15 years one-stop China custom CNC machining parts factory

Hey there I’m VMT Sam!
With 25 years of CNC machining experience we are committed to helping clients overcome 10000 complex part-processing challenges all to contribute to a better life through intelligent manufacturing. Contact us now
 3468 |
Published by VMT at Jun 20 2024
3468 |
Published by VMT at Jun 20 2024
Comparison of Ra Surface Smoothness and Rz Surface Roughness
Introduction
In the field of CNC machining parts manufacturing, surface smoothness and surface roughness are important indicators of part quality. Ra and Rz are commonly used surface roughness parameters, each with specific definitions and application scenarios. This article will provide a detailed comparison of Ra surface smoothness and Rz surface roughness, exploring their differences, measurement methods, implementation techniques, and applications in various industries, while also addressing some common questions.
What is Ra?
Ra, or Arithmetic Mean Roughness, is a commonly used parameter for measuring surface roughness. It represents the mean vector of all the fine asperities on the surface, reflecting the minimal measure of surface roughness. The smaller the Ra value, the smoother and more precise the surface. In CNC machining, Ra is often used to quantitatively evaluate the quality of machined surfaces.

What is Rz?
Rz, or Maximum Height of the Profile, is another common surface roughness parameter. It represents the total height difference from the highest peak to the lowest valley on the workpiece surface. The larger the Rz value, the greater the surface roughness, and vice versa. Rz is often used to describe and quantify the degree of surface irregularity, which is significant for scenarios requiring control over surface peak-to-valley height differences.
What is the Difference Between Ra and Rz?
Ra and Rz measure surface roughness differently. Ra calculates the average height of all surface asperities to evaluate surface roughness, indicating the overall smoothness of the surface. Rz, however, measures the maximum height difference between the surface peaks and valleys, focusing on the degree of surface irregularity. In practice, Ra is commonly used to quantify the quality of machined surfaces, while Rz is used to describe and control the impact of surface peak-to-valley height differences on part performance.
How to Measure Ra or Rz Surface Smoothness in CNC Machining Parts?
Various methods are used to measure surface smoothness and roughness in CNC machining. Common instruments include surface roughness testers, optical microscopes, and scanning electron microscopes. For Ra, a surface roughness tester is typically used for direct measurement. For Rz, the maximum height difference between the surface peaks and valleys is measured to calculate the Rz value indirectly. Additionally, non-contact measurement methods such as projection measurement and parallel light methods can be used for quick surface evaluation.

How to Achieve Different Surface Roughness Options for CNC Machining Parts?
Achieving different surface roughness options for CNC machined parts mainly involves adjusting machining process parameters and selecting appropriate machining tools. For example, in cutting, the surface roughness can be controlled by adjusting cutting speed, feed rate, and cutting depth. In grinding, selecting suitable grinding wheels, grinding fluids, and grinding parameters can meet different surface roughness requirements. Advanced techniques like CNC prototyping machining can also be used for high-precision machining of complex parts, achieving higher surface smoothness and roughness requirements.
We Provide Different Surface Roughness Levels
To meet various customer needs, we offer CNC machined parts with different surface roughness levels. Below are some common surface roughness levels, their application scenarios, and price ranges:
Ra 6.3μm: Suitable for general mechanical parts machining, such as automotive and motorcycle components. This is relatively low cost with high cost-effectiveness.
Ra 3.2μm: Suitable for industries requiring higher surface roughness standards, such as precision instruments and optical equipment. This has a moderate price with high machining precision and surface quality.
Ra 1.6μm: Suitable for industries with extremely high surface smoothness requirements, such as aerospace and semiconductors. This is relatively expensive but meets high precision and high-quality requirements.
Ra 0.8μm: Suitable for special industries with extremely high surface smoothness demands, such as medical devices and optical lenses. This is high cost but provides extremely high surface smoothness and precision.
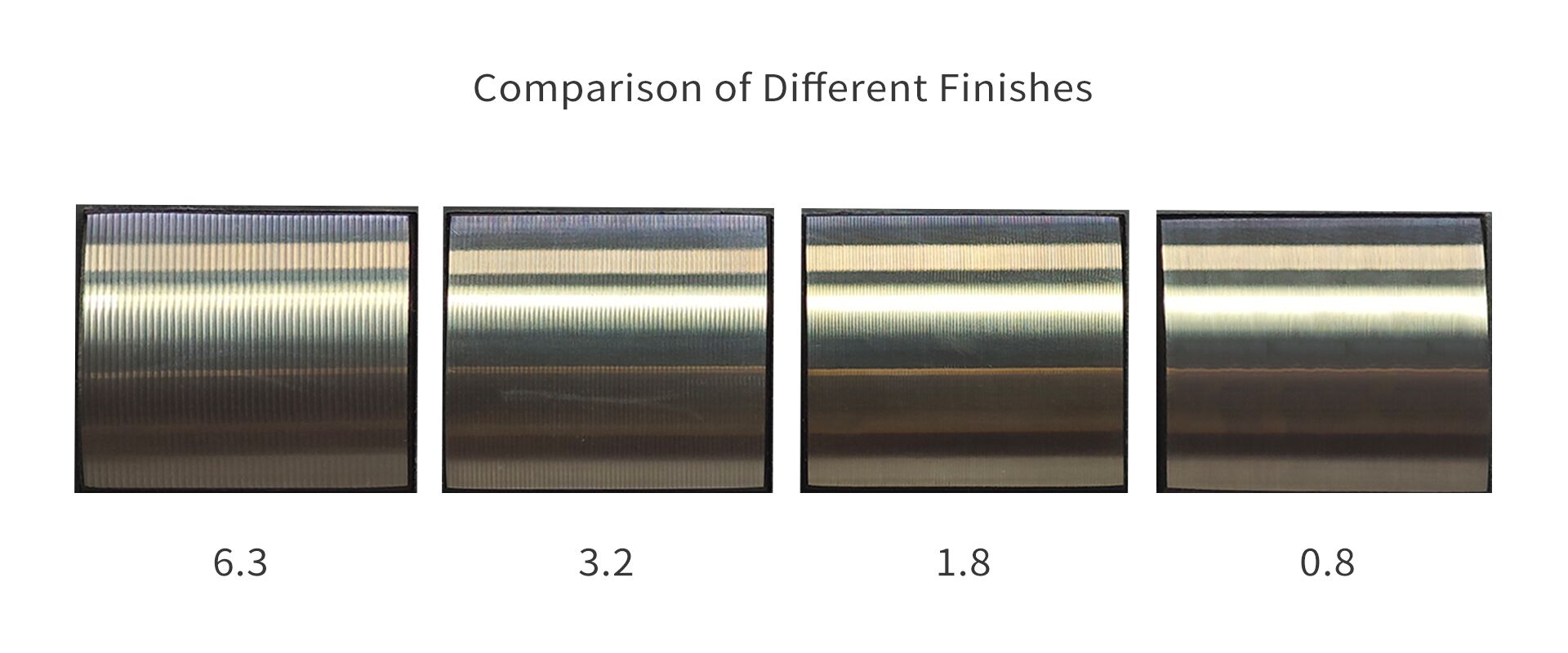
CNC Parts Surface Smoothness Ra and Rz Roughness Specifications
In CNC machining, we develop detailed surface smoothness and roughness specifications according to customer requirements and industry standards. Here are some common specifications:
Arithmetic Mean Roughness (Ra): We provide various Ra values ranging from Ra 0.8μm to Ra 6.3μm to meet different industry and application demands. Customers can choose the appropriate Ra value based on their specific needs.
Ten-Point Height of Irregularities (Rz, ISO): Rz values describe and quantify the degree of surface irregularity. We offer a range of Rz values from Rz 10μm to Rz 50μm to control the surface peak-to-valley height differences as required by customers.
Relationship Between Surface Smoothness and Granularity
Surface smoothness is related to granularity, which refers to the size and distribution of surface particles and directly affects surface smoothness. Generally, the smaller the granularity, the smoother and higher the surface smoothness. Surface smoothness is also influenced by machining processes, tools, cutting parameters, and other factors. Therefore, in CNC machining, various factors need to be considered comprehensively to achieve the desired surface smoothness and roughness requirements.
Plane and Reading
Ensuring the accuracy of the measurement plane and the precision of readings is crucial when measuring the surface roughness of CNC machined parts. For Ra and Rz measurements, a flat, scratch-free, and adequately large measurement plane is necessary to ensure accurate and reliable results. The precision of the reading equipment also directly impacts measurement accuracy. Therefore, it is essential to ensure that both the measurement plane and reading equipment meet relevant standards and requirements when selecting and performing measurements.
Conclusion
Ra and Rz are important parameters for measuring surface roughness in CNC machined parts, widely applied in the CNC machining field. Ra evaluates surface roughness by calculating the average height of all surface asperities, while Rz assesses surface roughness by measuring the maximum height difference between surface peaks and valleys. In practice, appropriate Ra and Rz values are chosen based on specific needs and industry standards, and surface roughness is achieved by adjusting machining process parameters and selecting suitable CNC machining tools.
Moreover, ensuring the accuracy of the measurement plane and the precision of readings is essential to obtain reliable and accurate results. Continuous research and practice can optimize CNC machining technology, improving the surface smoothness and roughness quality of parts to meet ever-evolving customer demands.

Frequently Asked Questions
What is 0.8 Ra Surface Smoothness?
0.8 Ra indicates a surface roughness arithmetic mean value of 0.8 microns, meaning the average height of the tiny peaks and valleys on the surface is 0.8 microns, indicating a relatively smooth surface.
What is the Relationship Between Ra and Rz Surface Smoothness?
Ra and Rz are different parameters for measuring surface roughness with no direct relationship. Ra reflects the overall smoothness, while Rz describes the degree of surface irregularity. Both parameters are chosen based on specific needs.
Which is Better, Ra or Rz?
Both Ra and Rz are effective parameters for measuring surface roughness, each with different application scenarios and advantages. The choice depends on specific requirements and industry standards. In some cases, both Ra and Rz may be considered to comprehensively evaluate surface roughness.
What is the Ra Value of Surface Smoothness?
The Ra value depends on specific machining requirements and application scenarios. Different industries and products have different surface roughness requirements, resulting in varying Ra values. Suitable Ra values are determined based on specific needs, and machining process parameters and tools are adjusted to achieve the required surface roughness.
How is Surface Smoothness Calculated?
Surface smoothness is usually calculated using specialized measuring equipment. For Ra, a surface roughness tester is used for direct measurement. For Rz, the maximum height difference between surface peaks and valleys is measured indirectly. Ensuring the accuracy of the measurement plane and reading equipment is essential for obtaining accurate results.
Through the above explanations and answers, readers should have a deeper understanding of Ra surface smoothness and Rz surface roughness. In practice, appropriate surface roughness parameters and measurement methods should be chosen based on specific needs and industry standards. Continuous optimization of CNC machining technology can improve the surface quality of parts, meeting the ever-increasing demands of customers.
Ready To Start Your Next Project?
Get Instant Quote

Request a Free Quote
Send us a message if you have any questions or request a quote. We will get back to you ASAP!