15 years one-stop China custom CNC machining parts factory

Hey there I’m VMT Sam!
With 25 years of CNC machining experience we are committed to helping clients overcome 10000 complex part-processing challenges all to contribute to a better life through intelligent manufacturing. Contact us now
 348 |
Published by VMT at Jan 31 2024
348 |
Published by VMT at Jan 31 2024
Introduction:
In the realm of CNC machining manufacturing, Statistical Process Control (SPC) stands out as a crucial tool for quality management, offering the means to monitor and improve product quality during the production process. By leveraging SPC technology, manufacturers can track real-time production data, identify anomalies, and take corresponding measures to enhance the stability of CNC machined parts' quality. This article delves into how CNC manufacturing firms can implement SPC and leverage the gathered data to improve the quality of CNC machined parts.

I. Implementing Statistical Process Control (SPC):
Data Collection:
Collect essential process parameters and product quality data during the production process, such as tool wear, cutting speed, feed rate, dimensional accuracy, etc. Ensure the reliability and accuracy of the data sources.
Control Chart Development:
Based on the collected data, develop corresponding control charts. Control charts are visual tools that display the variation of key variables over time in the production process. Common types include mean-range charts, mean-standard deviation charts, etc.
Monitoring and Anomaly Detection:
Continuously monitor the control charts in real-time, observing the trends in key variables. When data points on the control chart surpass predetermined control limits, it signals an anomaly. These anomalies may indicate instability in the production process, necessitating further investigation and analysis.
Investigation and Analysis:
Upon detecting anomalies, promptly conduct an investigation and analysis. By collecting relevant data, examining equipment status, verifying process parameters, etc., identify the root causes of the anomalies. This aids in recognizing bottlenecks and improvement opportunities in the production process.
Implementation of Improvement Measures:
Based on investigation and analysis results, formulate corresponding improvement measures. These measures may include adjusting process parameters, optimizing equipment settings, or replacing tools. Ensure the effectiveness and feasibility of improvement measures and track and assess their implementation progress.
Validation and Standardization:
After implementing improvement measures, validate their effectiveness and standardize the successful ones. Evaluate the impact of the improvements on the quality of CNC machined parts by comparing production data before and after the changes. If the improvements prove effective, incorporate them into standard operating procedures and continually apply them in the production process.
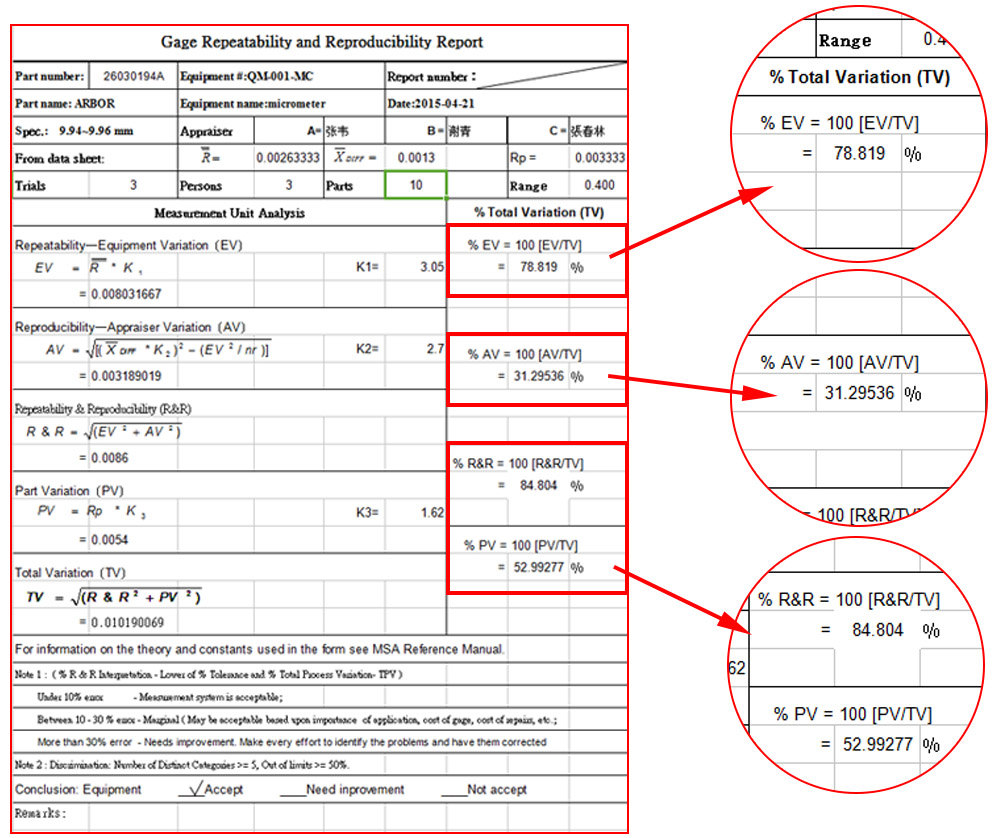
II. Using SPC Data for Quality Improvement:
Identifying Problem Areas:
Analyze SPC data to pinpoint critical issues and weak links in the production process. These issues may include unstable process parameters, insufficient equipment precision, fluctuations in raw material quality, etc.
Setting Improvement Goals:
For identified problem areas, set specific improvement goals. Goals should be measurable, achievable, and time-bound, ensuring the effectiveness and feasibility of improvement efforts.
Optimizing Process Parameters:
Adjust and optimize process parameters based on feedback from SPC data. Through experimentation and validation, identify the optimal combination of process parameters to enhance the quality and stability of CNC machined parts.
Enhancing Equipment Precision:
Analyze SPC data to assess and adjust the precision of existing equipment. If necessary, consider acquiring new equipment or implementing modifications to enhance the precision and stability of the CNC machining process.
Strengthening Raw Material Quality Control:
Through SPC data analysis, understand the impact of raw material quality on CNC machined part quality. Strengthen incoming inspection and quality control of raw materials to ensure the stability and reliability of raw material quality.
Training and Communication:
Conduct regular training sessions and communication meetings to ensure production and management personnel fully grasp the importance of SPC in quality improvement. Enhance employees' understanding and application of SPC methods, facilitating the smooth implementation of quality improvement initiatives.
Continuous Monitoring and Optimization:
Utilize SPC as a tool for continuous improvement, continually collecting and analyzing data during the production process. Adjust control limits and improvement measures based on real-world conditions, ensuring the continuous enhancement of CNC machined part quality. Stay attuned to the developments in new technologies and methods, applying them to quality improvement efforts to maintain a competitive edge.
In conclusion, CNC manufacturing firms can achieve significant improvements in CNC machined parts' quality by implementing Statistical Process Control (SPC) and leveraging the associated data. SPC offers a systematic approach to monitor production processes, identify anomalies, analyze issues, and implement corrective measures. Through continuous optimization of process parameters, enhanced equipment precision, and strengthened raw material quality control, manufacturers can elevate the quality of CNC machined parts while reducing production costs. This contributes to increased customer satisfaction, heightened market competitiveness, and greater economic benefits for the enterprise.
Ready To Start Your Next Project?
Get Instant Quote

Request a Free Quote
Send us a message if you have any questions or request a quote. We will get back to you ASAP!