15 years one-stop China custom CNC machining parts factory

Hey there I’m VMT Sam!
With 25 years of CNC machining experience we are committed to helping clients overcome 10000 complex part-processing challenges all to contribute to a better life through intelligent manufacturing. Contact us now
 102 |
Published by VMT at Jan 22 2024
102 |
Published by VMT at Jan 22 2024
Introduction:
In the manufacturing industry, copper CNC machined parts find widespread applications in various fields such as electronics, communication, aerospace, and more. Precision and quality are vital metrics for assessing copper CNC machined parts, representing focal points of customer attention. This article explores how to ensure that the precision and quality of copper CNC machined parts meet requirements, enhancing product competitiveness.

I. Material Selection and Treatment:
Choice of High-Quality Copper:
Selecting appropriate copper material types with excellent mechanical, thermal, and chemical properties.
Material Inspection:
Rigorous inspection of purchased copper materials to ensure they are free from defects and impurities, meeting technical requirements.
Material Preprocessing:
Performing preprocessing on copper materials, such as straightening and cutting, to eliminate internal stresses and ensure stability during the machining process.

II. Machining Equipment and Tools:
Advanced Equipment:
Utilizing high-precision CNC machining centers to ensure equipment accuracy and stability.
Tool Selection:
Choosing suitable cutting tools, fixtures, and measuring tools based on different machining requirements to guarantee precision and efficiency.
Equipment Maintenance:
Regularly maintaining and servicing equipment to ensure it remains in good condition.

III. Machining Process and Parameters:
Establishing Rational Machining Processes:
Developing scientifically sound machining processes based on copper material characteristics and part design requirements.
Parameter Optimization:
Optimizing machining parameters such as cutting speed, feed rate, and cutting depth to improve machining precision and efficiency.
Cooling Methods:
Selecting appropriate cooling fluids and methods to reduce the impact of cutting heat on the workpiece and prevent thermal deformation.
IV. Quality Inspection and Control:
Dimensional Inspection:
Accurately measuring the dimensions of copper CNC machined parts using measurement tools to ensure they meet design requirements.

Surface Quality Inspection:
Inspecting part surface quality, including smoothness, texture, and roughness, using visual inspection, tactile methods, and surface roughness measuring instruments.

Structural Integrity Inspection:
Utilizing methods such as tapping and vibration to check for internal flaws, cracks, or voids in machined parts.
Material Composition Inspection:
Employing chemical analysis or spectroscopy to inspect the material composition of copper CNC machined parts, ensuring compliance with standards.
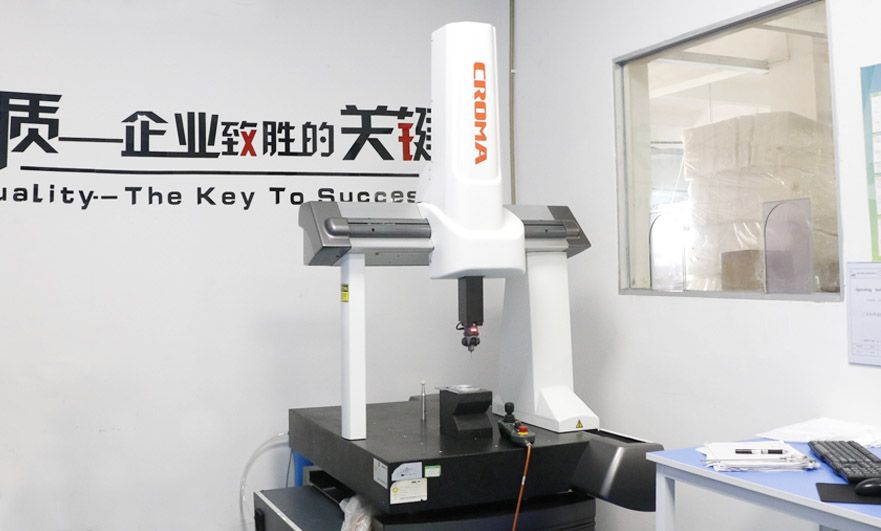

Mechanical Performance Testing:
Conducting mechanical tests such as tension, compression, and bending on copper CNC machined parts to assess whether they meet design requirements.
Statistical Process Control (SPC):
Applying SPC techniques for real-time monitoring and data analysis of the machining process, promptly identifying anomalies and implementing corrective measures.

First Article Inspection and Process Checks:
Conducting first article inspections during the machining process to ensure the accuracy of machining parameters and tooling. Strengthening process checks to promptly identify and correct issues, preventing batch defects.
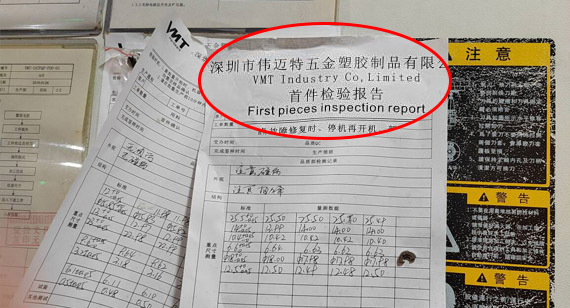
Final Inspection and Shipping Checks:
Performing final inspections on finished parts to ensure they meet customer requirements. Identifying, labeling, packaging, and conducting shipping checks on qualified products to ensure optimal product quality upon delivery.

V. Employee Training and Quality Awareness Cultivation:
Regular Training:
Providing regular skill and safety training for employees to enhance their operational skills and safety awareness.
Quality Awareness Cultivation:
Reinforcing employees' awareness of quality and instilling the importance of quality throughout the entire production process.
Incentive Mechanisms:
Establishing quality assessment and incentive mechanisms to encourage employee participation in quality management, boosting motivation and responsibility.
VI. Continuous Improvement and Innovation:
Process Optimization:
Continuously optimizing processes and management systems based on production practices and market feedback to improve production efficiency and product quality.
Technological Innovation:
Staying abreast of industry trends and technological developments, applying innovations to practical production, enhancing product quality, and competitiveness.
Quality Management System Construction:
Establishing a robust quality management system to ensure the effective implementation of quality testing. Conducting regular internal audits and management reviews to identify and address system issues, driving continuous improvement.
Customer Feedback and Communication:
Establishing an effective customer feedback mechanism to promptly understand customer evaluations and requirements. Addressing customer complaints and returns proactively, analyzing issues, and implementing improvements to enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Participation in Industry Exchanges and Collaboration:
Actively participating in industry exchange activities, sharing experiences and technological achievements with peers. Strengthening collaboration and communication with suppliers and customers to collectively address quality issues and elevate the overall quality level of the supply chain.
Preventive Maintenance and Care:
Implementing regular preventive maintenance and care for equipment, reducing the risk of equipment failures and production interruptions. Through checks, adjustments, and repairs of equipment's vulnerable parts and critical components, ensuring stable equipment operation and extending its lifespan. Simultaneously, enhancing equipment documentation management by recording maintenance and usage information, providing a basis for equipment fault diagnosis and performance evaluation.
VII. Continuous Improvement of the Quality Management System:
Setting and Achieving Quality Objectives:
Setting clear quality objectives based on business strategies and market demands, formulating implementation plans, and ensuring objective realization through regular assessments and adjustments.
Internal Audits of the Quality Management System:
Conducting regular internal audits of the quality management system to ensure its effectiveness and compliance. Identifying and addressing existing issues to enhance system operation.
Quality Management System Certification:
Obtaining quality management system certifications such as ISO 9001 to demonstrate the ability to consistently provide high-quality products. Continuously monitoring international standards and industry trends to ensure system consistency and advancement.

Data Analysis and Improvement:
Collecting quality data during the production process, conducting in-depth analysis to identify key factors affecting product quality. Formulating targeted improvement measures to enhance product quality and reduce defect rates.
Supply Chain Quality Management:
Establishing close cooperative relationships with suppliers to ensure the quality of raw materials and components. Ensuring supply chain quality stability and reliability through supplier assessments, audits, and quality agreements.
Cultivation of a Continuous Improvement Culture:
Cultivating a culture of continuous improvement within the organization, encouraging employees to actively participate in quality improvement activities. Stimulating innovation and improvement motivation through initiatives such as establishing quality awards and quality improvement teams.
Customer Satisfaction Surveys:
Regularly conducting customer satisfaction surveys to understand customer evaluations and demands. Formulating improvement measures based on customer feedback and opinions to enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty.
By implementing the above measures, a company can establish a comprehensive quality management system, ensuring that the precision and quality of copper CNC machined parts meet requirements. This will contribute to enhancing the company's competitiveness, gaining the trust of customers, and securing collaboration opportunities. Additionally, companies should stay attentive to industry dynamics and technological innovations, continuously improving the quality management system to adapt to evolving market demands and industry trends.
Ready To Start Your Next Project?
Get Instant Quote

Request a Free Quote
Send us a message if you have any questions or request a quote. We will get back to you ASAP!