15 years one-stop China custom CNC machining parts factory
 2472 |
Published by VMT at Jul 31 2024
2472 |
Published by VMT at Jul 31 2024
Washers are indispensable small components in mechanical connections, whose importance cannot be underestimated. They not only provide necessary spacing and alignment functions but also play crucial roles in load distribution, sealing, shock absorption, damage prevention, corrosion resistance, and insulation. This article aims to provide a comprehensive introduction to the types, materials, surface treatments, and size charts of washers, helping readers choose the right washers for CNC machining parts manufacturing and understand their application principles.

A washer is a metal or non-metal ring placed between two connecting parts to adjust gaps, distribute pressure, prevent loosening, seal, or insulate. They are widely used in various mechanical equipment, construction structures, and electrical systems to ensure the stability of connections and the normal operation of systems.
Washers are essential when using bolts and nuts to connect parts. The uses of washers include:

Spacing and Alignment: Washers adjust the gap between two connected parts to ensure they are correctly aligned.
Load Distribution: By distributing the pressure generated by bolts or screws, washers protect the connected parts from damage.
Sealing/Liquid Protection: Some washers (such as rubber washers) have sealing functions to prevent liquid or gas leaks.
Shock Absorption: In dynamic environments, washers absorb vibrations and reduce wear between mechanical parts.
Damage Prevention: Prevent scratches or corrosion caused by direct contact between connecting parts.
Corrosion Resistance: Specific materials like stainless steel washers resist corrosion, extending the service life.
Insulation: Insulating washers in electrical connections prevent current from passing through the connectors, ensuring safety.
Different types of washers play crucial roles in mechanical connections and assemblies, each with unique designs and functions to meet various application needs. Washers can be categorized by their function, shape, and material into multiple types. Here are some common types of washers:
Flat Washers
The most basic and widely used type of washer, usually used in general mechanical connections to increase the contact area and reduce pressure on the connected part from the bolt. Flat washers can be divided into small, standard, large, and extra-large series according to structure; and into A-grade and C-grade according to precision.

Torque Washers (Preload Washers)
Designed to generate a certain preload during tightening to ensure the tightness of the connection. They may achieve this function through special structures or material properties.

Fender Washers
Specifically used to prevent liquids, dust, or other contaminants from entering the connection area, commonly found in automotive and mechanical equipment sealing systems.

Finishing or Countersunk Washers
Designed with special recesses or grooves so that the washer can sink into or fit the surface of the connected part during installation, achieving a smoother appearance.

Shoulder Washers
Have one or more raised shoulders to increase thickness or provide additional positioning functions, ensuring precise alignment between connecting parts.

C Washers
Typically refer to washers with a specific C-shaped cross-section, commonly used for sealing and fixing on bearings, shafts, or rods.
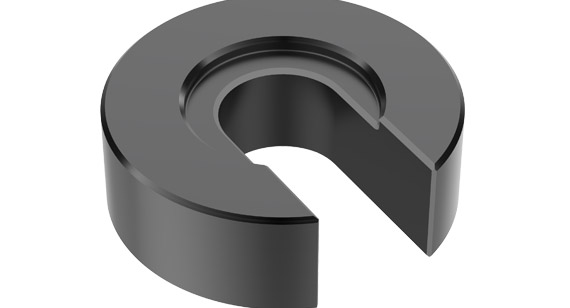
Known for their elastic properties, widely used in situations that require prevention of bolt loosening. Common types include standard spring washers, saddle-shaped spring washers, and wave spring washers. They press the connected parts through elastic deformation, preventing loosening.
Belleville Washers or Conical Washers: Spring washers with a conical cross-section providing preload through elastic deformation.
Dome Spring Washers: Spring washers with a domed top used to provide additional fastening force.
Wave Spring Washers: Washers with a wavy cross-section providing a larger range of elastic deformation and preload.
Finger Spring Washers and Crescent Spring Washers: Washers with specific shapes (like finger-shaped or crescent-shaped) for specific fastening and sealing needs.


Lock washers prevent bolts or screws from loosening under vibration or load through special designs like inner and outer teeth structures. Common types include split lock washers, external tooth lock washers, and internal tooth lock washers.
Split Lock Washers: Have one or more cuts that open and embed into the surface of the connected part when the bolt is tightened, providing a locking effect.
External Tooth Lock Washers and Internal Tooth Lock Washers: Have tooth structures on the outer or inner edges respectively, interacting with the surface of the connected part to prevent loosening.

Similar to Belleville washers but with a more pronounced conical structure, providing stronger preload and anti-loosening effects.
Each type of washer is designed according to its specific physical properties, material composition, and application scenarios to ensure stability, safety, and reliability between connecting parts.
Specialty washers are designed for specific application needs, such as Kapton nuts, dome washers, key washers, and insulating shoulder washers. These washers provide better connection effects or meet specific performance requirements in particular situations.
Kapton Nut (K-Lock Nut) Dome Washers
Definition and Purpose: K-lock nuts are typically used in high anti-loosening performance situations, such as machine tool spindles and lead screws, preventing loosening under vibration or impact through special locking mechanisms like slopes or threads. Dome washers, as part of or used with K-lock nuts, may have specific shapes or materials to enhance locking effect or protect contact surfaces.
Features: High strength and anti-loosening performance, may have specific shapes and sizes to meet different installation needs.

Key Washers
Definition and Purpose: Key washers are typically used in the assembly between shafts and key slots to prevent keys from sliding or loosening on shafts. They increase the contact area and provide additional locking force to ensure a stable connection between keys and shafts.
Features: Precise dimensions and shapes to ensure perfect fit with key slots and shafts, usually made of wear-resistant and corrosion-resistant materials.
Insulating Shoulder Washers
Definition and Purpose: Insulating shoulder washers are mainly used in situations requiring electrical insulation, such as electronic and electrical equipment. They provide a layer of insulating material to prevent current from passing through the washer's position, protecting equipment and personnel safety.
Features: Excellent electrical insulation performance, high temperature and corrosion resistance characteristics to adapt to different working environments.
Washers
Definition and Purpose: Washers are common fastener accessories usually used to fill gaps between two objects to reduce friction, prevent leakage, or provide additional support. They are widely used in machinery, automotive, aerospace, construction, and other fields.
Types and Materials: Washers come in various types, including flat washers, spring washers, conical washers, wave washers, etc. Materials include metals (like stainless steel, carbon steel), plastics (like nylon, PTFE), rubber, and more.
The material selection for washers is crucial for their performance and application scenarios. Common washer materials include rubber, nylon, metal, and plastic.
Rubber and Nylon Washers
Rubber washers have good sealing and waterproof properties, often used in pipe connections and automotive parts. Nylon washers, due to their excellent wear resistance and chemical resistance, are widely used in environments requiring wear and corrosion resistance.

Metal Washers
Metal washers have high strength and corrosion resistance, suitable for various mechanical connection scenarios. Stainless steel washers are commonly used in harsh environments such as marine environments and chemical industries due to their good corrosion resistance. Copper washers are often used in electrical connections or situations requiring conductivity due to their excellent conductivity and thermal conductivity. Aluminum washers are commonly used in applications requiring weight reduction due to their lightweight and good thermal conductivity.

Plastic Washers
Plastic washers like polyethylene washers have good chemical resistance and wear resistance, often used in waterproof and shock-absorbing scenarios. Metal-plastic composite washers combine the strength of metal and the corrosion resistance of plastic, suitable for complex environments.

Surface treatments for washers are essential to enhance their corrosion resistance, oxidation resistance, wear resistance, and aesthetics. Common washer surface treatments include natural finish, galvanizing, polishing, electroplating, anodizing, and spraying.
Galvanizing
Galvanizing involves coating the washer surface with a layer of zinc to prevent corrosion. Galvanized washers have good corrosion resistance and are suitable for outdoor or humid environments.
Polishing
Polishing smooths and brightens the washer surface through mechanical or chemical methods. Polished washers are not only aesthetically pleasing but also reduce friction and improve sealing performance.
Electroplating
Electroplating involves depositing metals on the washer surface, commonly including chromium, nickel, and zinc plating. Electroplating enhances the washer's corrosion resistance and oxidation resistance, providing a smooth and aesthetically pleasing surface.
Anodizing
Anodizing is an electrochemical process that forms an oxide layer on the surface of aluminum and its alloys. Anodized washers have excellent wear resistance, corrosion resistance, and decorative properties.
Spraying
Spraying involves using a spray gun to evenly coat the washer surface with paint. This method can be applied to various materials, including metal and plastic, providing corrosion, rust, wear resistance, or specific color effects. Sprayed washers not only enhance functionality but also improve the product's aesthetics and identification.
The size of a gasket is usually determined by three parameters: its inner diameter (ID), outer diameter (OD) and thickness (T). Different standards (such as SAE, USS, DIN, etc.) specify gaskets of different size series to meet the needs of different application scenarios.
The size of washers is crucial for their compatibility and functionality. Here is an overview of the size charts for some common washer types and specific examples.
Washer type chart
For easy reference, a washer type chart is usually made to list the size range, standard number and applicable scenarios of various types of washers. These charts are important reference tools for engineers and purchasers when selecting washers.
SAE flat washers
The SAE (Society of Automotive Engineers) standard specifies the sizes of various flat washers. For example, the SAE ASME B18.22.1 standard lists in detail the flat washers of different size series from #0 to #6, and each size series contains a variety of combinations of inner diameter, outer diameter and thickness.
| Size | Inside Diameter | Outside Diameter | Thickness |
| #6 | 5/32″ | 3/8″ | 3/64″ |
| #8 | 3/16″ | 7/16″ | 3/64″ |
| #10 | 7/32″ | 1/2″ | 3/64″ |
| 1/4 | 9/32″ | 5/8″ | 1/16″ |
| 1/16″ | 11/32″ | 11/16″ | 1/16″ |
| 3/8 | 13/32″ | 13/16″ | 1/16″ |
| 7/16 | 15/32″ | 59/64″ | 1/16″ |
| 1/2 | 17/32″ | 1-1/16″ | 3/32″ |
| 9/16 | 19/32″ | 1-3/16″ | 3/32″ |
| 5/8 | 21/32″ | 1-5/16″ | 3/32″ |
| 3/4 | 13/16″ | 1-1/2″ | 9/64″ |
| 7/8 | 7/8 | 1-3/4″ | 9/64″ |
| 1″ | 1-1/16″ | 2″ | 9/64″ |
| 1-1/8 | 1-3/16″ | 2-1/4″ | 9/64″ |
| 1-1/4 | 1-5/16″ | 2-1/2″ | 5/32″ |
| 1-1/2 | 1-7/16″ | 3″ | 3/16″ |
USS flat washers
The flat washer sizes under the USS (Unified Screw Threads) standard are different from the SAE standard, but they also provide a wide range of size options. USS flat washers are usually used in connections that need to match the US unified thread standard.
| Size | Inside Diameter | Outside Diameter | Thickness |
| 3/16 | 1/4″ | 9/16″ | 3/64″ |
| 1/4 | 5/16″ | 3/4″ | 1/16″ |
| 5/16 | 3/8″ | 7/8″ | 5/64″ |
| 3/8 | 7/16″ | 1″ | 5/64″ |
| 7/16 | 1/2″ | 1-1/4″ | 5/64″ |
| 1/2 | 9/16″ | 1-3/8″ | 7/64″ |
| 9/16 | 5/8″ | 1-1/2″ | 7/64″ |
| 5/8 | 11/16″ | 1-3/4″ | 9/64″ |
| 3/4 | 13/16″ | 2″ | 5/32″ |
| 7/8 | 15/16″ | 2-1/4″ | 11/64″ |
| 1″ | 1-1/16″ | 2-1/2″ | 11/64″ |
| 1-1/8 | 1-1/4″ | 2-3/4″ | 11/64″ |
| 1-1/4 | 1-3/8″ | 3″ | 11/64″ |
| 1-3/8 | 1-1/2″ | 3-1/4″ | 3/16″ |
| 1-1/2 | 1-5/8″ | 3-1/2″ | 3/16″ |
| 1-5/8 | 1-3/4″ | 3-3/4″ | 3/16″ |
| 1-3/4 | 1-7/8″ | 4″ | 3/16″ |
| 1-7/8 | 2″ | 4-1/4″ | 3/16″ |
| 2″ | 2-1/8″ | 4-1/2″ | 3/16″ |
| 2-1/2 | 2-5/8″ | 5″ | 15/64″ |
| 3″ | 3-1/8″ | 5-1/2″ | 9/32″ |
Flat Washer Size Chart (Metric & Imperial)
| Nominal Size (d1) | Inside Diameter (d1) | Outside Diameter (d2) | Thickness (h) | Material | Standard |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M3 | 3.2 | 7 | 0.5 | Stainless Steel | DIN 125 |
| M4 | 4.3 | 9 | 0.8 | Carbon Steel | ISO 7089 |
| 1/4" | 6.7 | 14 | 1.5 | Brass | ANSI B18.22.1 |
Spring Washer Size Chart
| Nominal Size (d1) | Inside Diameter (d1) | Outside Diameter (d2) | Thickness (h) | Material | Standard |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M6 | 6.4 | 11 | 1.6 | Spring Steel | DIN 127 |
| M8 | 8.4 | 15 | 2.0 | Stainless Steel | ISO 7090 |
Lock Washer Size Chart
| Nominal Size (d1) | Inside Diameter (d1) | Outside Diameter (d2) | Thickness (h) | Material | Standard |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M10 | 10.5 | 18 | 2.5 | Carbon Steel | DIN 7980 |
| M11 | 13 | 21 | 3.0 | Stainless Steel | ANSI/ASME B18.21.1 |
The tables above provide examples of common washer sizes in metric and imperial units, including inside diameter, outside diameter, thickness, material, and standard. By referencing these size charts, you can select the appropriate washers for different applications to ensure the stability and reliability of connections.
Conclusion
Understanding the types, materials, surface treatments, and size charts of washers helps you choose the right washers for CNC machining parts manufacturing. Whether in general mechanical connections or special applications requiring wear resistance, corrosion resistance, or electrical insulation, washers play a vital role in ensuring the stability and reliability of connections. By mastering the selection and application principles of washers, you can provide more reliable and efficient solutions for CNC machining parts manufacturing.
Washers, though small, play a significant role in mechanical connections by providing essential spacing, alignment, load distribution, sealing, shock absorption, damage prevention, corrosion resistance, and insulation. This article aims to provide a comprehensive introduction to washer shapes, standards, and selection criteria, helping readers choose the right washers for CNC machining parts manufacturing and understand their application principles.
Washers come in various shapes to meet different connection needs and application scenarios. Here are some common washer shapes:
Spherical
Spherical washers have a spherical contact surface, offering better sealing and reduced stress concentration. They are often used in high-pressure or high-temperature environments.
Square
Although not common, square or other polygonal washers may be used in specific applications requiring unique functions or design requirements.
Shoulder
Shoulder washers (such as insulating shoulder washers) have a protruding shoulder to increase contact area or provide specific insulating effects.
Wave
Wave washers (like wave spring washers) provide elastic support through their wavy structure, commonly used in connections requiring vibration reduction or anti-loosening features.
C Shape
C-shaped washers (also known as C-clips) are special washers shaped like the letter "C," used for clamping or securing pipes, cables, and other components.
Standards for washers are crucial to ensure their quality and interchangeability. Here are some common washer standards:
ASME ANSI B18.22.1 Flat Washers
This standard specifies the dimensions, tolerances, and material requirements for flat washers used in various mechanical connections.
ASME B18.21.1 Helical Spring Lock Washers
This standard details the dimensions, shapes, and material requirements for helical spring lock washers, ensuring effective bolt loosening prevention.
DIN 125A Flat Washers
DIN 125A is a commonly used European standard for flat washers, specifying the size and tolerance ranges for mechanical connections in Germany and other European regions.
DIN 6799 Retaining Washers
DIN 6799 standard specifies the dimensions and performance requirements for retaining washers, often used in applications requiring component fixation or clamping.
Selecting the appropriate washer involves considering multiple factors, including material type, strength matching with bolts, and environmental factors.
Material Type
Choosing the right washer material based on the application environment is crucial. For example, stainless steel or galvanized washers should be selected in humid or corrosive environments; rubber or nylon washers should be used in sealing applications.
Strength Matching with Bolts
The washer's strength should match the bolts or screws used to ensure connection stability and safety. Insufficient washer strength may lead to connection loosening or damage.
Environmental Factors
Factors such as temperature, humidity, and corrosive media affect the washer's performance and lifespan. Therefore, when selecting washers, these environmental factors must be considered, and washers with corresponding resistance capabilities should be chosen.
As a professional CNC machining parts manufacturer, VMT can provide customized washer solutions based on your specific requirements. With advanced CNC machining equipment and extensive production experience, we can produce washers in various materials, shapes, and sizes to meet the needs of different industries and applications.

Washers, though small, play a significant role in providing essential connection and sealing functions, protecting equipment, enhancing system stability, and extending service life. By understanding washer types, materials, surface treatments, and size charts, we can better select and use washers to ensure the safety and reliability of mechanical connections. With the continuous development of CNC machining technology, we look forward to producing more innovative and high-performance washer products to meet the increasingly complex and diverse industrial needs.
What are the three main types of washers?
The main types of washers can be broadly categorized based on their functional characteristics: flat washers, spring washers, and lock washers. Flat washers are primarily used to increase contact area and distribute pressure; spring washers use their elastic properties to prevent bolt loosening; lock washers enhance fastening effectiveness through special designs like inner and outer teeth structures.
Why do screws need washers?
Screws use washers for several reasons: to increase the contact area between the screw and the connected part, reduce the pressure per unit area, prevent damage to the connected part, disperse stress through the washer's elasticity or special structure, improve connection stability, and provide additional functions such as sealing, shock absorption, and insulation.
What is the difference between spring washers and flat washers?
The main difference between spring washers and flat washers lies in their structure and function. Spring washers have elasticity and deform under pressure to provide continuous fastening force, preventing bolt loosening. Flat washers, on the other hand, mainly increase contact area and distribute pressure without the elastic properties of spring washers. In terms of application scenarios, spring washers are more suitable for dynamic fastening and anti-loosening situations, while flat washers are more widely used in general mechanical connections.
How to use washers quickly?
The key to using washers quickly is to select the correct washer type and size and ensure compatibility with the bolts or screws used. During installation, pay attention to the direction and position of the washer to fully utilize its function. For certain special types of washers (such as lock washers), follow specific installation steps to ensure fastening effectiveness.
What are the different types of conical washers?
Conical washers, based on their structure and function, can be divided into various types. One typical type is the Belleville washer (also known as a conical spring washer), which deforms elastically under pressure due to its conical structure, providing continuous fastening force. Other forms of conical washers include conical spring washers and conical lock washers, each with distinct features and application scenarios.
What are the different forms of washers?
Washers come in various forms to meet different connection needs and application scenarios. Besides flat washers, spring washers, and lock washers, there are wave washers, C-shaped washers, finger washers, crescent washers, and more. These washers have unique shapes, structures, and functions to cater to different industry needs.
What is an A-type washer?
An A-type washer typically refers to washers conforming to specific A-series specifications under standards such as ASME or DIN. These washers meet A-series standard requirements in terms of size, shape, and material. However, note that the specific definition and specifications of A-type washers may vary under different standards and systems. Therefore, when selecting and using A-type washers, carefully refer to the relevant standards and technical specifications.
In conclusion, washers are crucial components in mechanical connections. Their types, materials, surface treatments, and size choices are vital for ensuring connection stability, safety, and reliability. By thoroughly understanding washer-related knowledge and selecting and using them based on actual application needs, we can better utilize washers' functions and provide strong support for the normal operation of mechanical equipment and systems.
