15 years one-stop China custom CNC machining parts factory
The VMT blog is dedicated to sharing our hard-earned knowledge in prototype manufacturing. We hope these articles will help you optimize your product designs and gain deeper insight into the world of rapid prototyping. Enjoy the read!
Get an Instant Quote VMT
VMT  2025 08 13
2025 08 13 Titanium is not magnetic under normal conditions. It is a weakly magnetic (diamagnetic) metal, meaning it is not attracted to magnets. Its atomic structure prevents strong magnetic alignment, making it ideal for applications like medical implants, aerospace components, and precision CNC machined parts that require minimal magnetic interference.
 66
66
 Read more
Read more
 VMT
VMT  2025 08 12
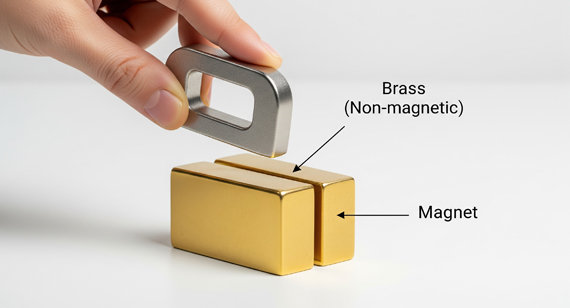
2025 08 12 Brass is generally non-magnetic because it is an alloy of copper and zinc, both of which are non-ferromagnetic. However, trace impurities or mechanical processing can induce slight magnetism. To ensure non-magnetic performance in brass CNC machined parts, choose high-purity alloys and verify properties before production.
 66
66
 Read more
Read more
 VMT
VMT  2025 08 11
2025 08 11 Yes, iron is magnetic because it is a ferromagnetic metal. Its unpaired electrons and aligned magnetic domains make it strongly attracted to magnets. Pure iron and many iron-based alloys retain magnetism, but some stainless steels and high-temperature conditions can reduce or eliminate this property.
 66
66
 Read more
Read more
 VMT
VMT  2025 08 08
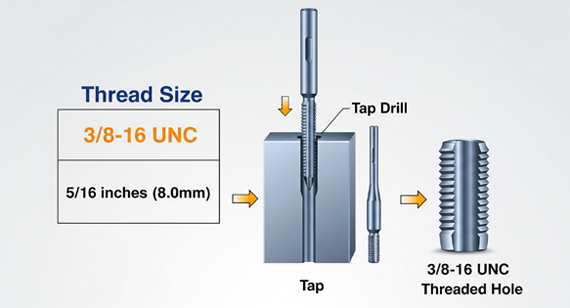
2025 08 08 To tap a standard 3/8-16 thread, use a 5/16 inch (0.3125") drill bit. This size ensures a proper thread engagement and minimizes the risk of stripping or tool wear, especially when producing CNC machining parts across various materials.
 66
66
 Read more
Read more
 VMT
VMT  2025 08 08
2025 08 08 Stainless steel can be anodized, but the process is more complex than with aluminum. Due to its passive oxide layer, stainless steel requires specialized electrolytes and tightly controlled conditions. Alternatively, finishes like PVD, passivation, and coating offer similar results with fewer challenges. For most CNC machining factories, these alternatives are more cost-effective and visually consistent.
 66
66
 Read more
Read more
 VMT
VMT  2025 08 07
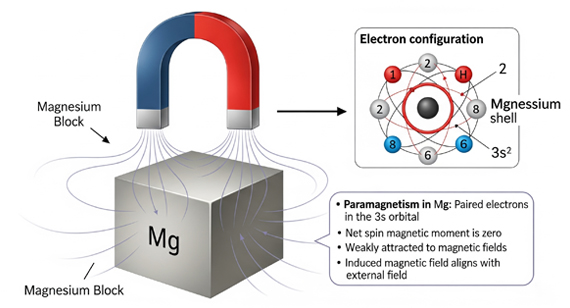
2025 08 07 Magnesium is not magnetic in the conventional sense. It is classified as a paramagnetic material, which means it exhibits very weak magnetism only in the presence of a strong external magnetic field. In typical applications—including magnesium CNC machined parts—magnetism is virtually negligible, making it a practical choice for non-magnetic component manufacturing.
 66
66
 Read more
Read more
 VMT
VMT  2025 08 06
2025 08 06 The main difference between 6061-T6 and 6061-T651 aluminum lies in their stress-relief processes. While both are heat-treated, T651 undergoes additional stretching to reduce internal stresses, making it more dimensionally stable than T6. This makes 6061-T651 the better choice for precision aluminum CNC machined parts requiring tight tolerances.
 66
66
 Read more
Read more
 VMT
VMT  2025 08 05
2025 08 05 416 stainless steel is a free-machining martensitic alloy ideal for applications requiring high precision and low corrosion exposure. In contrast, 316 stainless steel is an austenitic grade known for superior corrosion resistance, making it suitable for marine and chemical environments. Choosing between them depends on machinability needs, environment, and cost.
 66
66
 Read more
Read more
Ready To Start Your Next Project?
Get Instant Quote

Request a Free Quote
Send us a message if you have any questions or request a quote. We will get back to you ASAP!