15 years one-stop China custom CNC machining parts factory
 160 |
Published by VMT at Sep 09 2025 | Reading Time:About 5 minutes
160 |
Published by VMT at Sep 09 2025 | Reading Time:About 5 minutes
Choosing the right material for CNC machined parts can be overwhelming, especially with so many stainless steel grades available. The wrong choice can lead to higher costs, poor performance, or shorter product life. 440C stainless steel solves these challenges, offering a balance of hardness, strength, and corrosion resistance.
440C stainless steel is a high-carbon martensitic stainless steel known for its excellent hardness, wear resistance, and moderate corrosion resistance. It is widely used in knives, surgical instruments, and precision CNC machined parts. Combining strength and durability, 440C stainless steel offers a cost-effective solution for demanding applications.
Now that you know the overall strengths of 440C stainless steel, let’s take a closer look at its detailed properties, chemical composition, and applications to see if it fits your project.
440C stainless steel is a high-carbon martensitic stainless steel, widely recognized for its hardness and strength. Unlike common stainless steels such as 304 or 316, 440C offers a unique balance: it delivers exceptional wear resistance and edge retention while maintaining reasonable corrosion resistance. This makes it especially popular in applications where durability and precision matter most.
For CNC machining services, 440C stainless steel is a preferred choice in producing high-performance CNC machined parts like bearings, cutting tools, and surgical instruments. Its versatility allows CNC machining factories to deliver consistent quality, whether in custom prototypes or large-scale production runs.

440C stainless steel is often compared to other high-carbon stainless steels and tool steels due to its hardness and wear resistance. In international standards, it is equivalent to DIN X105CrMo17, JIS SUS440C, and EN 1.4125. These equivalents share similar chemical compositions and performance characteristics, making them interchangeable in many industrial applications.
For customers working with CNC machining services, knowing the equivalents is crucial. If 440C stainless steel is not available locally, CNC machining factories can often source its equivalents without affecting the quality of your CNC machined parts. This flexibility helps reduce sourcing delays and ensures consistent performance across global projects.
440C stainless steel stands out for its unique combination of hardness, wear resistance, and moderate corrosion resistance. Unlike softer stainless steels, it achieves very high strength after proper heat treatment, making it ideal for precision CNC machined parts that must withstand demanding conditions. From knives to medical instruments, its performance relies heavily on its chemical composition and processing.

440C Stainless Steel: Chemical Composition
The properties of 440C stainless steel are directly linked to its chemical makeup. Each element contributes to a specific characteristic, from hardness and strength to corrosion resistance. Below is an overview of the key alloying elements in 440C stainless steel.
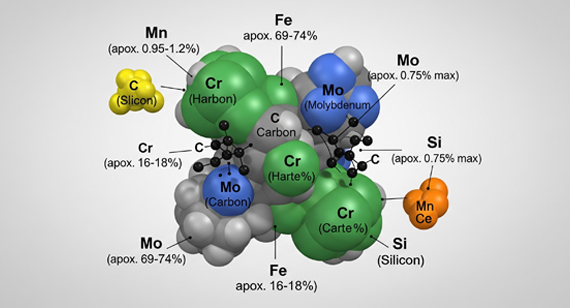
Carbon (C), 0.95–1.20%
High carbon content is the main reason for 440C’s exceptional hardness and wear resistance. It allows the steel to reach high Rockwell hardness levels after heat treatment, making it suitable for cutting tools and blades.
Chromium (Cr), 16.0–18.0%
Chromium enhances corrosion resistance and adds to the steel’s hardness. At this level, it forms a protective passive layer, though not as corrosion-resistant as lower-carbon stainless steels like 304 or 316.
Iron (Fe), Balance
Iron serves as the base element, providing structural integrity and ductility. It also binds with carbon and other elements to form martensitic structures during heat treatment.
Manganese (Mn), ≤ 1.00%
Manganese improves hardness and wear resistance slightly while also enhancing machinability. It helps remove oxygen during the steelmaking process, improving steel cleanliness.
Molybdenum (Mo), ≤ 0.75%
Molybdenum adds toughness and improves pitting resistance in corrosive environments. This makes 440C stainless steel more reliable in marine and chemical processing applications.
Nickel (Ni), ≤ 0.75%
Nickel contributes to toughness and corrosion resistance, although its presence is limited compared to austenitic grades like 316. It helps balance the hardness and brittleness of the steel.
Nitrogen (N), —
Nitrogen content is usually minimal or trace in 440C, and it does not play a major role compared to grades specifically alloyed with nitrogen.
Phosphorus (P), ≤ 0.040%
Phosphorus strengthens steel but can reduce toughness at higher levels. In 440C, it is tightly controlled to avoid brittleness.
Silicon (Si), ≤ 1.00%
Silicon improves strength and oxidation resistance, especially during high-temperature applications. It also helps improve machinability.
Sulfur (S), ≤ 0.030%
Sulfur is usually kept very low to avoid brittleness. Small traces can slightly improve machinability, but too much negatively affects toughness.
Vanadium (V), —
Vanadium is not a significant element in 440C stainless steel, but in trace amounts, it can refine grain structure, enhancing strength and wear resistance.
440C Stainless Steel: Chemical Composition
The chemical composition of 440C stainless steel directly influences its strength, hardness, and corrosion resistance. Below is a detailed breakdown of its key elements:
| Element |
Content (%) |
Function / Effect |
| Carbon (C) |
0.95 – 1.20 | Provides hardness and wear resistance through heat treatment. |
| Chromium (Cr) |
16.0 – 18.0 | Improves corrosion resistance and hardness. |
| Iron (Fe) |
Balance | Base metal, provides structure and ductility. |
| Manganese (Mn) |
≤ 1.00 | Enhances machinability and wear resistance. |
| Molybdenum (Mo) |
≤ 0.75 | Increases toughness and pitting resistance. |
| Nickel (Ni) |
≤ 0.75 | Adds toughness and limited corrosion resistance. |
| Nitrogen (N) |
Trace | Minimal effect in this grade. |
| Phosphorus (P) |
≤ 0.040 | Increases strength but reduces toughness if excessive. |
| Silicon (Si) |
≤ 1.00 | Improves oxidation resistance and strength. |
| Sulfur (S) |
≤ 0.030 | Enhances machinability but reduces toughness if high. |
| Vanadium (V) |
Trace | Refines grain structure, improves wear resistance. |
440C stainless steel is valued for its ability to reach very high hardness levels, making it suitable for wear-resistant CNC machined parts. Its strength, toughness, and fatigue resistance come from both its high carbon content and proper heat treatment. These mechanical properties define how well the material performs under stress, temperature, and long-term use.
Mechanical Properties of 440C Stainless Steel
| Property |
Typical Value |
Description / Impact |
| Hardness (HRC) |
58 – 60 | Very high hardness after heat treatment; excellent wear resistance. |
| Hardness (HV) |
~ 725 | High Vickers hardness, suitable for cutting tools. |
| Hardness (HRB) |
~ 99 (annealed) | Lower hardness in annealed condition for easier machining. |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) |
760 – 1,900 | Provides high load-bearing capacity. |
| Yield Strength (Rp0.2, MPa) |
~ 450 – 1,600 | Defines elastic limit before permanent deformation. |
| Elongation at Break (%) |
~ 2.0 | Low ductility; material is harder but less flexible. |
| Ductility (%) |
Low | Suited for hardness-focused applications. |
| Reduction of Area (Z/%) |
~ 35 | Indicates moderate toughness under stress. |
| Elastic (Young’s) Modulus (GPa) |
200 – 210 | Shows stiffness and resistance to deformation. |
| Heating Temperature (°C) |
1010 – 1065 (for hardening) | Heat treatment critical for achieving peak hardness. |
| Fatigue Strength (MPa) |
~ 440 | Resists cyclic loading in demanding applications. |
| Poisson’s Ratio |
0.27 – 0.30 | Standard value for steels. |
| Shear Modulus (GPa) |
~ 80 | Important for parts under torsional load. |
| Shear Strength (MPa) |
~ 550 | Good shear resistance, useful for blades and shafts. |
The physical properties of 440C stainless steel determine how it reacts to temperature changes, magnetic fields, and electrical or thermal conductivity. These values are critical for CNC machined parts used in industries like aerospace, medical devices, and precision tools, where stability and reliability are non-negotiable.
Physical Properties of 440C Stainless Steel
| Property |
Typical Value |
Description / Impact |
| Density (g/cm³) |
7.74 – 7.80 | Defines material weight; important for component balance and design. |
| Melting Point (°C) |
1480 – 1530 | High melting point ensures thermal stability in extreme applications. |
| Specific Heat (J/kg·K) |
~ 460 | Moderate heat capacity, useful in thermal processing. |
| Thermal Conductivity (W/m·K) |
~ 24.0 | Transfers heat moderately; lower than aluminum but stable. |
| Thermal Expansion Coefficient (10⁻⁶/K) |
10.2 – 10.4 | Predicts size changes under heat; critical in tight-tolerance CNC machined parts. |
| Electrical Resistivity (μΩ·m) |
~ 0.60 | Indicates moderate resistance to electrical current. |
| Modulus of Elasticity (kN/mm²) |
~ 200 | Reflects stiffness and structural strength. |
| Magnetic Properties |
Magnetic in hardened form | As a martensitic stainless steel, it becomes magnetic after heat treatment. |
| Conductivity (MS/m) |
~ 1.3 | Lower electrical conductivity compared to non-ferrous metals. |
Heat treatment is essential to unlock the full potential of 440C stainless steel. Without proper heat treatment, the steel remains relatively soft and cannot achieve its renowned hardness or wear resistance, which are critical for CNC machined parts like knives, bearings, and surgical instruments.
The typical heat treatment process for 440C stainless steel includes:

Annealing:
Hardening:
Tempering:
Stress Relieving:
Tip: Proper heat treatment directly affects 440C stainless steel CNC machined parts performance. Working with experienced CNC machining factories ensures consistent hardness, avoids cracking, and maintains dimensional accuracy. Always confirm heat treatment specifications before production.
Advantages
Disadvantages
Tip: When choosing 440C stainless steel for CNC machined parts, weigh its high wear resistance and hardness against machining complexity and corrosion requirements. Selecting an experienced CNC machining factory can help minimize costs and improve part quality.
440C stainless steel is highly versatile due to its hardness, wear resistance, and moderate corrosion resistance. It is widely used in industries requiring durable, precision CNC machined parts, from knives and medical devices to automotive and chemical processing components. Its reliability makes it a top choice for demanding applications.

Kitchen Knives
440C stainless steel is ideal for kitchen knives because it holds a sharp edge longer than many other stainless steels. Its corrosion resistance ensures the blades stay clean and rust-free even in humid kitchen environments.
Outdoor Knives
For outdoor and survival knives, 440C’s high hardness and wear resistance provide durability under rough conditions. It maintains edge retention after repeated use in cutting, chopping, or slicing tasks.
Surgical Instruments
Medical tools like scalpels and precision instruments benefit from 440C stainless steel’s hardness and corrosion resistance. It can withstand repeated sterilization without losing strength or sharpness.
Marine Applications
While not as corrosion-resistant as 316 stainless steel, 440C is still used in marine environments for components requiring high wear resistance, such as small fittings, locks, and specialized fasteners.
Chemical Processing
440C stainless steel handles moderate chemical exposure well, making it suitable for valves, pumps, and wear-resistant components in chemical plants. Proper sealing and surface treatment are recommended for harsh chemicals.
Building and Construction
440C is used in high-wear architectural hardware, such as hinges, locks, and tools, benefiting from its durability and long service life.
Food and Beverage Industry
Its corrosion resistance and ability to maintain cleanliness make 440C suitable for food processing equipment, cutting tools, and containers where wear resistance is crucial.
Beyond surgical instruments, 440C is used in orthopedic implants, dental tools, and precision instruments, where durability and dimensional stability are essential.
Wear-resistant parts like bearings, shafts, and small engine components leverage 440C stainless steel’s high hardness, ensuring long-term performance under mechanical stress.
440C Stainless Steel: Applications and Uses
| Application |
Description / Benefits |
| Kitchen Knives |
Holds a sharp edge longer; corrosion-resistant for humid kitchen environments. |
| Outdoor Knives |
Durable under rough conditions; maintains edge retention after repeated use. |
| Surgical Instruments |
High hardness and corrosion resistance; withstands repeated sterilization. |
| Marine |
Suitable for high-wear components like fittings, locks, and fasteners. |
| Chemical Processing |
Handles moderate chemical exposure; ideal for valves, pumps, and wear parts. |
| Building and Construction |
Used in hinges, locks, and hardware requiring durability and long service life. |
| Food and Beverage Industry |
Maintains cleanliness; ideal for cutting tools and processing equipment. |
| Medical Devices |
Applied in orthopedic implants, dental tools, and precision instruments. |
| Automotive |
Wear-resistant parts such as bearings, shafts, and small engine components. |
While 440C stainless steel is more expensive than standard stainless steels like 304 or 316, its high hardness, wear resistance, and durability often make it a cost-effective choice in the long run. Understanding both initial and long-term costs helps businesses make smart material decisions for CNC machined parts.
Initial Cost Comparison
440C stainless steel has a higher upfront cost due to its high carbon content and alloying elements like chromium and molybdenum. Machining can also be more challenging because of its hardness, requiring sharper tools and more precise CNC machining services. However, this investment pays off when durability and performance are critical.
Long-Term Cost-Effectiveness
Despite the higher initial cost, 440C stainless steel often reduces maintenance, replacement, and downtime expenses. Its excellent wear resistance and edge retention mean knives, bearings, and precision parts last longer. In applications where part failure is costly, the long-term savings outweigh the upfront price.
| Cost Aspect |
Details |
Impact on CNC Machined Parts |
| Initial Cost and Price |
Higher than 304/316 stainless steel due to alloy content and machining difficulty. | Requires sharper tools and more precise CNC machining services; upfront expense is higher. |
| Long-Term Cost and Price Benefits |
Excellent wear resistance and edge retention reduce maintenance and replacement costs. | Extends part life, minimizes downtime, and delivers overall cost savings for high-stress applications. |
440C stainless steel is recognized globally under multiple standards, which helps ensure consistent quality and interchangeability across CNC machining projects. Knowing these standards is crucial when sourcing materials or working with international suppliers.
| Standard / Country |
Equivalent Grade |
Notes |
| ASTM / USA |
440C | Common designation for high-carbon martensitic stainless steel. |
| JIS / Japan |
SUS440C | Japanese Industrial Standard equivalent; chemically similar to ASTM 440C. |
| DIN / Germany |
X105CrMo17 | German equivalent; widely used in European CNC machining projects. |
| EN / Europe |
1.4125 | European Norm standard for 440C stainless steel. |
| GB / China |
4Cr13 | Often considered similar in hardness and corrosion resistance, though slight composition differences exist. |
440C stainless steel is widely used in precision CNC machined parts due to its hardness, wear resistance, and moderate corrosion resistance. Understanding its specifications and equivalent steel grades ensures the right material is selected for your project, reducing errors and cost overruns.
| Specification / Standard |
Equivalent Steel Grade |
Key Notes |
| ASTM A276 / A582 |
440C | Standard for stainless steel bars and shapes used in CNC machining. |
| JIS G4305 |
SUS440C | Japanese standard equivalent for high-carbon martensitic stainless steel. |
| DIN 1.4125 |
X105CrMo17 | German standard; commonly used in European manufacturing. |
| EN 10088-1 / EN 1.4125 |
440C | European Norm; ensures quality consistency for machining and industrial use. |
| GB / China |
4Cr13 | Chinese equivalent; slightly lower carbon content in some cases but generally interchangeable. |
| ISO |
440C | International reference for high-carbon martensitic stainless steels. |
440C stainless steel is available in a wide range of stock shapes, allowing CNC machining factories to create customized parts for diverse applications. Selecting the right shape reduces material waste, simplifies machining, and ensures precision in finished CNC machined parts.
Common Stock Shapes of 440C Stainless Steel
| Stock Shape |
Description / Application |
| Rods |
Versatile for shafts, pins, and general CNC machined components. |
| T-Rods |
Specialized shape for structural or mechanical components requiring T-profile sections. |
| Flat Bars |
Used in wear plates, knives, and construction parts; easy to machine and finish. |
| Round Bars |
Ideal for shafts, fasteners, and cylindrical CNC machined parts. |
| Hexagonal Bars |
Suited for bolts, fasteners, and components needing multi-sided machining. |
| Square Bars |
Common in structural components, frames, and custom mechanical parts. |
| Triangular Bars |
Used for specialized tooling or decorative CNC parts requiring triangular cross-sections. |
| Hollow Bars |
Perfect for lightweight shafts, tubes, or fluid-carrying components. |
| Threaded Bars |
Ready-made threads reduce CNC machining time for fasteners and mechanical assemblies. |
| Pump Shafts |
Engineered for high wear and corrosion resistance in pumps and rotating machinery. |
| Ship Shafts |
Durable and corrosion-resistant for marine applications requiring high hardness and longevity. |
440C stainless steel stands out for its hardness and wear resistance, but how does it measure up against other popular metals? Understanding these differences helps customers select the best material for CNC machined parts, balancing strength, corrosion resistance, machinability, and cost.
Comparison of 440C Stainless Steel with Other Metals
| Metal / Steel Grade |
Comparison with 440C |
Best Use Cases |
| 304 Stainless Steel |
Much lower hardness, better corrosion resistance; easier to machine. | Food equipment, general corrosion-resistant applications. |
| 316 Stainless Steel |
Lower hardness than 440C, superior corrosion resistance especially in marine environments. | Marine components, chemical processing equipment. |
| Carbon Steel |
Higher ductility, easier to machine, but lower corrosion resistance and hardness. | Structural parts, machinery where corrosion is not critical. |
| 4116 Stainless Steel |
Similar hardness, slightly lower corrosion resistance; often used in knives and tools. | Kitchen knives, cutting tools, precision components. |
| 440A Stainless Steel |
Lower carbon content than 440C; softer, less wear-resistant but more corrosion-resistant. | Knives and tools needing moderate hardness with better corrosion protection. |
| D2 Stainless Steel |
Similar hardness and wear resistance; D2 slightly better at edge retention but lower corrosion resistance. | High-wear tools, dies, bearings. |
While 440C stainless steel is excellent for high hardness and wear resistance, certain applications may benefit from alternative materials depending on corrosion resistance, machinability, or cost requirements.
| Alternative Material |
Comparison / Advantage |
Best Use Cases |
| D2 Stainless Steel |
Similar hardness and wear resistance; slightly better edge retention, lower corrosion resistance. | High-wear tools, dies, bearings. |
| 440A Stainless Steel |
Softer than 440C but better corrosion resistance; easier to machine. | Knives, general-purpose wear parts. |
| 304 Stainless Steel |
Lower hardness but superior corrosion resistance; very easy to machine. | Food processing, kitchen equipment, chemical applications. |
| 316 Stainless Steel |
Excellent corrosion resistance in marine and chemical environments; lower hardness. | Marine components, chemical and medical equipment. |
| Carbon Steel (high-carbon) |
High strength and toughness; lower corrosion resistance; easier to machine. | Structural parts, shafts, and components not exposed to moisture. |
| Tool Steel (e.g., O1, A2) |
Excellent wear resistance; tailored heat treatment properties; may require protective coating. | Precision tools, cutting dies, industrial knives. |
Choosing the right material for your CNC machined parts can make or break a project. 440C stainless steel excels in hardness, wear resistance, and edge retention, making it ideal for applications that demand durability and precision. However, it is less corrosion-resistant than grades like 316 stainless steel and can be challenging to machine.
When 440C Stainless Steel is a Good Choice:
When You Might Consider Alternatives:
Tip: Before finalizing your choice, consult your CNC machining factory about tolerances, heat treatment, and part geometry. 440C stainless steel offers superior performance when applied in the right scenarios, but understanding its limitations ensures project success and cost efficiency.
Yes, 440C stainless steel is highly suitable for knives, and it’s one of the most popular grades used in both kitchen and outdoor blades. Its high carbon content allows it to reach very high hardness (HRC 58–60), which means it retains a sharp edge for a long time, even with frequent use.

Why 440C Works Well for Knives:
Considerations:
Tip: For custom CNC machined knife blades, choosing 440C stainless steel from a reputable CNC machining factory ensures consistent hardness, sharpness, and surface finish, maximizing performance and durability.
VMT is a leading CNC machining factory specializing in stainless steel parts, including precision components made from 440C stainless steel. With advanced CNC equipment and experienced technicians, VMT delivers high-quality, durable, and reliable CNC machined parts tailored to your project requirements.
Why Choose VMT for Your Stainless Steel CNC Machining Needs:
Tip: Partnering with a reliable CNC machining factory like VMT ensures your 440C stainless steel parts perform as intended, with superior hardness, wear resistance, and precision. Always discuss material specifications, tolerances, and heat treatment with the factory before production.

440C stainless steel stands out as a premium choice for CNC machined parts that demand exceptional hardness, wear resistance, and precision. Its chemical composition, mechanical and physical properties, and versatile stock shapes make it suitable for a wide range of applications—from knives and surgical instruments to automotive components and industrial machinery. While it requires proper heat treatment and skilled machining, the long-term performance and durability often justify the initial cost.
By understanding its advantages, limitations, and suitable applications, businesses can make informed decisions when selecting 440C stainless steel for their projects. Partnering with an experienced CNC machining factory like VMT ensures high-quality, precision components that meet international standards and deliver reliable performance in demanding environments.
1. Which is Better, D2 or 440C?
D2 and 440C are both high-carbon steels with excellent wear resistance. D2 has slightly better edge retention but lower corrosion resistance, while 440C is easier to maintain and offers better rust protection. Choose D2 for extreme wear and 440C for balanced performance and corrosion resistance.
2. Is 304 Stainless Steel Better than 440 Stainless Steel?
It depends on the application. 304 stainless steel has superior corrosion resistance and is easier to machine, but 440 stainless steel offers higher hardness and wear resistance, making it better for knives, bearings, and wear-intensive parts.
3. Which is Better, 420 Stainless Steel or 440 Stainless Steel?
420 stainless steel is softer, easier to sharpen, and more corrosion-resistant, while 440 stainless steel is harder, more wear-resistant, and holds edges longer. For cutting tools requiring long-term sharpness, 440 is preferred.
4. What is 440C Stainless Steel Made of?
440C stainless steel is a high-carbon martensitic stainless steel containing carbon, chromium, iron, and small amounts of manganese, molybdenum, nickel, nitrogen, phosphorus, silicon, sulfur, and vanadium. The high carbon and chromium give it exceptional hardness and wear resistance.
5. Is 440C Japanese Steel?
Yes, the Japanese equivalent of 440C stainless steel is SUS440C, following the JIS (Japanese Industrial Standards). Its chemical composition and properties are very similar to ASTM 440C.
6. Does 440C Rust?
440C stainless steel has good corrosion resistance but is not fully impervious to rust. It may corrode under prolonged exposure to saltwater or highly acidic environments, so proper care or coatings are recommended for such conditions.
7. What is the Best Steel for Knives?
The best steel depends on intended use. 440C is excellent for knives requiring high hardness and edge retention. For extreme corrosion resistance, consider 316 stainless steel, while 420 or 440A stainless steel is easier to sharpen and maintain.
8. Is 440C Steel Easy to Weld?
440C is challenging to weld due to its high carbon content and hardness. Specialized welding techniques and post-weld heat treatment are required to avoid cracking or loss of hardness.
9. Is 440C Stainless Steel Food Grade?
Yes, 440C stainless steel is considered food grade when properly processed. Its chromium content prevents rusting, making it suitable for kitchen knives, food processing equipment, and beverage industry applications.
10. What is the Safest Grade of Stainless Steel for Food Use?
304 and 316 stainless steels are widely recognized as the safest for food use due to their excellent corrosion resistance. 440C can also be used for food-grade applications if properly cared for.
11. Which Type of Stainless Steel is Best for Cooking?
For general cookware, 304 or 316 stainless steel is ideal due to corrosion resistance and ease of cleaning. 440C is better suited for kitchen knives or cutting tools that require high hardness.
12. What is FDA Food-Grade Stainless Steel?
FDA food-grade stainless steel meets the U.S. Food and Drug Administration standards for safety and corrosion resistance. It ensures no harmful chemicals leach into food, making it suitable for utensils, cookware, and processing equipment.
