15 years one-stop China custom CNC machining parts factory

Hey there I’m VMT Sam!
With 25 years of CNC machining experience we are committed to helping clients overcome 10000 complex part-processing challenges all to contribute to a better life through intelligent manufacturing. Contact us now
 994 |
Published by VMT at Jan 12 2023
994 |
Published by VMT at Jan 12 2023
Four standard threads of metric system, inch system, modulus and diameter control can be turned on the CNC lathe. No matter which kind of thread is turned, a strict motion relationship must be maintained between the lathe spindle and the tool: that is, each revolution of the spindle (that is, the workpiece One turn), the tool should move evenly by one lead (of the workpiece). Through the analysis of ordinary threads, the understanding of ordinary threads will be strengthened, so as to process ordinary threads better.
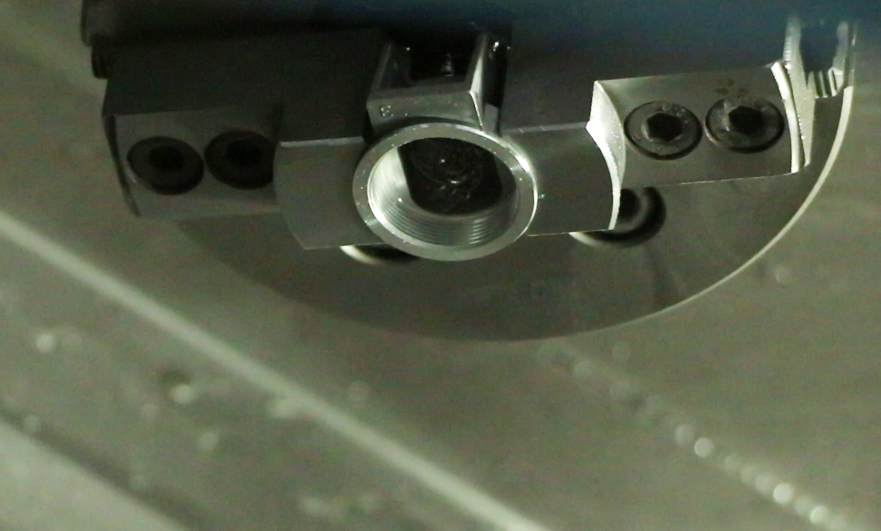
1.Dimensional analysis of ordinary thread
CNC lathes require a series of dimensions to process ordinary threads. The calculation and analysis of dimensions required for ordinary thread processing mainly include the following two aspects:
1). Workpiece diameter before thread machining
Considering the amount of expansion of the thread machining tooth profile, the diameter of the workpiece before thread processing is D/D-0.1P, that is, the major diameter of the thread minus 0.1 pitch. Generally, it is 0.1 to 0.5 smaller than the major diameter of the thread according to the small deformation capacity of the material.
2). Thread machining feed rate
The thread feed amount can refer to the thread bottom diameter, which is the final feed position of the thread cutter.
The small diameter of the thread is: major diameter - 2 times the tooth height; tooth height = 0.54P (P is the pitch)
The feed amount of thread machining should be continuously reduced, and the specific feed amount should be selected according to the tool and working material.

2. Tool installation and tool setting of common thread tool
If the turning tool is installed too high or too low or too high, when the tool reaches a certain depth, the flank surface of the turning tool will withstand the workpiece, increasing friction, and even bending the workpiece, resulting in the phenomenon of biting the tool; Chips are not easy to discharge, the direction of the radial force of the turning tool is the center of the workpiece, and the gap between the traverse screw and the nut is too large, so that the depth of the cutting tool continues to automatically tend to deepen, thereby lifting the workpiece and causing the cutting tool to bite. At this time, the height of the turning tool should be adjusted in time so that the tool tip is at the same height as the axis of the workpiece (the tip of the tailstock can be used for tool setting). In rough turning and semi-finishing turning, the position of the tool tip is about 1% D higher than the center of the workpiece (D represents the diameter of the workpiece to be processed).
The workpiece is not clamped firmly. The rigidity of the workpiece itself cannot withstand the cutting force during turning, so excessive deflection occurs, which changes the center height between the turning tool and the workpiece (the workpiece is raised), resulting in a sudden increase in cutting depth and tool biting. , At this time, the workpiece should be clamped firmly, and the top of the tailstock can be used to increase the rigidity of the workpiece.
Common thread tool setting methods include trial cutting method and automatic tool setting by tool setting instrument. You can directly use the tool for trial cutting and tool setting, or use G50 to set the workpiece zero point, and use the workpiece shifter to set the workpiece zero point for tool setting. The requirements for tool setting in thread processing are not very high, especially there is no strict restriction on tool setting in Z direction, which can be determined according to the programming processing requirements.
3. Programming and processing of ordinary thread
In the current CNC lathe, there are generally three processing methods for thread cutting: G32 straight-forward cutting method, G92 straight-forward cutting method and G76 oblique cutting method. Due to different cutting methods and different programming methods, the machining error is also large. different. We must carefully analyze the operation and use, and strive to process parts with high precision.
1. In the G32 straight-forward cutting method, because both sides of the cutting edge work at the same time, the cutting force is relatively large, and cutting is difficult, so the two cutting edges are easy to wear during cutting. When cutting a thread with a large pitch, due to the large cutting depth and fast wear of the blade, an error occurs in the pitch diameter of the thread; however, the precision of the processed tooth shape is high, so it is generally used for small pitch thread processing. Since the tool movement and cutting are all completed by programming, the processing program is relatively long; since the blade is easy to wear, frequent measurement should be done during processing.
2. The G92 straight-forward cutting method simplifies the programming and improves the efficiency compared with the G32 command.
3. For the G76 oblique cutting method, due to the single-side edge processing, the CNC machining blade is easy to damage and wear, so that the thread surface of the CNC machining is not straight, and the angle of the tool tip changes, resulting in poor tooth shape accuracy. However, because it works on a single side edge, the tool load is small, chip removal is easy, and the cutting depth is decreasing. Therefore, this CNC machining method is generally suitable for large-pitch thread machining. Because this CNC processing method is easy to remove chips and the cutting edge processing conditions are better, this processing method is more convenient when the thread accuracy is not high. When CNC machining high-precision threads, it can be completed by two-knife machining, that is, rough turning with G76 machining method, and then fine turning with G32 machining method. But it should be noted that the starting point of the tool must be accurate, otherwise it is easy to buckle randomly and cause the parts to be scrapped.
4. After the thread processing is completed, you can judge the thread quality by observing the thread profile and take timely measures. When the thread crest is not sharp, increasing the cutting amount of the knife will increase the major diameter of the thread instead. The increase depends on the plasticity of the material. When the crest has been sharpened, increasing the cutting amount of the knife will reduce the major diameter proportionally. According to this feature, the cutting amount of the thread should be treated correctly to prevent scrapping.
4. Detection of ordinary thread
For general standard threads, thread ring gauges or plug gauges are used to measure. When measuring external threads, if the thread "over-end" ring gauge is just screwed in, but the "stop end" ring gauge cannot be screwed in, it means that the processed thread meets the requirements, otherwise it is unqualified. When measuring internal threads, use a thread plug gauge and measure in the same way. In addition to thread ring gauge or plug gauge measurement, other measuring tools can also be used for measurement. Use a thread micrometer to measure the pitch diameter of the thread, and use a tooth thickness vernier caliper to measure the pitch diameter of the trapezoidal thread and the tooth thickness of the worm pitch diameter. Measurement method to measure the pitch diameter of the thread.
The above are the skills of CNC turning thread, I hope it will be helpful to you.
Ready To Start Your Next Project?
Get Instant Quote

Request a Free Quote
Send us a message if you have any questions or request a quote. We will get back to you ASAP!
