15 years one-stop China custom CNC machining parts factory
 149 |
Published by VMT at Nov 09 2024 | Reading Time:About 6 minutes
149 |
Published by VMT at Nov 09 2024 | Reading Time:About 6 minutes
:
Are you struggling with the challenges of producing lightweight yet durable CNC machining parts? Frustrated by materials that either weigh too much or don't offer the necessary strength for your custom CNC machining projects? The problem lies in finding a metal that strikes the perfect balance between weight and performance. Aluminum, with its unique density properties, could be the solution your CNC machining factory needs to enhance efficiency and product quality.
The density of aluminum is approximately 2.70 g/cm³, making it one of the lightest commercially available metals. This low density is crucial in CNC machining parts manufacturing, as it allows for the production of lightweight yet strong components, improving performance and fuel efficiency in industries like aerospace and automotive.
Understanding the significance of aluminum's density is essential for optimizing CNC machining services. Let's delve deeper into what density means, explore the properties of aluminum and its alloys, and discover how these factors play a pivotal role in custom CNC machining and prototype development.
Preface
In the world of CNC machining parts manufacturing, material selection is a critical factor that determines the success of a project. Aluminum stands out due to its low density, excellent machinability, and a host of other beneficial properties. This article explores the concept of density, specifically focusing on aluminum, and how it impacts CNC machining services. We will also examine the properties of various aluminum alloys, factors affecting their density, and practical applications in the industry.
Definition of Density
Density is a fundamental physical property defined as mass per unit volume. Mathematically, it is expressed as:
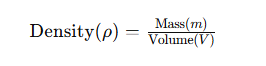
Density provides insight into how much material is contained within a specific space. In CNC machining, understanding the density of materials like aluminum is crucial for designing components that meet weight and strength requirements.
Units of Measurement of Density
The standard unit of density in the International System of Units (SI) is kilograms per cubic meter (kg/m³). However, in the context of CNC machining parts and material specifications, density is often expressed in grams per cubic centimeter (g/cm³) or pounds per cubic inch (lb/in³). For aluminum:
Understanding these units allows engineers and machinists to perform accurate calculations during the design and manufacturing processes in custom CNC machining projects.
Aluminum has a density of approximately 2.70 g/cm³ (2,700 kg/m³). This low density is one of aluminum's most significant advantages, especially in industries where weight reduction is essential without compromising strength. In CNC machining services, using aluminum allows for the creation of lightweight yet robust components suitable for a wide range of applications, from aerospace to consumer electronics.
The density of aluminum is about one-third that of steel (approximately 7.85 g/cm³) and copper (approximately 8.96 g/cm³), making it a preferred material when weight savings are critical. This characteristic contributes to improved fuel efficiency in automotive and aerospace applications and easier handling and installation in construction and manufacturing settings.
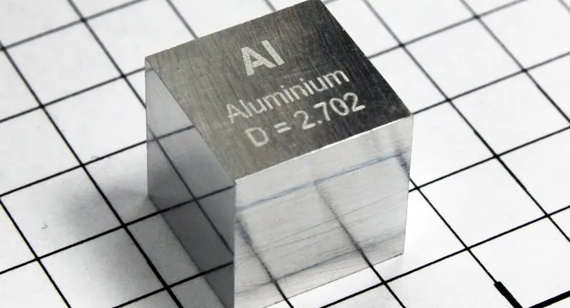
Aluminum's properties can be tailored by creating alloys with various elements such as copper, magnesium, silicon, zinc, and manganese. These aluminum alloys exhibit different densities and mechanical properties, making them versatile for numerous applications in CNC machining parts manufacturing.
Lightness
The inherent low density of aluminum makes it lightweight, which is advantageous in producing CNC machined parts that require ease of transport and installation. In industries like aerospace and automotive, reducing component weight leads to better fuel efficiency and performance.
Corrosion Resistance
Aluminum naturally forms a thin oxide layer when exposed to air, providing excellent corrosion resistance. This property is particularly beneficial in CNC machining services for parts exposed to harsh environments, such as marine or industrial applications.
Recyclability
Aluminum is 100% recyclable without degradation of its inherent properties. Recycling aluminum requires only about 5% of the energy used to produce primary aluminum, making it a sustainable choice for CNC machining factories focused on environmental responsibility.
Electrical and Thermal Conductivity
Aluminum has high electrical and thermal conductivity, making it suitable for electrical components and heat exchangers. In custom CNC machining, this property is leveraged to produce parts that efficiently dissipate heat or conduct electricity.
Physical Properties
These physical properties make aluminum ideal for various CNC machining applications where weight, heat dissipation, and conductivity are concerns.
Chemical Properties
Aluminum is a highly reactive metal but resists corrosion due to the formation of an inert oxide layer. It reacts with acids and bases but is stable in neutral environments. Understanding these chemical properties is essential in CNC machining services to prevent undesirable reactions during processing and in the end-use environment.
While pure aluminum has a consistent density, the addition of alloying elements can alter this property. In CNC machining parts manufacturing, recognizing the factors that affect aluminum's density helps in selecting the appropriate alloy for specific applications.
Alloy Composition
The primary factor influencing the density of aluminum alloys is their composition. Adding elements like copper, magnesium, silicon, zinc, and others can increase or decrease the overall density. For example:
Understanding the specific alloy composition is crucial in custom CNC machining to meet precise weight and performance specifications.
8 Factors That Cause Density Changes
Machining: Mechanical processing can introduce stress and microstructural changes, slightly affecting density.
In CNC machining services, controlling these factors ensures consistency and quality in the manufactured parts.

Different aluminum alloys have varying densities due to their unique compositions. Below is a table summarizing the densities of common aluminum alloys used in CNC machining parts manufacturing:
| Alloy |
Density (g/cm³) |
| Aluminum 1050 | 2.71 |
| Aluminum 1100 | 2.72 |
| Aluminum 2024 | 2.78 |
| Aluminum 3003 | 2.73 |
| Aluminum 5052 | 2.68 |
| Aluminum 6061 | 2.70 |
| Aluminum 7075 | 2.81 |
Understanding these densities aids in material selection for custom CNC machining projects, ensuring that the final product meets the required specifications.
Comparing aluminum's density with other metals highlights its advantages in weight-sensitive applications. Here's how aluminum stacks up against common metals used in CNC machining services:
| Metal | Density (g/cm³) |
| Density of Titanium |
4.51 g/cm³ |
| Density of Iron |
7.87 g/cm³ |
| Density of Steel (various grades) |
7.85 g/cm³ |
| Density of Copper |
8.96 g/cm³ |
| Density of Bronze |
8.80 g/cm³ |
| Density of Nickel |
8.90 g/cm³ |
| Density of Magnesium |
1.74 g/cm³ |
| Density of Zinc |
7.14 g/cm³ |
| Density of Tungsten |
19.25 g/cm³ |
| Density of Gold |
19.32 g/cm³ |
| Density of Platinum |
19.32 g/cm³ |
| Density of Platinum |
21.45 g/cm³ |
Aluminum's low density compared to these metals makes it an attractive option for CNC machining factories aiming to reduce component weight without sacrificing performance.
Why is Aluminum Low in Density?
Aluminum's low density is due to its atomic structure and the relatively low atomic mass of its constituent atoms. The metallic bonding in aluminum involves delocalized electrons spread over a lattice of atoms, resulting in a less tightly packed structure compared to heavier metals like iron or copper.
The Importance of Low Density Includes:
Different aluminum grades have varying densities and properties, making them suitable for specific CNC machining applications. Below, we explore some common grades used in CNC machining services.
1100 Series
2024 Grade
3003 Grade
5052 Grade
6061 Grade
7075 Grade
Accurately calculating the density of aluminum and its alloys is essential in CNC machining services to ensure components meet design specifications and performance criteria.
How to Calculate the Density of Aluminum?
Mass Measurement
Measure the mass of the aluminum sample using a precise scale or balance, ensuring accuracy by calibrating the equipment and accounting for any environmental factors.
Volume Measurement
Determine the volume of the sample, which can be calculated geometrically for regular shapes or measured using displacement methods for irregular shapes.
Density Formula
Use the density formula:
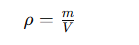
Where:
