15 years one-stop China custom CNC machining parts factory
The VMT blog is dedicated to sharing our hard-earned knowledge in prototype manufacturing. We hope these articles will help you optimize your product designs and gain deeper insight into the world of rapid prototyping. Enjoy the read!
Get an Instant Quote VMT
VMT  2025 08 04
2025 08 04 High-carbon steel knives are known for their excellent edge retention, hardness, and sharpness. They’re ideal for precision cutting but require careful maintenance to prevent rust. These knives are commonly used in kitchen tools and outdoor gear, and can be produced with precision using CNC machining services for high-carbon steel CNC machined parts.
 66
66
 Read more
Read more
 VMT
VMT  2025 08 01
2025 08 01 Austenitic stainless steel is non-magnetic, high in nickel, and highly corrosion-resistant, while ferritic stainless steel is magnetic, contains little to no nickel, and offers moderate corrosion resistance with better thermal conductivity. The key difference lies in their crystal structure, which affects weldability, formability, cost, and suitability for specific CNC machined parts.
 66
66
 Read more
Read more
 VMT
VMT  2025 08 01
2025 08 01 304 stainless steel offers superior corrosion resistance, aesthetics, and strength, making it ideal for high-end or demanding applications. 409 stainless steel is a more affordable, heat-resistant option commonly used in automotive exhaust systems. Your best choice depends on your project's environmental conditions, budget, and performance needs in stainless steel CNC machined parts.
 66
66
 Read more
Read more
 VMT
VMT  2025 07 31
2025 07 31 304 stainless steel offers superior corrosion resistance and versatility, making it ideal for general industrial, food-grade, and architectural uses. 420 stainless steel provides higher hardness and wear resistance, ideal for cutting tools and blades. Choosing between them depends on your project’s needs for durability, corrosion protection, and machinability.
 66
66
 Read more
Read more
 VMT
VMT  2025 07 30
2025 07 30 316 stainless steel is generally better than 18-10 stainless steel for CNC machined parts requiring superior corrosion resistance, especially in marine or chemical environments. However, 18-10 stainless steel is ideal for food-grade, decorative, or general-purpose applications. The choice depends on your project's environment, performance requirements, and cost considerations.
 66
66
 Read more
Read more
 VMT
VMT  2025 07 29
2025 07 29 18-10 stainless steel and 304 stainless steel are essentially the same alloy, both classified as austenitic stainless steel with similar chromium and nickel content. However, 18-10 emphasizes nickel content for enhanced corrosion resistance and luster. For CNC machining projects, 304 stainless steel offers a more standardized, cost-effective solution, while 18-10 is preferred in high-end consumer or decorative applications.
 66
66
 Read more
Read more
 VMT
VMT  2025 07 28
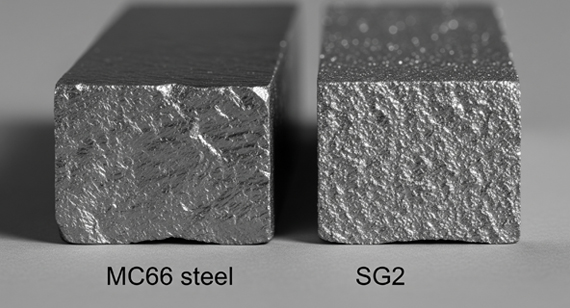
2025 07 28 The key difference between MC66 steel and SG2 steel lies in their chemical composition and mechanical performance. MC66 steel offers enhanced wear resistance and edge retention, making it ideal for high-end knives, while SG2 steel excels in toughness and corrosion resistance. Choosing between them depends on your application’s priority: durability, machinability, or cutting performance.
 66
66
 Read more
Read more
 VMT
VMT  2025 07 26
2025 07 26 The best knife steels offer a balance of hardness, toughness, corrosion resistance, edge retention, and cost-efficiency. Popular choices include M390, CPM-S35VN, VG-10, and D2 steel. Selecting the right steel depends on intended use, maintenance preferences, and compatibility with CNC machining services for consistent, precision manufacturing.
 66
66
 Read more
Read more
Ready To Start Your Next Project?
Get Instant Quote

Request a Free Quote
Send us a message if you have any questions or request a quote. We will get back to you ASAP!