15 years one-stop China custom CNC machining parts factory

Hey there I’m VMT Sam!
With 25 years of CNC machining experience we are committed to helping clients overcome 10000 complex part-processing challenges all to contribute to a better life through intelligent manufacturing. Contact us now
 112 |
Published by VMT at Oct 14 2023
112 |
Published by VMT at Oct 14 2023
DFM Analysis (Design for Manufacturability): Ensuring that the design is optimized for efficient manufacturing and minimal defects.

Dimensional Tolerance Inspection: Checking that parts adhere to specified dimensional tolerances.

Material Testing: Verifying the material's properties and quality to ensure it meets requirements.

CNC Machining Production: The actual CNC machining process where parts are manufactured using CNC machining equipment.

FQC Inspection (First Article Inspection): Inspecting the first piece produced to confirm it meets design and quality standards.

SPC / CKP (Statistical Process Control / Continuous Key Process): Implementing statistical analysis to monitor and control the manufacturing process.

Issue Detection: Identifying any deviations, defects, or irregularities in the production process.
Problem Solving: Addressing and resolving any issues or problems detected in the manufacturing process.

Factory Outbound Inspection: Ensuring that all parts leaving the factory meet the required quality criteria.

Surface Treatment: Applying surface finishes or treatments as needed for corrosion resistance or aesthetics.

100% Inspection: Conducting a thorough inspection of all produced parts to verify their quality and conformance to specifications.

Packaging: Preparing parts for shipment, including proper packaging to prevent damage during transit.

These 12 quality inspection processes are crucial in a CNC machining factory to maintain high standards of quality, efficiency, and customer satisfaction. Each step contributes to ensuring that the final products meet or exceed the required specifications and standards.
Quality Control Process in CNC Machining Factory:
Quality control is a critical aspect of CNC machining to ensure that the produced parts meet the required specifications and standards. Here are 12 quality control steps commonly followed in CNC machining factories:
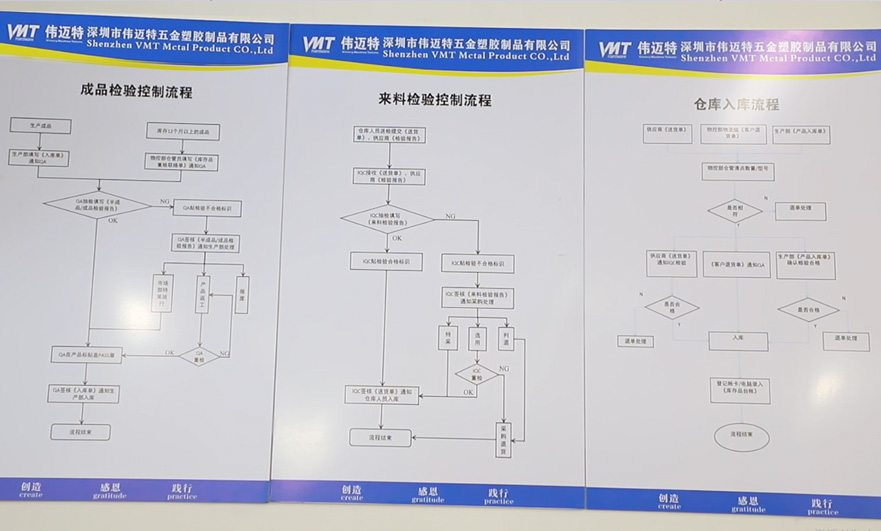
Material Inspection: The first step is to inspect the raw materials. This involves verifying the material type, grade, and dimensions to ensure they match the specifications.
Incoming Inspection: When the materials are received at the factory, an initial inspection is conducted to check for any visible defects or damage during transit.
First Article Inspection (FAI): For new or complex parts, a FAI is performed on the initial piece to confirm that it meets all design requirements. This includes dimensional checks and visual inspection.
Tool Inspection: Before machining begins, the cutting tools are inspected for wear and sharpness. Dull or damaged tools can result in poor-quality parts.
Setup Verification: The machine setup is checked to ensure that it aligns with the CAD design and the machining program.
In-Process Inspection: During machining, operators periodically check the workpiece's dimensions to make sure they are within tolerance.
Surface Finish Inspection: Surface roughness and finish are measured to ensure they meet the specified requirements. This may involve using instruments like profilometers.
Dimensional Verification: After machining is complete, a thorough dimensional inspection is performed using precision measuring equipment such as calipers, micrometers, and coordinate measuring machines (CMMs).
Visual Inspection: A visual inspection is conducted to identify any visible defects, such as surface scratches, dents, or blemishes.
Functional Testing: For parts with functional requirements (e.g., moving components), functional testing is performed to ensure they operate as intended.
Final Inspection: Once all machining and secondary processes are complete, a final inspection is carried out to confirm that the parts meet all specifications and quality standards.
Documentation and Reporting: Throughout the entire process, meticulous records are kept, and inspection reports are generated. This documentation ensures traceability and quality control.
These quality control steps are essential to maintain the integrity of CNC machining processes and deliver parts that meet the highest quality standards. Quality assurance is a continuous process, and any deviations or non-conformities are addressed and corrected promptly to maintain consistency and customer satisfaction.
Ready To Start Your Next Project?
Get Instant Quote

Request a Free Quote
Send us a message if you have any questions or request a quote. We will get back to you ASAP!