15 years one-stop China custom CNC machining parts factory
Home / Product / Stainless Steel Parts /
Choose us as your stainless steel CNC machining manufacturer, you can rest assured. We use different processes combined with CNC machining to meet your needs. Available in a variety of stainless steel materials, strict quality control processes are carefully monitored at each step to ensure stainless steel CNC parts meet the highest industry standards for performance and durability.
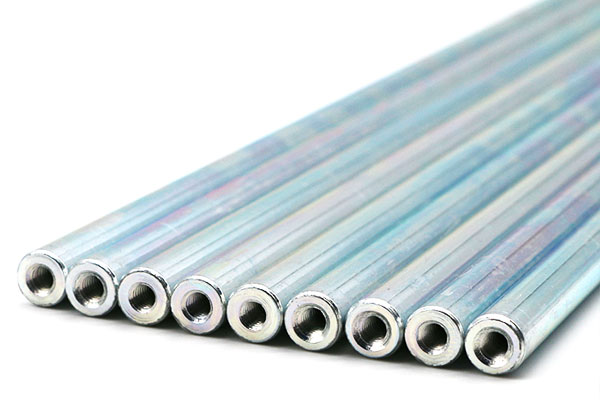

Product Specification:
13 years |
1 day |
0 pc |
90% |
|
Experience |
Lead time |
MOQ |
Countries customers |
| Custom Stainless Steel Galvanized CNC Machining Parts Precision Machining - OEM ODM CNC Milling Services Manufacturer - China VMT |
Custom Stainless Steel Galvanized CNC Machining Parts Services

Custom Stainless Steel Galvanized CNC Machining Parts Prototyping Machining
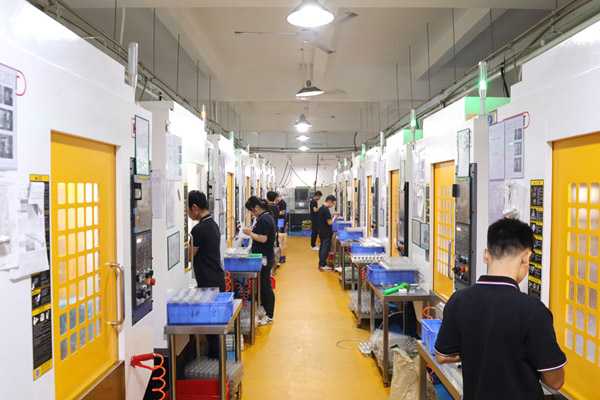
100 CNC machining equipment provide you with prototype manufacturing, evaluation, design and testing. We can complete CNC machining and delivery of stainless steel galvanized CNC machining prototype parts according to your specific requirements within 1 day. |
|
|
|
|
||
Custom Stainless Steel Galvanized CNC Machining Parts Surface Treatment |
Custom Stainless Steel Galvanized CNC Machining Parts Material |
||
|
Our own material library can provide you with special materials such as stainless steel, brass, copper, aluminum, etc., with material testing reports attached. There are professional CNC stainless steel galvanized CNC machining machining project engineers to choose the right materials for you. |
We can provide a variety of surface treatment services based on your Custom CNC stainless steel galvanized CNC machining machining project: polishing, anodizing, powder coating, laser engraving, custom graphics, etc. 12 quality inspection processes ensure that your CNC machined parts have a yield rate of 98%. |
| Still selecting materials for your custom CNC machined metal stainless steel galvanized CNC machining? Different materials have different properties, and you can customize the CNC stainless steel galvanized CNC machining to your liking. Here are some common materials used in manufacturing metal stainless steel galvanized CNC machining: |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
12 Quality Inspection Processes
| Refined production standards, providing you with precision parts with a pass rate of up to 98% |
|
|
|
|
||
| DFM Analysis | Dimensional Tolerance | Material Testing | ||
|
|
|
|
||
| CNC Machining | FQC detection | SPC / CKP | ||
|
|
|
|
||
| Problem Found | Problem Solving | OQC Detection | ||
|
|
|
|
||
| Surface Treatment | Full Inspection | Package |
| The following is the manufacturing process of customized CNC machined metal stainless steel galvanized CNC machining. Due to the need to protect the rights and interests of customers, the following picture is not the manufacturing process of this part and is for reference only: |
 |
 |
 |
||
| DFM Analysis | Material | CNC Machining | ||
|
|
|
 |
||
| Surface Treatment | Quality Inspection | Package |
|
Quality Testing Equipment |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
Custom Stainless Steel Galvanized CNC Machining Parts Quality Assurance
|
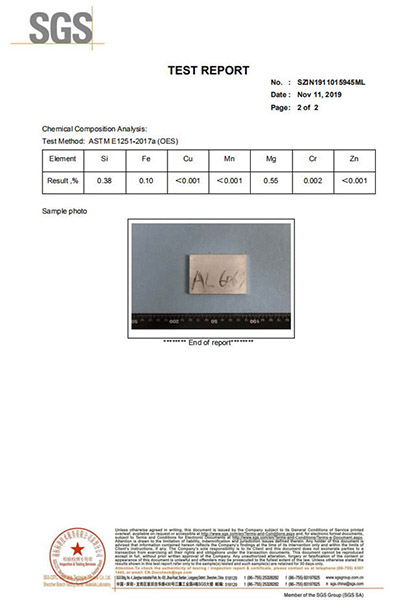
Quality inspection reports are an important tool to ensure the quality and precision of your CNC machining work. We can provide a comprehensive overview of the finished product with a detailed test report on material and product performance, either from an in-house auditor or a third-party laboratory. Ensure finished product meets all customer requirements. |
|
Qualify Evaluation Report
For each order we receive, we can provide a list of quality inspection reports according to your processing requirements.
Inspection report
Certificate
ISO 9001:2015 IATF 16949:2015 ROHS Directive 12 patent certifications
|
 |
|
|
Custom Stainless Steel Galvanized CNC Machining Parts FAQs
|
1. What is galvanization, and how is it applied to CNC-machined stainless steel parts?
Galvanization is a process where a protective zinc coating is applied to metal, typically to prevent rust and corrosion. For CNC-machined stainless steel parts, galvanization is generally applied via hot-dip galvanizing or electro-galvanizing. This coating enhances the part’s durability, especially in environments prone to moisture or chemical exposure.
2. Can stainless steel parts be galvanized, and why would this be necessary?
While stainless steel is naturally corrosion-resistant due to its chromium content, galvanizing can offer additional protection in extremely harsh environments where even stainless steel may corrode over time. It also provides sacrificial protection, where the zinc coating corrodes first, protecting the stainless steel underneath.
3. What are the differences between hot-dip galvanizing and electro-galvanizing for CNC stainless steel parts?
Hot-dip galvanizing: The part is dipped into molten zinc, resulting in a thicker, more durable coating that offers excellent corrosion protection. However, it may produce a rougher surface finish. Electro-galvanizing: A thinner zinc layer is applied using an electrochemical process, offering a smoother finish with moderate corrosion resistance. This method is often preferred for parts requiring finer aesthetics or tighter tolerances.
4. Why would you galvanize stainless steel if it’s already corrosion-resistant?
While stainless steel offers good resistance to corrosion, galvanization provides an extra layer of protection in highly corrosive environments, such as marine or industrial settings. Galvanization can also serve as a barrier against oxidation or to extend the lifespan of parts subjected to extreme conditions.
5. What industries use galvanized stainless steel CNC parts?
Construction: Galvanized stainless steel is used in structural components, fasteners, and hardware exposed to outdoor environments. Marine: In saltwater environments, galvanization provides extra corrosion protection for marine hardware, dock fittings, and other components. Automotive: Galvanized CNC parts are used in undercarriage components, brackets, and other areas prone to moisture and road salt. Electrical: Galvanized parts are used for outdoor electrical enclosures and hardware to protect them from moisture and rust.
6. How does galvanization affect the appearance of stainless steel CNC parts?
The zinc coating from galvanization typically gives the part a dull gray or silvery appearance. Hot-dip galvanizing may result in a rough, textured finish, while electro-galvanizing provides a smoother and more uniform finish. The appearance may not be as polished or reflective as untreated stainless steel, so it may affect aesthetic applications.
7. Does galvanization affect the dimensions of CNC-machined stainless steel parts?
Yes, galvanization adds a thin layer of zinc to the surface, which can increase the overall dimensions of the part. The thickness of this layer varies: Hot-dip galvanizing typically adds 80 to 150 microns of coating. Electro-galvanizing adds a thinner layer, usually between 5 and 20 microns. It’s important to account for this coating when designing parts with tight tolerances, or masking areas that should not be coated.
8. What are the advantages of galvanizing CNC stainless steel parts?
Enhanced corrosion resistance: Galvanization provides an additional layer of protection in highly corrosive or outdoor environments. Longer lifespan: The zinc coating acts as a barrier and a sacrificial layer, ensuring the stainless steel underneath lasts longer. Low maintenance: Galvanized parts generally require less maintenance, as the coating self-heals to a certain extent when scratched. Cost-effective protection: Especially for applications where extended durability is crucial, galvanizing offers a relatively low-cost solution for enhancing corrosion resistance.
9. What are the limitations of galvanizing CNC stainless steel parts?
Aesthetic limitations: The appearance of galvanized parts may not be suitable for applications requiring a high-end or polished look, especially with hot-dip galvanizing. Thickness control: The added coating thickness can affect dimensional accuracy, especially for precision CNC-machined parts with tight tolerances. Heat resistance: Zinc coatings have lower heat resistance compared to bare stainless steel, making galvanized parts unsuitable for high-temperature environments. Not suitable for all applications: In some cases, stainless steel’s natural corrosion resistance may be sufficient, making galvanization unnecessary.
10. How long does galvanization last on CNC-machined stainless steel parts?
The lifespan of a galvanized coating depends on the thickness of the zinc layer and the environmental exposure. In mild environments, galvanized coatings can last 20 to 50 years. In more corrosive environments, such as coastal or industrial areas, the lifespan may be shorter, around 10 to 20 years.
11. Can you galvanize CNC parts with complex geometries?
Yes, both hot-dip galvanizing and electro-galvanizing can be applied to parts with complex shapes. However, hot-dip galvanizing can result in inconsistent coating thickness in recesses or corners, while electro-galvanizing is more precise, providing an even coating on intricate designs.
12. How is galvanization different from other protective coatings like powder coating or anodizing?
Powder coating: Provides a colorful and more aesthetically pleasing finish compared to galvanization. However, powder coating is more prone to scratches and damage, while galvanization offers better corrosion resistance in harsh environments. Anodizing: Primarily used on aluminum, anodizing creates a hard oxide layer but doesn’t offer the sacrificial protection that zinc galvanization does. Anodizing is better suited for decorative purposes and wear resistance, whereas galvanization is focused on corrosion protection.
13. Can galvanized stainless steel parts be welded?
Welding galvanized parts requires extra precautions. The zinc coating produces toxic fumes when heated, so proper ventilation and safety gear are essential. In most cases, the zinc coating near the weld area is removed before welding. After welding, the area can be re-galvanized to restore corrosion protection.
14. What is the typical lead time for galvanized CNC stainless steel parts?
The lead time depends on the complexity of the part, the method of galvanization, and the production volume. Generally, lead times for galvanized CNC parts range from 2 to 6 weeks. Hot-dip galvanizing may take longer due to the curing process, while electro-galvanizing is typically faster.
15. What should be considered when designing CNC-machined parts for galvanization?
When designing parts for galvanization, it’s important to: Allow for coating thickness: Incorporate tolerance allowances for the added zinc layer. Avoid narrow gaps: Hot-dip galvanizing can result in uneven coating on very narrow gaps or corners, so it’s best to avoid overly tight spaces. Use masking for critical surfaces: Areas that need to remain uncoated, such as threads or bearing surfaces, should be masked during the galvanization process.
16. Is it possible to remove or repair galvanization on CNC parts?
Yes, galvanization can be removed through chemical stripping or abrasive blasting. If the coating is damaged, minor scratches may self-heal as the zinc sacrificially corrodes. However, larger areas of damage will require re-galvanizing or applying zinc-rich paints for spot repairs.
17. How is quality controlled in the galvanization process?
Quality control involves checking: Coating thickness: Using gauges to ensure the zinc layer meets specifications. Adhesion testing: Ensuring the zinc adheres properly to the stainless steel substrate. Visual inspection: Checking for uniformity of the coating and identifying any uncoated areas, pinholes, or rough surfaces.
18. What factors influence the cost of galvanizing CNC stainless steel parts?
Method of galvanization: Hot-dip galvanizing generally costs more than electro-galvanizing due to the thicker coating and the resources required. Size and complexity of the part: Larger or more complex parts require more zinc and time to coat, increasing the cost. Quantity: High-volume production typically reduces the cost per part. Surface preparation: Additional cleaning, blasting, or chemical treatments before galvanization may increase the overall cost.
19. How can I ensure the best performance for galvanized CNC stainless steel parts?
To ensure the best performance: Choose the appropriate galvanization method based on the application and environment. Design parts with coating thickness in mind to ensure proper fit and function after galvanization. Regularly inspect parts for damage to the coating, especially in highly corrosive environments, and repair any areas where the zinc layer has been compromised. |
| We hope these CNC metal stainless steel galvanized CNC machining faqs answer your questions. If you have more questions or require further assistance, please feel free to contact our dedicated customer support team. We're here to help you build the perfect custom CNC stainless steel galvanized CNC machining just for you. |
Contact Us
 Related suggestion
Related suggestionGive us a call or send an inquiry to our emailbox, we will answer your doubts according to your customers' requirements, and quote you immediately.
