15 years one-stop China custom CNC machining parts factory
 2249 |
Published by VMT at Dec 21 2022
2249 |
Published by VMT at Dec 21 2022
Die casting is a metal casting process characterized by the use of a mold cavity to apply high pressure to molten metal, similar to plastic injection molding. Die casting is especially suitable for manufacturing a large number of small and medium-sized castings, so die casting is the most widely used of various casting processes. Compared with other casting technologies, die casting has a flatter surface and higher dimensional consistency. However, irregular operations and parameters can also produce a wide variety of defects.
1. Flow marks and patterns
Appearance inspection: There are stripes on the surface of the casting that are consistent with the flow direction of the molten metal, and there are obvious non-directional lines that are different in color from the metal matrix, and there is no development trend.

The reasons for flow marks are as follows:
1) The mold temperature is too low;
2) Poor runner design and poor ingate position;
3) The material temperature is too low;
4) Low filling speed and short filling time;
5) The gating system is unreasonable;
6) Poor exhaust;
7) The spray is unreasonable.
The reason for the pattern is that the paint in the cavity is sprayed too much or the quality of the paint is poor. The solutions and prevention methods are as follows:
1) Adjust the cross-sectional area or position of the ingate;
2) Increase the mold temperature;
3) Adjust the speed and pressure of the inner runner;
4) Appropriate selection of paint and adjustment of dosage.
2. Mesh burrs (tortoise cracks)
Appearance inspection: There are raised or sunken marks on the surface of die-casting parts, which are enlarged and extended with the increase of die-casting times.

The reasons are as follows:
1) There are cracks on the surface of the die-casting cavity;
2) Die-casting mold preheating is uneven.
The ways to solve and prevent it are:
1) The die-casting mold should be annealed regularly or after a certain number of times of die-casting to eliminate the stress in the cavity;
2) If cracks have appeared on the surface of the cavity, the molding surface should be polished to remove the crack layer;
3) The mold should be preheated evenly.
3.Cold Insulation
Appearance inspection: There are obvious, irregular, and sunken linear lines on the surface of die-casting parts (there are two kinds of penetrating and non-penetrating).

The reasons are as follows:
1) The two metal streams are docked with each other, but they are not completely fused and there is no inclusion in between, and the bonding force of the two metals is very weak;
2) Pouring temperature or die-casting mold temperature is low;
3) The position of the sprue is wrong or the flow path is too long;
4) The filling speed is low.
The ways to solve and prevent it are:
1) Properly increase the pouring temperature;
2) Improving the injection ratio, shortening the filling time and increasing the injection speed;
3) Improve exhaust and filling conditions.
4. Recession (dent)
Visual inspection: There are smooth indentations (like a dish) on most of the surface after die casting parts.

The reasons are as follows:
1) Caused by contraction
2) The cooling system design is unreasonable;
3) Opening the mold too early;
4) The pouring temperature is too high.
The ways to solve and prevent it are:
1) The wall thickness should be uniform;
2) The thickness transition should be eased;
3) Correctly select the alloy liquid introduction position and increase the cross-sectional area of the inner runner;
4) Increase the injection pressure and prolong the holding time;
5) Properly reduce the pouring temperature and die-casting mold temperature;
6) Local cooling is required for local high temperatures;
7) Improve overflow conditions.
5. Imprints
Appearance inspection: traces left by the contact between the surface of the casting and the surface of the die-casting mold cavity or step marks on the surface of the casting.
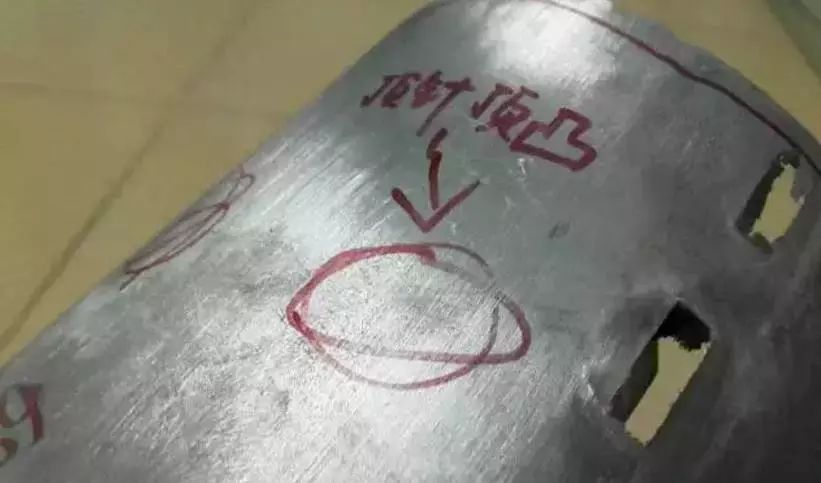

The reasons are as follows:
1). Caused by ejected components;
2) The end face of the ejector rod is worn;
3) The length of the ejector rod adjustment is inconsistent;
4) The splicing part of the die-casting model cavity does not fit well with other parts.
Caused by spliced or active parts:
1) The mosaic part is loose;
2) Loose or worn moving parts;
3) The side wall surface of the casting is formed by inserts interspersed between the movable and fixed molds.
The ways to solve and prevent it are:
1) The length of the ejector rod should be adjusted to an appropriate position;
2) fastening inserts or other movable parts;
3) Eliminate sharp corners during design, and adjust the fit with the clearance;
4) Improve the structure of the casting to eliminate the interspersed mosaic form of the die-casting mold and improve the structure of the die-casting mold.
6. Traces of adhesion
Appearance inspection: Small flakes and metal or non-metallic and metal matrix parts are welded, and the small flakes are peeled off under the action of external force. Some of the peeled casting surfaces are shiny, and some are dark gray.
The reasons are as follows:
1) There are metal or non-metal residues on the surface of the die-casting model cavity;
2) When pouring, impurities are first brought in and attached to the surface of the cavity.
The ways to solve and prevent it are:
1) Before die-casting, the cavity pressure chamber and pouring system should be cleaned to remove metal or non-metallic adherents;
2) The poured alloy should also be cleaned up;
3) Choose the right paint, and the coating should be uniform.
7. Layering (folding and peeling off)
Appearance inspection or damage inspection: There are obvious layers of metal in parts of the casting.

The reasons are as follows:
1) The rigidity of the mold is not enough. During the filling process of the molten metal, the template shakes;
2) The punch crawls during the injection process;
3) Improper design of the runner system.
The ways to solve and prevent it are:
1) Strengthen the rigidity of the mold and fasten the mold parts to make them stable;
2) Adjust the cooperation between the injection punch and the pressure chamber to eliminate the crawling phenomenon;
3) Reasonably design the inner runner.
8. Friction Ablation
Appearance inspection: The surface of die-casting parts has rough surfaces in some positions.

The reasons are as follows:
1) Improper position, direction and shape of the ingate caused by the die-casting type (mold);
2) Insufficient cooling of the part where the molten metal scours violently at the inner runner caused by casting conditions.
The ways to solve and prevent it are:
1) Improving the location and direction of the ingate for inappropriate pouring;
2) Improve the cooling conditions, especially to improve the parts where the molten metal scours violently;
3) Add paint to the ablated part;
4) Adjust the flow rate of the alloy liquid so that no cavitation occurs;
5) Eliminate the alloy adhesion on the mold (mold).
9. Erosion
Appearance inspection: There are pitting or embossing in some parts of the die-casting parts.

The reasons are as follows:
1) The position of the ingate is improperly set;
2) The cooling condition is not good.
The ways to solve and prevent it are:
1) The thickness of the inner runner should be appropriate;
2) Modify the position, direction and setting method of the ingate;
3) Strengthen cooling of the eroded parts.
10. Cracks
Appearance inspection: Put the casting in alkaline solution, and the cracks are dark gray. The damage and cracking of the metal matrix are linear or wavy, with narrow and long lines, which tend to develop under the action of external force.

Causes of cracks in aluminum alloy castings:
1) The iron content in the alloy is too high or the silicon content is too low; the content of harmful impurities in the alloy is too high, which reduces the plasticity of the alloy; the aluminum-silicon alloy, aluminum-silicon-copper alloy contains too much zinc or copper; the aluminum-magnesium alloy contains too much magnesium;
2) The mold retention time is too short, and the pressure holding time is short; the wall thickness of the casting has drastic changes;
3) The partial tightening force is too large, and the force is uneven when ejecting.
Ways to solve and prevent:
1) Correctly control the alloy composition, in some cases: add pure aluminum ingot to the alloy to reduce the magnesium content in the alloy; or add aluminum-silicon intermediate alloy to the alloy to increase the silicon content;
2) Increase the temperature of the mold (mold); change the structure of the casting, adjust the core-pulling mechanism or make the push rod evenly stressed;
3) Increase the draft angle and use a strong release agent locally;
4) Increase the mold retention time and pressure holding time.
11. The aluminum clip is depressed
Reasons for the depression of the clamped aluminum sheet:
1. Most of the aluminum clips are caused by the residue of the gold mold from the last die-casting, mixed with the newly injected aluminum liquid, and concentrated in the vacuum part because the vacuum part has a small cross-sectional area, and most of the depressions are caused by the aluminum clip. The second part of the profile clamp aluminum will be dented at the beginning, and then the mold will be dented;
2. The cooling of the material barrel is too large, the aluminum liquid has cooled in the material barrel, and the aluminum flakes are mixed at the feeding port after the die-casting is completed.
The above are the defects and solutions that are prone to appear in the 11 major aluminum die castings, and I hope you can help them.
