15 years one-stop China custom CNC machining parts factory
 213 |
Published by VMT at Nov 11 2024 | Reading Time:About 3 minutes
213 |
Published by VMT at Nov 11 2024 | Reading Time:About 3 minutes
Are you struggling to find the ideal material for your CNC machining parts that offer both excellent conductivity and durability? Frustrated by materials that don't meet the specific requirements of your custom CNC machining projects? You're not alone. Many manufacturers face the challenge of selecting the right material that balances performance and machinability. But what if understanding the density of red copper could be the key to unlocking superior quality in your CNC machining services?
The density of red copper is approximately 8.96 g/cm³. This high density contributes to its excellent electrical and thermal conductivity, making it an ideal material for CNC machining parts in industries like electronics, aerospace, and automotive. Understanding red copper's density is crucial for precise calculations and optimal performance in custom CNC machining projects.
Now that we've highlighted the importance of red copper's density in CNC machining, let's delve deeper into what density means, the unique characteristics of red copper, and how these factors impact your CNC machining services. This comprehensive guide will equip you with the knowledge to make informed decisions in your CNC machining factory.
Preface
In the realm of CNC machining parts manufacturing, material selection is paramount. Red copper, also known as pure copper or electrolytic tough pitch (ETP) copper, stands out due to its exceptional properties. Understanding the density of red copper is essential for engineers and machinists in custom CNC machining, as it influences material behavior, machining parameters, and the final product's performance.
Definition of Density
Density is a fundamental physical property defined as the mass per unit volume of a material. It quantifies how much matter is packed into a given space and is mathematically expressed as:
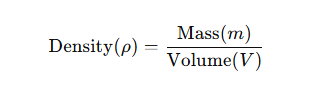
In CNC machining, knowing the density of materials like red copper helps in calculating weight, designing components, and ensuring structural integrity.
Units of Measurement of Density
Density is typically measured in:
Understanding these units allows for accurate calculations in CNC machining services and ensures compatibility with various engineering standards.
Red copper has a density of approximately 8.96 g/cm³ (or 8,960 kg/m³). This high density is one of the reasons red copper is prized in CNC machining parts manufacturing. The density affects not only the weight but also the material's mechanical properties, such as strength and durability.
In custom CNC machining, accurate knowledge of red copper's density is crucial for:

Red copper is renowned for its remarkable properties that make it suitable for a wide range of applications. In a CNC machining factory, these characteristics translate into benefits like ease of machining, superior product performance, and customer satisfaction.
Excellent Electrical Conductivity
Red copper boasts the highest electrical conductivity among commercial metals, at about 100% IACS (International Annealed Copper Standard). This makes it the material of choice for electrical components, wiring, and conductors in CNC machining parts.
Good Thermal Conductivity
With a thermal conductivity of approximately 401 W/(m·K), red copper efficiently dissipates heat. This property is essential in applications like heat exchangers and thermal management systems, where custom CNC machining can create intricate designs for optimal performance.
Corrosion Resistance
Red copper naturally forms a protective oxide layer when exposed to the atmosphere, providing resistance to corrosion. This enhances the longevity of CNC machined parts, especially in harsh environments.
Good Ductility and Plasticity
Red copper's ductility allows it to be drawn into thin wires without breaking, and its plasticity enables it to be formed into complex shapes. In CNC machining services, this means it can be machined into intricate components without compromising structural integrity.
Antibacterial Properties
Copper possesses inherent antibacterial properties, making it ideal for medical equipment, touch surfaces, and antimicrobial applications. CNC machining factories can produce red copper parts that contribute to healthier environments.
Beautiful Color
The distinctive reddish hue of red copper adds aesthetic appeal, making it popular in architectural elements and decorative items. Custom CNC machining can craft visually appealing components that also serve functional purposes.
High Temperature Resistance
Red copper maintains its mechanical properties at elevated temperatures, with a melting point of 1,085°C (1,985°F). This makes it suitable for applications requiring thermal stability, such as in industrial furnaces or high-temperature electrical systems.
Recyclability
Copper is 100% recyclable without loss of quality. This sustainability aspect is increasingly important in modern manufacturing and aligns with eco-friendly practices in CNC machining services.
Low Magnetism
Red copper is diamagnetic, meaning it exhibits very weak magnetic properties. This is advantageous in applications where magnetic interference must be minimized, such as in sensitive electronic equipment.
Excellent Processability
Red copper's softness and malleability make it easy to machine, cut, and form. In a CNC machining factory, this translates to reduced tool wear and faster production times, enhancing efficiency.
Physical Properties
Chemical Properties
Understanding these properties helps CNC machining services optimize processes, select appropriate tooling, and ensure the final product meets the desired specifications.
While red copper is known for its consistent density, certain factors can cause slight variations. Recognizing these factors is crucial in custom CNC machining to maintain precision and quality.
3 Factors That Cause Density Changes
Purity
Impurities in copper can alter its density. Higher purity levels ensure consistent density and predictable material behavior. In CNC machining parts, using high-purity red copper guarantees uniformity and reliability.
Alloying Elements
Adding other metals to copper forms alloys, which can change the density significantly. For instance, adding zinc to create brass lowers the density, while adding nickel to create cupronickel slightly increases it. CNC machining services must account for these changes when selecting materials.
Temperature
Thermal expansion causes materials to expand at higher temperatures, slightly decreasing density. While this effect is minimal in solids like copper, it's essential in high-precision CNC machining where thermal effects can impact dimensional accuracy.

Copper alloys are created to enhance certain properties like strength, corrosion resistance, or machinability. Understanding the density of these alloys is important in CNC machining factory operations.
Brass (Copper-Zinc Alloy)
Bronze (Copper-Tin Alloy)
Cupronickel (Copper-Nickel Alloy)
In custom CNC machining, selecting the appropriate copper alloy involves considering both the material properties and the density to meet the specific requirements of the project.

Comparing red copper's density with other metals helps in material selection for CNC machining parts, especially when weight is a critical factor.
| Metal | Density (g/cm³) |
| Density of Red Copper |
8.96 g/cm³ |
| Density of Titanium |
4.51 g/cm³ |
| Density of Iron |
7.87 g/cm³ |
| Density of Steel |
7.85 g/cm³ |
| Density of Tool Steel |
7.70 - 8.00 g/cm³ |
| Density of Alloy Steel |
7.80 - 8.00 g/cm³ |
| Density of Carbon Steel |
7.85 g/cm³ |
| Density of Stainless Steel |
7.75 - 8.05 g/cm³ |
| Density of Brass |
8.40 - 8.70 g/cm³ |
| Density of Bronze |
8.70 - 8.90 g/cm³ |
| Density of Nickel |
8.90 g/cm³ |
| Density of Magnesium |
1.74 g/cm³ |
| Density of Zinc |
7.14 g/cm³ |
| Density of Tungsten |
19.25 g/cm³ |
| Density of Gold |
19.32 g/cm³ |
| Density of Platinum |
21.45 g/cm³ |
Red copper's relatively high density compared to many metals means that weight considerations are crucial in design and machining. In CNC machining services, balancing performance with weight is essential, especially in industries like aerospace and automotive.
Accurate calculation of red copper's density is fundamental in custom CNC machining for quality control and design purposes.
How to Calculate the Density of Copper?
Mass Measurement
Use a precision balance to measure the mass of the copper sample. Ensure the balance is calibrated and accurate to at least 0.01 grams for precision.
Volume Measurement
For regular shapes, calculate the volume using geometric formulas. For irregular shapes, use displacement methods.
Density Formula
Apply the density formula:
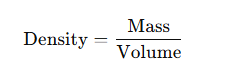
Unit Conversion
Ensure that mass and volume are in consistent units (e.g., grams and cubic centimeters) to calculate density in g/cm³.
Archimedes Principle
Submerge the copper sample in water and measure the displaced water volume to determine the sample's volume.
Hydrostatic Weighing
Measure the apparent weight loss of the sample when submerged in a fluid to calculate its density.
Pycnometer Method
Use a pycnometer, a specialized flask, to accurately measure the volume of liquids or small solid samples.
Gas Displacement
Employ gas pycnometry for powdered or porous materials, measuring the volume by the amount of gas displaced.
X-ray Crystallography
Analyze the crystal structure to determine density at the atomic level, typically used in research settings.
Ultrasonic Detection
Use ultrasonic waves to measure material properties that correlate with density, useful for detecting internal flaws in CNC machining parts.
Digital Density Meter
Utilize digital instruments that measure density through oscillation techniques for quick and accurate results.
Temperature Correction
Adjust calculations for temperature, as thermal expansion can slightly alter density.
Pressure Correction
Consider pressure effects in high-pressure environments, though negligible for most CNC machining applications.
Material Purity
Account for impurities that can affect mass and volume, altering density.
Alloy Composition
If dealing with alloys, adjust calculations based on the percentage of each element present.
Understanding red copper's density is vital in various industries where custom CNC machining plays a significant role.
Aerospace
Red copper's excellent conductivity and high-temperature resistance make it suitable for aerospace components like heat exchangers and electrical systems, where precision CNC machining is essential.
Its antibacterial properties are ideal for medical equipment and devices. CNC machining services produce red copper parts for surgical instruments and hospital fixtures.
In automotive applications, red copper is used in radiators, brakes, and electrical systems. CNC machining factories produce components that require high precision and reliability.
Red copper's superior electrical conductivity makes it indispensable for PCBs, connectors, and semiconductor components, all of which benefit from custom CNC machining for miniaturization and accuracy.
In industrial machinery, red copper parts are used for heat exchangers, fittings, and valves, where durability and thermal properties are critical.
Architectural Decoration
The aesthetic appeal of red copper makes it popular for decorative elements like roofing, cladding, and sculptures. CNC machining allows for intricate designs and patterns.
Electrical Engineering
Red copper is fundamental in electrical engineering for busbars, conductors, and transformers. CNC machining services ensure components meet exacting specifications.
Understanding the density of red copper is essential for anyone involved in CNC machining parts manufacturing. It influences material selection, machining parameters, and the performance of the final product. By grasping the factors that affect red copper's density and its comparison with other metals, you can optimize your custom CNC machining processes, produce high-quality red copper CNC machining parts, and meet the diverse needs of your clients.
What Is the Density of Copper in g/cm³?
The density of copper is approximately 8.96 g/cm³. This value is essential for calculations in CNC machining services and material selection.
The Density of Copper Is 8.83 g/cm³, How Much?
There might be a slight discrepancy due to measurement conditions or impurities. However, pure red copper's accepted density is 8.96 g/cm³. If your measurement is 8.83 g/cm³, consider factors like temperature, purity, and measurement accuracy.
What Is the Density of Copper Pipe in kg/m³?
The density of copper pipe, assuming it's made of pure copper, is 8,960 kg/m³. This value is used in calculating the weight of copper pipes in engineering applications.
What Is the Density of Copper (kg/m³) Calculator?
To calculate the density of copper in kg/m³:
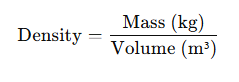
For pure copper, use 8,960 kg/m³ unless specific conditions indicate otherwise.
What Is the Density of Copper in Kilograms?
Density itself is mass per unit volume, expressed in kg/m³. Copper's density is 8,960 kg/m³, meaning one cubic meter of copper weighs 8,960 kilograms.
What Is the Current Density of Copper?
Current density refers to the electric current per unit area flowing through a conductor. For copper, it varies based on application but is often designed to be around 1.2 A/mm² to 6 A/mm² in electrical systems.
What Is the Density of Scrap Copper?
Scrap copper density is similar to pure copper, around 8.96 g/cm³, but may vary slightly due to impurities or alloying elements present in the scrap material.
What Is the Melting Point of Copper?
Copper has a melting point of 1,085°C (1,985°F). This property is important in processes like casting and welding in CNC machining services.
Will Brass Rust?
Brass, a copper-zinc alloy, does not rust because it contains no iron. However, it can tarnish or develop a patina over time due to oxidation.
What Is the Density of Copper Ore in kg/m³?
Copper ore density varies depending on the type and purity of the ore but typically ranges from 2,200 kg/m³ to 5,000 kg/m³.
What Is the Volume of 1 kg of Copper?
Using the density formula:
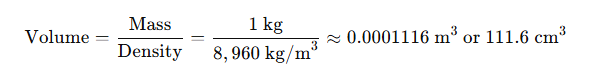
What Is the Density of Natural Copper?
Natural (native) copper has the same density as pure copper, approximately 8.96 g/cm³.
What Is the Atomic Mass of Copper?
The atomic mass of copper is 63.546 atomic mass units (u). This value is used in chemistry and physics calculations, not directly in CNC machining.
