15 years one-stop China custom CNC machining parts factory
 543 |
Published by VMT at Sep 13 2023
543 |
Published by VMT at Sep 13 2023
What is Powder Coated Brass?
Powder coating brass refers to the process of applying a dry powder coating material to the surface of brass objects or components. This coating material is typically a mixture of finely ground particles of pigment and resin. The process involves electrostatically charging the powder particles and then applying them to the grounded brass surface. Once the powder is evenly distributed on the brass, the object is heated in an oven. During the curing process, the powder melts, flows, and forms a continuous, durable, and protective coating on the brass surface.
Powder coating is often used for its ability to provide a uniform and long-lasting finish to brass items. It offers several advantages, including corrosion resistance, a wide range of color options, durability, and environmental friendliness (low VOC emissions).
The choice to powder coat brass is typically made for decorative and protective purposes, enhancing the appearance of brass objects and providing them with an additional layer of resistance to corrosion, wear, and environmental factors.
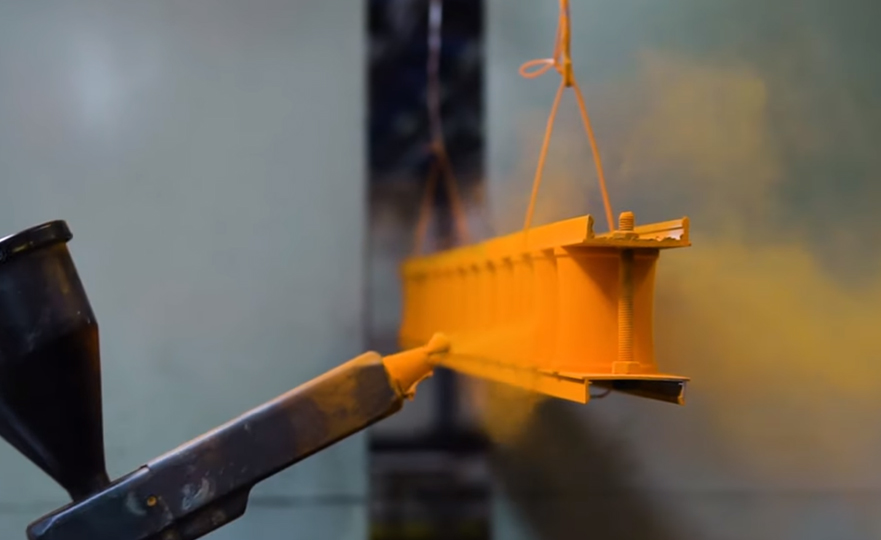
Can Brass be Powder Coated?
Yes, it is possible to apply powder coating as a surface treatment to brass. While powder coating is more commonly associated with other metals like steel and aluminum, brass can also be powder coated to achieve certain benefits. Here are some key considerations when powder coating brass:
Surface Preparation: Proper surface preparation is essential. The brass surface should be thoroughly cleaned, degreased, and free of any contaminants or oxidation before applying the powder coating.
Adhesion Promoters: To improve adhesion, it may be necessary to use adhesion promoters or primers designed for use on non-traditional substrates like brass.
Curing Temperatures: Be mindful of curing temperatures. Brass has a lower melting point than some other metals, so it's important to select a powder coating material and curing process that does not exceed the brass's melting point to avoid damage.
Color and Finish: Choose the desired color and finish for the powder coating carefully. Powder coating offers a wide range of colors and finishes, including gloss, matte, textured, and metallic effects.
Durability: Powder coating can provide brass with added durability, corrosion resistance, and resistance to chipping and fading, enhancing its longevity and appearance.
Consult Professionals: For powder coating brass, it's advisable to consult with experienced powder coating professionals who have expertise in handling brass substrates. They can recommend the appropriate materials and processes for your specific application.
While powder coating brass is possible, it's not as common as other surface treatments for this metal. The choice to use powder coating on brass should be based on your specific needs, design preferences, and the expertise of professionals in the field.
Why Choose Brass Powder Coating? Can Plastic be Powder Coated?
Choosing powder coating for brass or plastic surfaces depends on the specific requirements of your project. Here's why you might consider each option:
Why Choose Powder Coating for Brass:
Enhanced Durability: Powder coating can significantly improve the durability of brass objects. It provides resistance to chipping, fading, wear, and corrosion, which can extend the lifespan of brass items.
Customization: Powder coating offers a wide range of color options and finishes. It allows you to customize the appearance of brass items to meet design and aesthetic preferences.
Environmental Friendliness: Powder coating is an environmentally friendly process with low VOC emissions and minimal waste generation, making it a sustainable choice.
Protection: Powder coating acts as a protective barrier, shielding brass from environmental factors, moisture, and chemicals.
Uniform Finish: Powder coating provides a uniform and consistent finish, even on complex or irregularly shaped brass objects.
Can Plastic Be Powder Coated?
While it is technically possible to powder coat certain types of plastic, it's not a common practice. Powder coating is primarily designed for use on metal surfaces, as the process relies on the electrostatic attraction between the charged powder particles and the grounded metal substrate.
Powder coating plastic can be challenging due to the insulating properties of most plastics, which can interfere with the electrostatic coating process. To overcome this, some plastics are pre-treated with conductive materials or coatings to make them suitable for powder coating.
In general, if you need to coat plastic items, other methods like spray painting, dip coating, or specialized plastic coatings may be more suitable and effective.
In summary, choosing powder coating for brass can offer durability, customization, and environmental benefits. However, powder coating is not commonly used on plastic surfaces due to the technical challenges involved and the availability of more suitable coating methods for plastic materials.
Which Metals are Suitable for Powder Coating Finishes?
Powder coating is a versatile surface treatment method that is suitable for a wide range of metals. Some of the metals that are commonly used with powder coating include:

Steel: Powder coating is extensively used on steel surfaces in various industries. It provides excellent corrosion resistance and durability, making it ideal for applications exposed to harsh environments.
Aluminum: Aluminum is another metal commonly powder coated. Powder coating enhances aluminum's corrosion resistance and provides a durable finish. It's widely used in architectural, automotive, and industrial applications.

Copper: While less common than steel and aluminum, copper can also be powder coated. Powder coating adds a layer of protection to copper surfaces and can be used for decorative purposes.

Stainless Steel: Stainless steel is known for its corrosion resistance, but powder coating can further improve its aesthetics and provide additional protection against environmental factors.

Cast Iron: Cast iron parts, such as ornamental pieces and machinery components, can benefit from powder coating. It helps prevent rust and enhances the appearance of cast iron.
Galvanized Steel: Powder coating can be applied to galvanized steel to improve its appearance and increase its resistance to corrosion.
Brass: While less common, brass can also be powder coated for added protection and to achieve specific aesthetic finishes.
Bronze: Bronze is occasionally powder coated, especially in artistic and decorative applications, to protect against environmental factors and enhance the appearance.
Mild Steel: Mild steel is frequently powder coated in industrial settings to provide rust protection and a durable finish.
It's important to note that the success of powder coating depends on proper surface preparation, the choice of the appropriate powder coating material, and adherence to curing processes. Different metals may require specific pretreatment steps to ensure adhesion and longevity of the powder coating.
Overall, powder coating is a versatile and effective method for enhancing the durability and appearance of various metal surfaces. The choice of metal should be based on the specific application, environmental conditions, and desired performance characteristics.
Brass Parts Powder Coating Process
The powder coating process for brass parts involves several steps to ensure a successful and durable finish. Here's a general outline of the powder coating process for brass components:
1. Surface Preparation:
Clean the brass parts thoroughly to remove dirt, oils, and contaminants. This can be done through solvent cleaning or chemical cleaning methods.
2. Pre-Treatment (Optional):
Depending on the condition of the brass and the desired finish, you may choose to apply a pre-treatment. For some brass alloys, this can include chemical etching or a conversion coating to improve adhesion.
3. Masking (Optional):
If certain areas of the brass components need to remain uncoated, use masking materials to cover those areas. This ensures that only the intended surfaces receive the powder coating.
4. Powder Application:
Electrostatically charge the powder coating material and spray it onto the grounded brass parts. The charged powder particles adhere to the brass surface.
5. Curing:
Transfer the coated brass parts to a curing oven. Heat the parts to the recommended curing temperature, typically around 350°F to 400°F (177°C to 204°C). The exact temperature and curing time will depend on the specific powder coating material used.
6. Cooling:
Allow the brass parts to cool down naturally after curing. Avoid rapid temperature changes that could affect the coating's integrity.
7. Inspection and Quality Control:
Inspect the powder-coated brass parts for uniformity, defects, and adhesion. Ensure that the finish meets the desired quality standards.

8. Touch-Up (If Necessary):
If any defects or imperfections are found, address them through touch-up or rework as needed. This may involve re-coating and re-curing the affected areas.
9. Final Inspection:
Conduct a final inspection to ensure that all quality standards have been met, and the powder coating adheres properly to the brass surfaces.
10. Packaging and Shipping:
Once the powder coating is complete and the parts pass quality control, they can be packaged for shipping or further assembly.
It's essential to follow the manufacturer's recommendations for the specific powder coating material and curing parameters, as these can vary based on the powder coating formulation and the brass alloy being used. Additionally, working with experienced professionals or powder coating specialists is advisable to ensure the best results for powder coating brass components.
Brass Parts Powder Coating Thickness
The thickness of the powder coating applied to brass parts can vary depending on the specific application and the desired performance characteristics. However, a typical powder coating thickness for brass parts falls within the range of 1.5 to 4.5 mils (38 to 114 microns).
Here's a breakdown of what these thickness measurements mean:
1 mil = 0.001 inch (1/1000 of an inch).
1 micron = 0.001 millimeter (1/1000 of a millimeter).
1.5 mils (38 microns): This is considered a standard minimum thickness for powder coating and provides basic protection and appearance enhancement.
4.5 mils (114 microns): This thickness offers enhanced durability and corrosion resistance, making it suitable for applications exposed to more challenging environmental conditions.
The choice of powder coating thickness should be based on the specific requirements of your project. Thicker coatings generally provide better protection and durability, but they can affect the appearance, texture, and fit of the parts. Thinner coatings may be more suitable for parts where a sleek appearance is crucial.
It's essential to follow the recommendations of the powder coating manufacturer and consider factors such as the intended use, environmental exposure, and design preferences when determining the appropriate coating thickness for brass components.
What Colors can be Powder Coated on Brass Parts?
Powder coating offers a wide range of color options for brass parts, allowing for customization to meet specific design and aesthetic preferences. Here are some common colors and finishes that can be achieved through powder coating for brass components:
Solid Colors: Powder coating can produce a broad spectrum of solid colors, including traditional options like black, white, gray, red, blue, green, and many more.
Metallic Finishes: Metallic powder coatings can mimic the appearance of metals like gold, silver, bronze, and copper. These finishes can enhance the luxurious look of brass parts.
Gloss Finish: Glossy powder coatings provide a shiny and reflective surface that adds elegance and visual appeal to brass components.
Satin Finish: Satin or semi-gloss finishes offer a subtle sheen that strikes a balance between matte and gloss. They can provide a refined appearance.
Matte Finish: Matte powder coatings create a non-reflective and smooth surface, often used for a more understated or industrial look.
Texture Finishes: Powder coating can produce textured or wrinkled finishes, adding depth and tactile interest to brass parts.
Antique and Patina Finishes: Specialized powder coatings can replicate antique or aged brass appearances, as well as patina effects, to achieve a weathered or vintage look.
Custom Colors: Powder coating manufacturers can create custom colors to match specific design requirements, corporate branding, or unique project needs.
It's important to work with a reputable powder coating supplier or specialist who can provide a wide selection of color options and finishes. Additionally, consider requesting color samples or swatches to ensure that the chosen powder coating aligns with your design vision for the brass components.
What Effect does Powder Coating have on Brass Parts?
Powder coating can have several effects on brass parts, including changes in dimensions, precision, and other characteristics. It's essential to consider these factors when deciding to powder coat brass components:
1. Coating Thickness: Powder coating adds a layer to the surface of brass parts, which can slightly increase their overall dimensions. The thickness of the coating is typically measured in mils (thousandths of an inch) or microns (thousandths of a millimeter). Thicker coatings can have a more noticeable impact on dimensions.
2. Tolerance Considerations: Depending on the tightness of the tolerances required for your brass parts, you may need to account for the added thickness of the powder coating during the design and manufacturing stages. Consult with your powder coating specialist and consider whether adjustments are needed to meet specific size and precision requirements.
3. Threaded Areas: Threads on brass parts may need to be masked or post-processed to ensure that the powder coating does not interfere with the functionality of threaded components. The coating can fill in threads or alter their dimensions if not properly addressed.
4. Masking and Precision: Masking is often used to protect specific areas of brass parts from receiving the powder coating. Proper masking is crucial to maintaining precision in critical areas, such as mating surfaces, bearing journals, or precise fitments.
5. Surface Texture: Powder coating can affect the surface texture of brass parts, potentially masking fine details or surface imperfections. The choice of powder coating finish (e.g., matte, glossy, textured) can also influence the appearance and feel of the surface.
6. Impact on Electrical Conductivity: Brass is known for its electrical conductivity. Powder coating, being an insulator, can reduce or interfere with the electrical conductivity of brass components. This is an important consideration if electrical conductivity is a critical requirement for your parts.
7. Coating Uniformity: Ensuring uniform and consistent coating thickness across all parts is crucial to maintaining dimensional precision. Quality control measures during the powder coating process help achieve this.
8. Post-Coating Inspection: After powder coating, it's essential to inspect the brass parts for dimensional accuracy and any coating-related issues. Address any discrepancies or defects promptly.
In summary, powder coating can impact the dimensions, precision, and functionality of brass parts. Proper design considerations, tolerance adjustments, masking techniques, and post-coating inspections are essential to ensure that the powder coating process enhances both the appearance and functionality of your brass components without compromising their critical dimensions or features. Working closely with experienced powder coating professionals can help you achieve the desired results for your specific application.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Powder Coating of Brass Parts
Powder coating brass parts offers several advantages and disadvantages that should be considered when deciding whether it's the right surface treatment for your specific application. Here's a breakdown of the pros and cons of powder coating brass components:
Advantages of Powder Coating Brass Parts:
Enhanced Durability: Powder coating provides a durable and robust finish, making brass parts more resistant to chipping, scratching, and wear.
Corrosion Resistance: Powder coating can significantly improve the corrosion resistance of brass, protecting it from environmental factors and extending its lifespan.
Customization: Powder coating offers a wide range of color and finish options, allowing you to achieve specific design and aesthetic preferences.
Uniform Finish: Powder coating provides a uniform and consistent finish, even on complex or irregularly shaped brass components.
Environmental Friendliness: Powder coating is an eco-friendly process with low volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions and minimal waste generation.
Cost-Effective: Powder coating can be cost-effective for large production runs due to its efficiency and low material waste.
Disadvantages of Powder Coating Brass Parts:
Thickness Considerations: Powder coating adds a layer to the surface, which can impact the dimensions of brass parts. This may require adjustments or considerations in precision applications.
Electrical Conductivity: Powder coating is an insulator and can reduce the electrical conductivity of brass components. This may be a concern for parts requiring electrical contact.
Preparation Complexity: Proper surface preparation, including cleaning and potential pre-treatment, is essential for adhesion. This can add complexity to the production process.
Complex Geometry: Powder coating may not be suitable for brass parts with intricate or internal features that are difficult to coat evenly.
Masking Challenges: Masking of critical areas (e.g., threads, precise fitments) can be challenging to ensure that the powder coating does not interfere with functionality.
Rework Difficulties: If defects or imperfections are found after powder coating, rework or touch-up can be challenging and may require recoating and curing.
In summary, powder coating brass parts offers numerous advantages, including enhanced durability, corrosion resistance, customization options, and environmental benefits. However, it's essential to consider potential disadvantages related to dimensional changes, electrical conductivity, surface preparation, and masking challenges. The decision to powder coat brass components should align with the specific requirements and constraints of your project.
What Surface Finish does Powder Coated Brass Parts Exhibit?
Powder-coated brass parts can exhibit a wide range of surface effects and finishes, depending on the specific powder coating material and application technique used. Here are some common surface effects that can be achieved with powder-coated brass components:
Solid Colors: Powder coating can produce a smooth, solid color finish on brass parts. This effect is ideal for achieving a clean and consistent appearance in various shades.
Glossy Finish: A glossy surface effect is achieved when the powder coating material forms a smooth and reflective layer. This finish adds shine and depth to the brass components, giving them an elegant and polished look.

Matte Finish: Matte surfaces have a non-reflective, flat appearance. Matte powder coatings create a subdued and understated look that can be appealing in certain design contexts.
Satin Finish: Satin or semi-gloss finishes strike a balance between matte and glossy. They offer a subtle sheen that adds sophistication and a touch of luster to brass parts.
Metallic Finishes: Metallic powder coatings can replicate the appearance of various metals, including gold, silver, bronze, and copper. These finishes can enhance the luxurious look of brass components.
Texture Finishes: Powder coating can produce textured or wrinkled finishes, adding tactile interest and depth to the surface. Textured effects can be used for both aesthetics and grip-enhancing purposes.
Hammered Finish: A hammered finish mimics the appearance of hand-hammered metalwork. It creates a unique and rustic texture on the brass parts.
Antique and Patina Effects: Specialized powder coatings can replicate antique or aged brass appearances, as well as patina effects, to achieve a weathered or vintage look.
Custom Effects: Powder coating allows for custom effects and designs, including stencils, patterns, and intricate detailing. Custom effects can be tailored to meet specific design and branding requirements.
It's important to note that the choice of surface effect and finish depends on the desired aesthetics, functionality, and the overall design vision for the brass components. Powder coating offers flexibility in achieving various surface effects, making it a versatile choice for enhancing the appearance of brass parts while providing durability and protection.
Brass Powder Coating and Other Surface Treatments: Differences, Effects and Cost Comparison
Comparing powder coating on brass to other surface treatments involves considering differences, effects, and cost factors. Let's explore how powder coating on brass differs from other surface treatments in terms of effects and cost:
Powder Coating on Brass:
Differences:
Powder coating involves applying a dry powder material to the brass surface, which is then cured to form a protective and decorative coating.
It offers a wide range of color options, gloss levels, and finishes, including solid colors, metallic effects, and textures.
Powder coating is known for its durability, corrosion resistance, and eco-friendliness.
Effects:
Enhances the durability and corrosion resistance of brass components.
Provides customizable aesthetics with various color and finish choices.
Can replicate metallic appearances, such as gold or copper, for a luxurious look.
Cost Comparison:
Powder coating is generally cost-effective for large production runs due to its efficiency and low material waste.
Costs can vary depending on factors like coating thickness, complexity, and customization.
Other Surface Treatments (e.g., Plating, Patinas):

Differences:
Plating involves depositing a thin layer of metal (e.g., chrome, nickel) onto the brass surface for improved aesthetics and corrosion resistance.
Patinas are chemical treatments that create unique and often antique or aged appearances on brass.
Effects:
Plating provides a reflective and lustrous finish, enhancing aesthetics and corrosion resistance.
Patinas can create distinctive and artistic appearances, such as weathered or vintage looks.
Cost Comparison:
Plating may be costlier due to the use of precious metals and complex processes.
Patina treatments can vary in cost, depending on the complexity of the desired effect.
Painting (e.g., Epoxy, Polyurethane):

Differences:
Painting involves applying liquid paint or coating materials to the brass surface, which then dries or cures to form a protective layer.
Epoxy and polyurethane coatings are common choices for brass due to their durability.
Effects:
Provides a wide range of color options and finish effects.
Offers good durability and resistance to wear.
Cost Comparison:
The cost of painting or coating can vary based on the type of material used and the complexity of the application process.
Costs may include surface preparation, priming, and multiple layers of coating.
In summary, the choice between powder coating on brass and other surface treatments depends on your specific requirements, including aesthetics, durability, and cost considerations. Powder coating is favored for its versatility, durability, and eco-friendliness. However, plating, patinas, and painting may be preferred for achieving certain visual effects or meeting specific project needs. Consulting with experts in surface treatments can help you make the best choice for your brass components.
Powder Coated Brass Parts Applications
Powder-coated brass components find application across various industries and sectors due to the combination of durability, aesthetics, and corrosion resistance they offer. Here are some common applications for powder-coated brass parts:
Architectural and Decorative Elements:
Powder-coated brass is used for architectural features such as railings, balusters, door handles, and decorative trims. Its durability and aesthetic appeal make it a popular choice in high-end architectural design.
Furniture and Home Decor:
Brass components in furniture and home decor, including cabinet hardware, lighting fixtures, and furniture frames, benefit from powder coating for both protection and style.
Brass parts used in the automotive sector, such as interior and exterior trim components, emblems, and badges, can be powder coated to enhance their appearance and resist corrosion.

Electrical and Electronics:
Brass electrical components and connectors may be powder coated to provide protection against moisture, corrosion, and wear while maintaining electrical conductivity.

Industrial Equipment:
Powder-coated brass parts are used in various industrial machinery and equipment, where they benefit from enhanced durability and resistance to environmental factors.
Marine Applications:
Brass components on boats and ships, including cleats, hardware, and fixtures, are often powder coated to withstand the harsh marine environment and prevent corrosion.
Plumbing and Bathroom Fixtures:
Powder-coated brass is employed for plumbing fixtures, faucets, showerheads, and bathroom accessories, combining aesthetics with corrosion resistance.
Lighting Fixtures:
Powder-coated brass is a common choice for the frames and housings of lighting fixtures, providing both durability and the ability to achieve various finishes.
Art and Sculptures:
Artists and sculptors use powder-coated brass to create both indoor and outdoor artworks due to its resistance to weathering and the ability to achieve customized appearances.
Jewelry and Accessories:
While less common, powder-coated brass can be used in jewelry and fashion accessories, offering unique color and finish options.
Consumer Goods:
Powder-coated brass components can be found in a range of consumer goods, including household appliances, kitchenware, and sporting equipment.
Military and Aerospace:
Brass components used in military and aerospace applications benefit from powder coating to withstand extreme conditions and maintain their functionality.
These applications highlight the versatility and broad utility of powder-coated brass parts in various industries, where they provide both functional advantages and aesthetic appeal. The specific application will determine the required coating thickness, color, and finish to meet the intended purpose effectively.
Powder-Coated Brass Parts Problems and Considerations
When dealing with powder-coated brass parts, there are specific issues and considerations that should be addressed to ensure successful outcomes. Here are some common problem points and key precautions when working with powder-coated brass components:
1. Surface Preparation:
Problem Point: Inadequate surface preparation can lead to poor adhesion of the powder coating, resulting in chipping or peeling.
Precaution: Ensure thorough cleaning and, if necessary, pre-treatment of the brass surface to remove contaminants and provide a suitable substrate for adhesion.
2. Masking and Protection:
Problem Point: Failure to properly mask or protect critical areas, such as threads or mating surfaces, can lead to functional issues or difficulties during assembly.
Precaution: Carefully mask or protect areas where the powder coating should not be applied to maintain precise dimensions and functionality.
3. Powder Coating Thickness:
Problem Point: Applying excessive powder coating thickness may affect tolerances and fit, especially in precision components.
Precaution: Control the thickness of the powder coating to meet design specifications and consider adjustments if necessary.
4. Electrical Conductivity:
Problem Point: Powder coating is an insulator and can affect the electrical conductivity of brass parts if not managed properly.
Precaution: If electrical conductivity is required, plan for proper masking or post-coating treatments to maintain conductivity in specific areas.
5. Quality Control:
Problem Point: Insufficient quality control can result in defects, uneven coating, or imperfections that affect the appearance and functionality of the parts.
Precaution: Implement rigorous quality control measures, including inspections for coating thickness, adhesion, and overall appearance.
6. Rework and Repair:
Problem Point: Addressing defects or imperfections in powder-coated brass parts can be challenging and may require recoating and curing.
Precaution: Develop protocols for identifying and addressing defects promptly, including procedures for rework or touch-up if needed.
7. Compatibility of Materials:
Problem Point: Ensure that the selected powder coating material is compatible with brass and any pre-treatment or adhesion promoters used.
Precaution: Consult with experts or powder coating specialists to choose the appropriate coating material for brass components.
8. Environmental Considerations:
Problem Point: Environmental factors, such as temperature and humidity, can affect the curing and adhesion of powder coatings.
Precaution: Control the curing environment to ensure optimal conditions for the powder coating process.
9. Handling and Storage:
Problem Point: Mishandling or improper storage of powder-coated brass parts can lead to surface damage or contamination.
Precaution: Handle parts with care, protect them from contaminants, and store them in a clean, controlled environment.
10. Post-Coating Testing:
Problem Point: Skipping post-coating testing and inspections can result in overlooked defects or quality issues.
Precaution: Implement a comprehensive testing and inspection process to verify that parts meet specifications and quality standards.
By addressing these issues and taking appropriate precautions, you can ensure the successful powder coating of brass components, achieving both aesthetic appeal and functional integrity. Collaboration with experienced powder coating professionals can also be valuable in navigating these considerations effectively.
Conclusion
Do you know how to choose the right finish for your project? VMT has 15 years of experience in surface treatment experts to choose the appropriate surface treatment for you to improve the surface texture and performance of CNC parts.
Learn about the powder coating surface treatment process, benefits and applications in this article. If you want to know more about powder coating surface treatment, please contact us today. VMT can provide a wide range of CNC machining and manufacturing capabilities and surface treatment services for steel, aluminum, titanium, brass and other materials. Our team of professional engineers can choose the appropriate surface treatment for you to meet all your CNC machined parts production needs and obtain Best, competitive price. Why not give VMT a try and contact us now to get a quote.
Powder Coated Brass Parts FAQs
Certainly, here are some common questions and answers related to powder-coated brass parts:
1. What is powder coating, and why is it used on brass parts?
Answer: Powder coating is a surface treatment process where dry powder is applied to a surface and then cured to create a durable and protective finish. It is used on brass parts to enhance their appearance, provide corrosion resistance, and improve overall durability.
2. Does powder coating affect the electrical conductivity of brass parts?
Answer: Yes, powder coating is an insulator and can reduce the electrical conductivity of brass components. If electrical conductivity is critical, consider masking or post-coating treatments for the specific areas requiring conductivity.
3. Can powder-coated brass parts be customized in terms of color and finish?
Answer: Yes, powder coating offers a wide range of color options and finishes, allowing for customization to meet specific design and aesthetic preferences.
4. What should be considered when masking or protecting critical areas on brass parts during powder coating?
Answer: Proper masking is crucial to maintain dimensions and functionality. Consider the type of masking material, its adhesion to the brass surface, and precise coverage to prevent powder coating in critical areas.
5. How thick is the powder coating typically applied to brass parts?
Answer: The thickness of the powder coating can vary but typically falls within the range of 1.5 to 4.5 mils (38 to 114 microns), depending on the specific application and requirements.
6. Are there any post-coating inspections or tests that should be conducted on powder-coated brass parts?
Answer: Yes, post-coating inspections are essential to ensure quality. Inspections may include checking coating thickness, adhesion, appearance, and overall quality to verify that parts meet specifications.
7. What are the advantages of using powder-coated brass parts in architectural and decorative applications?
Answer: Powder-coated brass offers enhanced durability, corrosion resistance, and a wide range of color and finish options, making it a popular choice for architectural and decorative elements where both aesthetics and functionality are important.
8. How can defects or imperfections in powder-coated brass parts be addressed?
Answer: Defects or imperfections can be addressed through rework or touch-up procedures, which may involve re-coating and re-curing the affected areas to achieve the desired quality.
9. Is powder coating environmentally friendly?
Answer: Yes, powder coating is known for its eco-friendliness. It has low volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions and minimal waste generation, making it a sustainable choice.
10. Can powder coating be applied to intricate or complex brass parts?
Answer:Yes, powder coating can be applied to intricate or complex brass parts, but it may require careful planning and specialized techniques to achieve even and consistent coating coverage. Complex geometries, recessed areas, and tight corners can pose challenges for powder coating because the powder particles need to adhere uniformly to all surfaces.
These questions and answers provide insights into the common considerations and aspects of powder-coated brass parts, addressing both practical and technical aspects of the powder coating process.
