15 years one-stop China custom CNC machining parts factory
 232 |
Published by VMT at Jan 08 2025 | Reading Time:About 2 minutes
232 |
Published by VMT at Jan 08 2025 | Reading Time:About 2 minutes
In the world of manufacturing, creating precise and complex parts efficiently is a constant challenge. Many businesses struggle with producing high-quality CNC machining parts that meet strict specifications while keeping costs down and production times short. This can lead to delays, increased expenses, and unsatisfied customers. However, 4-axis CNC machining offers a powerful solution to these problems by enhancing the capabilities of traditional CNC machines. Understanding what 4-axis CNC machining is and how it can benefit your manufacturing processes can make a significant difference in your production quality and efficiency.
4-axis CNC machining is an advanced method that adds an extra rotational axis to traditional 3-axis machines, allowing for more complex and precise manufacturing. This extra movement enhances the flexibility and accuracy of CNC machining parts, making it a valuable option for custom CNC machining and CNC machining services.
Choosing the right CNC machining technology is crucial for achieving optimal results in your manufacturing projects. To fully utilize the benefits of 4-axis CNC machining, it is essential to explore its functionalities, advantages, and applications. This comprehensive guide will walk you through everything you need to know about 4-axis CNC machining, helping you make informed decisions that enhance the quality and efficiency of your CNC machining factory operations.
Preface
CNC machining has transformed the manufacturing industry by enabling the creation of highly precise and intricate parts. As technology evolves, CNC machines have become more sophisticated, incorporating additional axes of movement to tackle more complex tasks. Among these advancements, 4-axis CNC machining stands out for its ability to produce parts with greater detail and accuracy compared to traditional 3-axis machining. This guide aims to provide a clear and simple understanding of what 4-axis CNC machining is, how it works, and why it might be the right choice for your manufacturing needs.
4-axis CNC machining is an extension of the traditional 3-axis CNC machining process. While a standard 3-axis machine moves the cutting tool along the X, Y, and Z axes (left-right, front-back, and up-down), a 4-axis machine adds a fourth axis of movement, typically a rotational axis called the A-axis. This additional movement allows the workpiece to rotate, enabling the machine to work on multiple sides of the part without needing to reposition it manually.
This rotational capability means that 4-axis CNC machines can create more complex shapes and features with greater precision. For example, parts with cylindrical shapes, intricate angles, or multiple levels can be machined more efficiently. By adding this extra axis, manufacturers can reduce the number of setups required, minimize the risk of errors, and improve the overall quality of the machined parts.

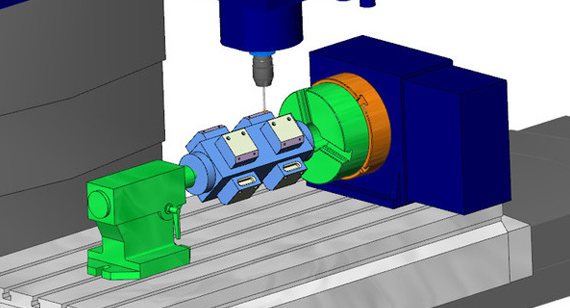
The 4-axis CNC machining process involves several key steps that ensure the production of high-quality parts. Here's a simple breakdown of how it works:
There are several types of 4-axis CNC machines, each designed to handle specific machining tasks. The most common types include milling machines, lathes, and routers.
Milling Machines
4-axis milling machines are widely used in various industries for creating complex parts. These machines can handle a range of materials, including metals, plastics, and composites. The additional rotational axis allows for precise cutting and shaping of intricate features, making them ideal for automotive components, aerospace parts, and custom CNC machining projects.

4-axis CNC lathes combine the traditional turning capabilities of a lathe with the added rotational movement of the A-axis. This makes them perfect for producing cylindrical parts with detailed features, such as shafts, pins, and knobs. The rotational axis enhances the machine's ability to create complex geometries without the need for multiple setups.

Routers
4-axis CNC routers are used primarily for cutting and shaping softer materials like wood, plastics, and composites. They are popular in the construction and furniture industries for creating detailed designs and intricate patterns. The added axis allows for more precise cuts and the ability to work on multiple sides of a workpiece efficiently.
4-axis CNC machines are versatile and used across a wide range of industries. Here are some common applications:

Aerospace Industry
In the aerospace sector, precision and reliability are critical. 4-axis CNC machines are used to create complex parts such as turbine blades, structural components, and intricate fittings that require high accuracy and durability.
The automotive industry benefits from 4-axis CNC machining in producing engine parts, transmission components, and custom fixtures. The ability to create detailed and precise parts helps improve vehicle performance and safety.
Electronics manufacturers use 4-axis CNC machines to produce intricate components like connectors, housings, and circuit boards. The precision offered by 4-axis machining ensures that electronic parts meet strict performance and quality standards.
Oil and Gas Industry
In the oil and gas sector, 4-axis CNC machines are used to manufacture robust and precise components such as valves, fittings, and piping parts that must withstand harsh environments and high pressures.
The medical industry relies on 4-axis CNC machining to produce precise and reliable parts for medical devices, surgical instruments, and implants. The high level of accuracy ensures that medical components perform effectively and safely.
Construction
Construction companies use 4-axis CNC machines to create detailed architectural elements, custom fixtures, and structural components. The ability to produce complex shapes and features efficiently helps streamline construction projects and improve building quality.
4-axis CNC machining offers several benefits that enhance the manufacturing process and the quality of CNC machined parts.
Enhanced Capabilities
The addition of the fourth axis significantly expands the range of shapes and features that can be machined. This allows manufacturers to produce more complex and detailed parts without needing multiple machines or setups.
Increased Efficiency
With the ability to rotate the workpiece, 4-axis CNC machines reduce the number of setups required for machining different sides of the part. This saves time and increases overall production efficiency, allowing for faster turnaround times on orders.
Higher Precision
4-axis CNC machines provide greater accuracy in machining complex features. The coordinated movement along the X, Y, Z, and A axes ensures that parts are machined to exact specifications, reducing the risk of errors and improving the consistency of the finished products.
Versatility
4-axis CNC machining is highly versatile, capable of handling a wide range of materials and part types. Whether you are producing metal components, plastic parts, or composite structures, 4-axis machines can adapt to various manufacturing needs.
While 4-axis CNC machining offers many advantages, it also has some limitations that manufacturers should consider.
Expensive Setup
Implementing 4-axis CNC machining can involve higher initial costs compared to traditional 3-axis machines. The additional rotational axis requires more complex machinery and software, which can increase the overall investment needed for setup.
Requires Skilled Operators
Operating a 4-axis CNC machine requires a higher level of expertise compared to 3-axis machining. Skilled operators are needed to program and manage the additional axis of movement, which may necessitate additional training and higher labor costs.
Limited Geometries
Although 4-axis CNC machines can handle more complex shapes than 3-axis machines, they are still limited compared to 5-axis machines. Parts with extremely intricate geometries or multiple simultaneous angles may still require 5-axis CNC machining for optimal production.
Understanding the differences between 3-axis, 4-axis, and 5-axis CNC machining helps manufacturers choose the right technology for their specific needs.
Flexibility
Rotation Along Axis
Cost
When selecting a CNC machining service provider, it's essential to choose experts who have extensive experience with 4-axis CNC machining. Look for a CNC machining factory that offers custom CNC machining services, has a proven track record of producing high-quality parts, and utilizes advanced CNC prototype machining techniques. A reliable CNC machining service provider will work closely with you to understand your specific needs, provide accurate quotations, and ensure timely delivery of your CNC machined parts. By partnering with experienced professionals, you can ensure that your projects are executed efficiently and that the final products meet your exact specifications.

4-axis CNC machining is a powerful tool that enhances the capabilities of traditional 3-axis machines, allowing for the production of more complex and precise CNC machined parts. By adding an extra rotational axis, 4-axis machines improve flexibility, efficiency, and accuracy in the manufacturing process. This makes them ideal for a wide range of applications across various industries, including aerospace, automotive, electronics, and medical. While 4-axis CNC machining involves higher setup costs and requires skilled operators, the benefits of enhanced capabilities and increased production efficiency often outweigh these drawbacks. Understanding the process, advantages, and applications of 4-axis CNC machining can help manufacturers make informed decisions, optimize their production workflows, and deliver high-quality parts that meet the demanding standards of today's market.
FAQs
What is the difference between 3-axis and 4-axis CNC machines?
3-axis CNC machines move the cutting tool along the X, Y, and Z axes, allowing for the creation of basic shapes and profiles. 4-axis CNC machines add a fourth rotational axis, typically the A-axis, which allows the workpiece to rotate. This extra movement enables the machining of more complex parts with greater precision and reduces the need for multiple setups.
What is 3-axis CNC Machining?
3-axis CNC machining involves moving the cutting tool along three perpendicular axes: X (left-right), Y (front-back), and Z (up-down). This method is suitable for producing simple to moderately complex parts with basic shapes and profiles.
Is 3-axis better than 4-axis?
Whether 3-axis is better than 4-axis depends on your specific needs. 3-axis machining is more cost-effective and simpler, making it ideal for basic parts. However, 4-axis machining offers greater flexibility and precision for more complex parts, making it a better choice if your projects require intricate details and multi-angle machining.
What is the difference between 4-axis and 5-axis CNC machines?
4-axis CNC machines add one rotational axis (A-axis) to the standard 3-axis setup, allowing the workpiece to rotate. 5-axis CNC machines include two rotational axes (B and C), providing even more flexibility and enabling the creation of highly intricate and detailed parts by allowing simultaneous movement along five different axes.
What is the difference between CNC axis and VMC axis?
CNC axes refer to the movement directions in any CNC machine, including milling, turning, or grinding machines. VMC (Vertical Machining Center) axes specifically pertain to vertical milling machines and typically include X, Y, and Z axes, along with additional rotational axes in multi-axis VMCs. The difference lies mainly in the application and orientation of the machine’s movement.
By understanding these key differences and the capabilities of 4-axis CNC machining, manufacturers can better decide which machining process aligns with their production needs and helps them achieve high-quality CNC machined parts efficiently.
