed for various automotive parts like trim, wheels, and decorative elements to enhance aesthetics while maintaining durability.

Sporting Goods: Sports equipment, such as bicycle frames, golf clubs, and racquets, can benefit from Color Anodizing to achieve a desired appearance and corrosion resistance.
Applications of Anodizing:
Aerospace: Anodizing is extensively used in the aerospace industry for its exceptional corrosion resistance properties. Aircraft components, such as structural parts and fasteners, often undergo Anodizing for protection against harsh environmental conditions.
Automotive Manufacturing: Anodizing plays a vital role in automotive applications. It is used for various parts, including pistons, cylinder heads, and suspension components, to enhance corrosion resistance and improve wear resistance.
Construction: Anodized aluminum is commonly used in the construction industry for building facades, window frames, and structural components. It provides durability and an attractive finish.
Electronics: Anodizing is employed in electronic devices and components for its insulating properties. It helps prevent electrical short circuits and provides protection against corrosion.
Medical Equipment: Anodizing is utilized in medical equipment to ensure a clean and corrosion-resistant surface, crucial for maintaining sterility and durability.
Military and Defense: Anodized parts are used in military applications for their durability and resistance to harsh environments. They can be found in weapons, vehicles, and communication equipment.
Industrial Machinery: Anodizing enhances the performance and longevity of various industrial machinery components, ensuring they can withstand rigorous use.
In summary, Color Anodizing is prized for its ability to provide vibrant colors and is often used in industries where aesthetics are essential. Anodizing, on the other hand, excels in providing functional benefits like corrosion resistance and is widely employed in industries where durability and protection against environmental factors are critical. The choice between these methods depends on the specific requirements of each project and the balance between aesthetics and functionality.
Find a reliable partner to make a choice
Do you know how to choose the right finish for your project? VMT has 15 years of experience in surface treatment experts to choose the appropriate surface treatment for you to improve the surface texture and performance of CNC machining parts.
We provide custom CNC metal machining surface treatment services for steel, aluminum, titanium, copper and more. Whether it is prototyping or small batch parts production,our team of professional engineers can choose the right surface treatment for you, and meet your needs with high standards. Then, simply upload your CAD files to our email: inquiry@vimetal.com.cn to get a project quote.
Frequently Asked Questions about Color Anodizing and Anodizing
Let's address some common questions and concerns regarding Color Anodizing and Anodizing to provide you with a better understanding of these surface treatment processes.
FAQs about Color Anodizing:
1. What is Color Anodizing?
Answer: Color Anodizing is a specialized variation of the anodizing process that introduces vibrant colors to the oxide layer on metals, primarily aluminum. It involves the use of dyes or special electrolytes during the anodizing process to achieve the desired colors.
2. Can I choose custom colors with Color Anodizing?
Answer: Yes, Color Anodizing offers the flexibility to select custom colors based on your project's requirements. You can achieve a wide range of colors, gradients, and even two-tone effects.
3. Is Color Anodizing as durable as traditional Anodizing?
Answer: Color Anodizing provides good durability and corrosion resistance, but there might be a slight reduction in corrosion resistance due to the introduction of colorants. It's suitable for applications where aesthetics are crucial.
4. What industries commonly use Color Anodizing?
Answer: Color Anodizing is prevalent in industries such as consumer electronics, architectural components, jewelry, and any application where vibrant aesthetics are essential.
5. Is Color Anodizing more expensive than traditional Anodizing?
Answer: Yes, Color Anodizing is typically more expensive due to the additional steps and materials required for coloration. The customization options can also affect the cost.
FAQs about Anodizing:
1. What is Anodizing?
Answer: Anodizing is an electrochemical process that forms a protective oxide layer on metals, primarily aluminum. It enhances corrosion resistance and durability while maintaining a natural silver or grayish appearance.
2. What industries commonly use Anodizing?
Answer: Anodizing is widely used in aerospace, automotive manufacturing, construction, electronics, medical equipment, and various industrial applications where corrosion resistance and durability are paramount.
3. Does Anodizing change the metal's appearance?
Answer: Traditional Anodizing typically results in a natural silver or grayish finish, which is the color of the oxide layer. It provides a clean and uniform appearance without introducing vibrant colors.
4. Is Anodizing eco-friendly?
Answer: Anodizing is considered relatively eco-friendly as it produces minimal waste compared to some other surface treatment methods. The process relies on natural oxide formation without the need for additional colorants or chemicals.
5. Can Anodizing be used for decorative purposes?
Answer: While Anodizing is primarily valued for its functional benefits like corrosion resistance, it can also provide a clean and attractive finish. However, it may not offer the same range of vibrant colors as Color Anodizing for purely decorative applications.
These FAQs should help clarify the key aspects of both Color Anodizing and Anodizing, allowing you to make informed decisions based on your project's requirements.
