15 years one-stop China custom CNC machining parts factory
 392 |
Published by VMT at Dec 16 2024 | Reading Time:About 5 minutes
392 |
Published by VMT at Dec 16 2024 | Reading Time:About 5 minutes
Are you struggling to ensure consistent quality, safety, and efficiency in your manufacturing operations, especially when producing precision machining parts or providing custom CNC machining services? Perhaps you’ve experienced issues with meeting customer expectations or complying with international regulations. Without a standardized framework, your CNC machining factory might face unnecessary rework, missed deadlines, or even product recalls—all of which can damage your reputation and bottom line. These problems become even more pressing when operating in competitive global markets, where the slightest lapse can result in lost business opportunities.
This ongoing frustration may leave you feeling overwhelmed, questioning whether there’s a reliable, recognized system to guide your processes and ensure continuous improvement. Without a structured approach, you risk inconsistent outcomes, worker safety hazards, environmental compliance issues, and weaker trust from clients who expect flawless CNC prototype machining. Over time, operational chaos can erode profit margins, strain customer relationships, and stall growth in a market that demands precision, reliability, and accountability.
Fortunately, ISO certification standards provide a proven solution. By adhering to well-established ISO benchmarks—such as ISO 9001 for quality management, ISO 45001 for occupational health and safety, or ISO 14001 for environmental responsibility—you can create a robust framework for delivering consistent quality in CNC machining parts. ISO certification standards guide you in implementing best practices, reducing errors, enhancing safety, and improving environmental performance. By understanding and applying these standards, you’ll attract new customers who trust your CNC machining services, streamline processes, and cultivate a culture of continuous improvement in your CNC machining factory. In other words, ISO certification standards empower you to meet global expectations, maintain a competitive edge, and ensure the success of your manufacturing endeavors.
To ensure consistent quality, safety, and environmental compliance in manufacturing, adhere to ISO certification standards like ISO 9001, ISO 45001, and ISO 14001. These frameworks streamline processes, reduce errors, enhance trust, and improve competitiveness, ensuring your CNC machining parts meet global expectations and boost your CNC machining factory’s reputation.
Now that you recognize how ISO certification standards can address common manufacturing challenges and enhance your CNC machining operations, let’s delve deeper into the details. Understanding ISO standards goes beyond knowing a few acronyms—it involves comprehending their structure, scope, and application in different segments of your CNC machining factory. By exploring what ISO is, why these standards matter, and how they fit into the manufacturing landscape, you’ll gain clarity on integrating them into your everyday processes.
In the upcoming sections, we’ll break down what ISO and ISO standards are, especially in relation to precision machining parts and custom CNC machining. We’ll discuss why ISO standards are crucial—from ensuring quality assurance and safety to supporting environmental responsibility and boosting customer confidence. We’ll then highlight the most common ISO certification standards encountered in the manufacturing industry, explaining their goals and relevance. Additionally, we’ll examine how adopting these standards influences your CNC machining services, affecting factors like efficiency, innovation, and international trade compliance.
By following this structured guide, you’ll move from simply acknowledging the importance of ISO certification standards to actively planning how to implement them. Through a clear understanding of these standards, your CNC prototype machining operations can align with global best practices, paving the way for continuous improvement, cost savings, and reliable product quality. Let’s begin by examining the basics: what exactly is ISO, and how do these standards influence the manufacturing industry?
Foreword
The world of manufacturing has grown increasingly complex, with demands for quality, safety, environmental stewardship, and consistency now as crucial as meeting production volumes. Customers expect that CNC machining parts, produced through custom CNC machining services, will be reliable, durable, and compliant with various regulations. ISO certification standards emerge as guiding lights, offering frameworks that help manufacturers navigate these challenges. Before diving into the nuances of each standard, it’s essential to understand the broader context these standards operate in.
In essence, ISO (International Organization for Standardization) is a global body that develops and publishes standards across myriad industries. These standards serve as blueprints for best practices, assisting manufacturers, including CNC machining factories, in refining their processes. They don’t dictate how to run your business but provide structured guidelines that, when adopted, can lead to uniformity, improved quality, reduced waste, and enhanced sustainability.
This foreword sets the stage: integrating ISO standards into your manufacturing ecosystem means embracing a culture of continuous improvement and global relevance. By doing so, you transform your CNC machining services into a reliable hub for precision machining parts that earn trust, loyalty, and recognition. In the following sections, we’ll explore the fundamentals of ISO standards, their importance, and the common certifications that have shaped the modern manufacturing landscape.
ISO stands for the International Organization for Standardization, an independent, non-governmental entity that brings together experts from around the world to develop international standards. These standards cover an extensive range of topics, from environmental management and occupational health to quality assurance and energy efficiency. For the manufacturing industry, ISO standards provide widely recognized benchmarks that help producers align their operations with global best practices.
In manufacturing, including custom CNC machining and precision machining parts production, ISO standards serve as reference points. They ensure that products are made consistently, meet quality requirements, and adhere to international regulations. For instance, ISO 9001 outlines criteria for a quality management system, guiding a CNC machining factory in optimizing workflow, monitoring processes, and continuously improving product quality. By implementing these standards, manufacturers can better communicate expectations internally and externally, ensuring everyone from the production floor to top management works cohesively.
Moreover, ISO standards facilitate interoperability and compatibility across different markets. If your CNC machining services follow ISO guidelines, clients worldwide can trust that your processes adhere to internationally recognized protocols. This fosters smoother trade relations, reduces technical barriers, and supports growth. In short, ISO standards provide a common language that standardizes expectations, ensuring manufacturing companies can excel in quality, compliance, and innovation while appealing to a global customer base.

ISO standards are not mere formalities; they are strategic tools that influence nearly every aspect of manufacturing. They matter because they create a structured environment for companies to produce high-quality, safe, and sustainable products. Let’s examine the key reasons why ISO standards hold such significance:
Adhering to ISO standards ensures consistent quality, minimizing defects in CNC machining parts and promoting customer satisfaction.
Safety:
Standards addressing occupational health and safety help protect employees, reducing workplace accidents and enhancing morale.
Environmental Responsibility:
ISO environmental standards guide manufacturers in reducing waste, conserving resources, and minimizing ecological impact—appealing to eco-conscious clients.
Interoperability and Consistency:
Uniform standards enable better communication, compatibility, and consistency in processes, materials, and documentation.
Customer Confidence:
ISO certification instills trust among clients and end-users, proving that a CNC machining factory meets recognized quality benchmarks.
Innovation and Continuous Improvement:
Standards encourage regular assessment and refinement, sparking innovation and ensuring that CNC prototype machining evolves efficiently over time.
International Trade and Regulatory Compliance:
Adhering to ISO standards eases entry into global markets, reduces trade barriers, and ensures compliance with various regulations.
Efficiency and Cost Reduction:
By streamlining processes and reducing errors, ISO standards help cut costs and increase profit margins.
Consumer Protection:
Quality standards ensure safer products, safeguarding consumers from subpar or hazardous items.
Collectively, these factors underscore the importance of ISO standards, driving growth, competitiveness, and resilience in the manufacturing industry.
Achieving ISO certification is about more than hanging a certificate on the wall. It’s a tangible demonstration that a manufacturing company operates under internationally recognized best practices. For CNC machining shops offering CNC machining services, obtaining ISO certification validates their commitment to quality and reliability. But what does this really mean for the business?

Gain Competitive Advantage:
In a crowded marketplace, being ISO-certified can distinguish your CNC machining factory from competitors. Clients feel more comfortable partnering with certified suppliers, knowing they’ll receive consistent, top-notch products.
Government and Legislative Recognition:
Regulatory bodies and government agencies often look favorably upon companies that adhere to ISO standards. Compliance with these standards can simplify navigating legal requirements, making it easier to win public contracts or meet industry-specific regulations.
Increase Revenue and Sales:
Satisfied customers return for more business. By proving that your precision machining parts align with recognized quality norms, you attract clients who value predictability, safety, and ongoing improvement. This fosters repeat business, referrals, and enhanced market presence.
Ultimately, ISO certification offers a strategic edge. It reassures customers that your custom CNC machining processes follow a rigorous, internationally approved blueprint. This confidence translates into opportunities for growth, diversification, and long-term success, as you continuously improve and adapt to evolving industry demands.
Though ISO publishes countless standards, a handful stand out as particularly impactful for manufacturers. These certifications shape how products are made, tested, and delivered, ensuring a universal language of quality and compliance. For companies specializing in CNC machining parts, understanding these standards is crucial.

ISO 9001: Quality Management Systems
Arguably the most popular standard, ISO 9001 sets the foundation for consistent quality across every manufacturing step. This framework helps CNC machining factories identify inefficiencies, reduce defects, and meet customer expectations. By applying the principles of ISO 9001, custom CNC machining operations can bolster their credibility and encourage long-term client relationships.
ISO 45001: Occupational Health and Safety Management Systems
Worker safety is paramount. ISO 45001 helps create safer workplaces, minimizing accidents and improving morale. A secure environment fosters a productive workforce, ultimately boosting efficiency and reducing downtime.
ISO 14001: Environmental Management Systems
Sustainability matters in today’s market. ISO 14001 guides manufacturers in managing waste, emissions, and resource consumption. By adopting eco-friendly practices, CNC machining services not only reduce costs but also appeal to clients who value environmental responsibility.
ISO 50001: Energy Management Systems
Energy efficiency is vital for cutting costs and lowering carbon footprints. ISO 50001 provides a framework for optimizing energy use, leading to savings and improved sustainability.
ISO 10204 and Others
Industry-specific standards like ISO 10204 ensure proper documentation and traceability of materials, supporting transparency and reducing the risk of non-compliance or disputes.
By knowing these common ISO standards, manufacturers can develop strategies that address quality, safety, environment, and energy efficiency, ultimately enhancing their global competitiveness.
ISO 9001 is a cornerstone standard for ensuring quality management within organizations. It outlines the criteria for a comprehensive quality management system (QMS) that helps manufacturers deliver consistent products and services. For a CNC machining factory, adhering to ISO 9001 means refining processes, monitoring performance, and embedding continuous improvement into daily operations. By implementing this standard, you ensure your CNC machining services maintain a culture of excellence, from raw material sourcing to final inspection.

What are the 7 Quality Management Principles?
The 7 QMPs form the backbone of ISO 9001, guiding decisions and actions that enhance quality.
By embracing ISO 9001, a CNC machining factory aligns its operations with global best practices, achieving reduced errors, increased customer trust, and a clear pathway to business growth.
The 7 QMPs are listed below
Principle 1: Customer Focus
Everything revolves around understanding customer requirements and striving to surpass them. For a CNC machining shop, this means tailoring custom CNC machining operations to deliver precision machining parts that match exact specifications. Satisfied customers return, fueling growth.
Principle 2: Leadership
Leaders must inspire a culture that values quality. By setting goals, allocating resources, and empowering teams, leadership ensures everyone works toward common objectives, reflecting consistency and reliability in CNC machining services.
Principle 3: People Involvement
When employees at all levels contribute ideas, identify improvement areas, and share expertise, the quality level increases. Skilled operators and engineers drive innovation and reduce inefficiencies.
Principle 4: Process Approach
Viewing tasks as processes ensures understanding of inputs, outputs, and how steps interconnect. A process approach optimizes efficiency, traceability, and predictability, beneficial for CNC prototype machining and large-scale production.
Principle 5: Improvement
No system is perfect. Continual improvement urges companies to review performance, learn from mistakes, and incrementally enhance methods.
Principle 6: Evidence-Based Decision Making
Basing decisions on data rather than intuition reduces guesswork, leading to stable, repeatable outcomes. For a CNC machining factory, metrics like cycle times, defect rates, and tool wear guide better planning.
Principle 7: Relationship Management
Building trust with suppliers, partners, and customers ensures reliable material quality, timely deliveries, and long-term collaboration, all crucial for consistent product excellence.
Provides you with a creative approach to what you need to do in running your business:
PDCA Cycle (Plan-Do-Check-Act):
The PDCA cycle is a foundational tool for managing continuous improvement within manufacturing. It encourages organizations to carefully plan improvements, execute them, assess results, and then act on findings. By applying PDCA to processes such as CNC machining parts production, you systematically refine workflows. For example, if a certain machining step shows inefficiencies, you plan changes (e.g., better tooling), implement them (do), measure output improvements (check), and either standardize successful modifications or revisit the approach (act). Over time, this cycle fosters responsiveness to evolving conditions and reduces waste.
Risk-Based Thinking:
ISO standards promote identifying potential risks early. By evaluating what might go wrong—from supply chain disruptions to tool failures—manufacturers can implement preventive measures. With risk management integrated into decision-making, CNC machining factories can avoid unexpected downtime or subpar product batches, keeping operations stable and clients satisfied.
Quality Standards, Inspection and Quality Control:
ISO standards emphasize rigorous inspection and control throughout production. This involves calibrating measurement tools, verifying material properties, and conducting final inspections. These steps ensure that each finished precision machining part matches the desired specifications.
Continuous Improvement and Documentation:
ISO frameworks encourage documenting procedures, instructions, and results. This documentation preserves institutional knowledge, simplifies training, and ensures consistent performance even if staff change. Continuous improvement relies on historical data and lessons learned, strengthening the organization’s ability to adapt and grow.
Overall, these approaches align perfectly with ISO standards, enabling manufacturers to sustainably enhance operations, cut costs, reduce defects, and build trust with customers relying on CNC machining services.
ISO 45001: Occupational Health and Safety Management Systems
ISO 45001 focuses on fostering safe, healthy work environments. It sets out requirements for establishing a systematic approach to managing occupational health and safety (OH&S). For manufacturers, including CNC machining shops, adopting ISO 45001 helps reduce workplace incidents, protect employees from hazards, and minimize downtime due to injuries. By providing a structured OH&S framework, companies can proactively identify risks—like machine operator fatigue or tool handling hazards—and take corrective measures.
Implementing ISO 45001 involves several steps. Initially, you assess your current safety protocols and identify areas needing improvement. Next, you establish policies and objectives aligned with OH&S principles. The process includes hazard identification, risk assessment, and implementing controls to mitigate these dangers. For example, ensuring proper guarding on CNC machines, training operators to safely handle sharp cutting tools, and enforcing personal protective equipment (PPE) usage all help prevent accidents.
Continual monitoring, internal audits, and management reviews ensure the system stays effective. When everyone understands safety responsibilities and follows clear procedures, you create a culture that values employee well-being. As a result, you reduce absenteeism, boost morale, and enhance productivity. Clients also appreciate suppliers who prioritize safety, reinforcing your CNC machining services brand as both reliable and ethically responsible. Ultimately, ISO 45001 helps sustain smooth operations, protect assets—both human and material—and fortify a long-term, stable production environment.
ISO 14001: Environmental Management Systems
In an era of growing environmental awareness, ISO 14001 helps manufacturers balance economic goals with ecological responsibilities. This standard provides a roadmap for managing environmental aspects—like energy use, waste generation, water consumption, and emissions—to reduce environmental footprints without sacrificing productivity or quality.
Adopting ISO 14001 involves identifying environmental aspects of your processes, setting objectives for improvement, and implementing measures to achieve them. For instance, a CNC machining factory might reduce coolant waste, optimize energy consumption by upgrading machinery, or recycle metal chips generated during custom CNC machining. These actions not only conserve resources but also enhance your brand image, attracting eco-conscious clients who value sustainable sourcing.
There are many benefits to complying with this standard:
Applicable to the implementation of ISO 14001. The steps are as follows:
Ultimately, ISO 14001 lets you safeguard natural resources, improve operational efficiency, and maintain a positive brand image, all while delivering high-quality, environmentally conscious precision machining parts.
ISO 50001
ISO 50001 focuses on energy management, offering guidance on optimizing energy consumption in manufacturing. By standardizing how companies measure, analyze, and manage their energy use, ISO 50001 helps lower energy costs and reduce greenhouse gas emissions. For a CNC machining factory, implementing ISO 50001 means systematically evaluating machine operation cycles, tooling selection, and even building utilities (lighting, HVAC) to identify efficiency opportunities.
Applying this standard involves developing an energy management policy, setting objectives, and determining energy performance indicators (EnPIs). Through regular monitoring, you can detect areas of inefficiency—like a CNC machining process that runs longer than necessary or a heat treatment cycle that consumes more energy than expected—and implement targeted improvements. Over time, these incremental changes add up, reducing overhead costs and environmental impact.
By emphasizing continuous improvement, ISO 50001 ensures energy optimization remains an ongoing priority rather than a one-time initiative. Suppliers embracing this standard can differentiate themselves as eco-friendly, cost-effective partners, appealing to customers who value both sustainable practices and competitive pricing. In a world increasingly driven by environmental awareness, ISO 50001 aligns manufacturing operations with responsible energy stewardship, helping secure a future that balances economic growth with environmental care, all while maintaining the production of top-quality CNC machined parts.
ISO 10204
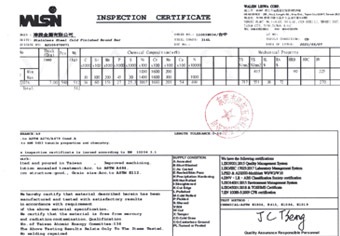
ISO 10204 (often referenced as EN 10204) relates to material test certificates and documentation requirements for steel and related materials. While not as widely discussed as ISO 9001 or 14001, ISO 10204 ensures that manufacturers provide transparent, traceable, and reliable documentation about material quality. For industries like automotive, aerospace, or heavy equipment manufacturing—where CNC machining parts must meet stringent criteria—this standard plays an important role.
The list of information includes:
Under ISO 10204, material certificates detail various attributes that assure buyers and end-users of a component’s quality and provenance. These may include:
By providing these details, ISO 10204 supports informed decision-making, enhances supplier credibility, and improves supply chain accountability. CNC machining factories can rely on this standardized documentation to ensure the materials they use align with client specs, reducing the risk of product failure and reinforcing customer trust.
ISO 9013
ISO 9013 concerns the quality classification and dimensional tolerances of thermal cutting processes. Although focused on processes like oxyfuel, plasma, and laser cutting rather than CNC machining directly, understanding this standard can still benefit CNC machining services. After all, the quality and consistency of cut blanks often influence the final machining steps.
By adhering to ISO 9013, suppliers ensure that semi-finished products entering the CNC machining factory meet strict geometric tolerances, surface roughness levels, and edge quality criteria. For instance, parts laser-cut from sheet metal can approach the CNC machining stage with more accurate initial dimensions, reducing the amount of material to be removed and simplifying fixturing.
Following ISO 9013 also ensures more predictable part fit and assembly further down the production line. If initial cuts are consistent and well-defined, CNC prototype machining becomes more streamlined, accelerating product development cycles. Moreover, ISO 9013 compliance builds customer confidence—clients know their suppliers follow recognized benchmarks, resulting in fewer surprises and less time spent troubleshooting dimensional inconsistencies.
In essence, while ISO 9013 focuses on thermal cutting, its influence reaches into the machining arena. By ensuring uniform, well-prepared raw materials, it enhances subsequent processes and contributes to efficient production of precision machining parts that meet or exceed customer expectations.
EN 1090
EN 1090 pertains to the execution of steel and aluminum structures, ensuring that load-bearing, structural components are fabricated and assembled to uniform European standards. Although EN 1090 is a European norm, it is recognized worldwide for projects requiring robust, safe, and compliant construction elements. For CNC machining factories that produce structural components—such as brackets, frames, or supports—understanding EN 1090 can be vital.
Standards that fall into this category are:
By adhering to EN 1090, manufacturers can confidently supply parts that integrate into large-scale constructions, from bridges and buildings to heavy machinery frameworks. Compliance includes rigorous controls, traceability of materials, and documentation of welding, assembly, and finishing processes. Moreover, EN 1090 may be required for projects within the European Economic Area, unlocking opportunities in international markets.
For CNC machining services, aligning with EN 1090 promotes trust among architectural, engineering, and construction clients. It demonstrates that their custom CNC machining capabilities meet recognized structural integrity standards, facilitating smoother approvals, fewer reworks, and stronger market presence.
Beyond the commonly mentioned ISO standards like ISO 9001, 14001, or 45001, numerous industry-specific standards guide specialized manufacturing niches. These standards target unique challenges and regulatory requirements, ensuring that products are safe, reliable, and tailored to particular applications. For CNC machining services catering to sectors like aerospace, medical devices, or food production, familiarizing oneself with industry-specific ISO standards can open doors to high-value markets.
ISO 25.x series of certificates:
In testing and calibration laboratories, ISO/IEC 17025 ensures that measurement and testing activities meet consistent quality. While not exclusive to CNC machining parts production, accurate measurement data influence manufacturing precision, helping ensure that your CNC machining factory’s final products meet exacting specifications.
ISO 22000:
Focuses on food safety management systems. If your CNC machined parts pertain to food processing equipment (e.g., cutting blades or mixing components), ensuring hygienic design and contamination avoidance becomes crucial.
ISO 13485:
For medical devices, ISO 13485 provides a framework ensuring the highest quality, safety, and regulatory compliance. Precision machining parts used in medical devices must meet strict cleanliness and tolerance criteria. By following ISO 13485, CNC machining shops prove their capability to produce components that pass stringent healthcare industry scrutiny.
ISO 27001 and IATF 16949:
For automotive suppliers, IATF 16949 aligns with ISO 9001 but adds automotive-specific requirements. Similarly, ISO 27001 addresses information security, safeguarding sensitive design and intellectual property data in an increasingly digital manufacturing world.

ISO 55000 series:
Asset management standards help maintain and extend the life of equipment, reducing downtime and improving reliability. For a CNC machining factory, this means ensuring cutting tools, machinery, and infrastructure are optimally managed.
By embracing these industry-specific ISO standards, manufacturers can differentiate themselves, target specialized markets, and ensure their CNC machining services remain competitive, compliant, and respected worldwide.
ISO standards offer a powerful foundation, but other certifications often come into play depending on product type, industry regulations, or regional requirements. These additional certifications complement ISO frameworks by addressing specific safety, environmental, or technical standards not fully covered by ISO.
CE mark / UKCA mark:
The CE mark (for the EU) and UKCA (for the UK) indicate that products comply with essential health, safety, and environmental protection requirements. A CNC machining factory that produces components for European or UK markets may need these marks, proving that their CNC machined parts meet regulatory directives.
RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances):
For electronics, RoHS limits hazardous substances like lead or cadmium in components. By adhering to RoHS guidelines, manufacturers ensure their precision machining parts for electronic assemblies are safe, eco-friendly, and legally allowed in certain markets.
UL certification:
In North America, UL (Underwriters Laboratories) certification confirms that products—often electrical, electronic, or mechanical—comply with safety standards. Although UL focuses on product safety rather than management systems, it’s crucial for CNC machining services that produce enclosures, housings, or structural parts integral to certified products.
By combining ISO certification standards with these additional approvals, manufacturers strengthen their compliance profile. This holistic approach fosters greater trust from global customers, regulators, and end-users, allowing CNC machining operations to tap into broader markets, meet complex specification demands, and reinforce their credibility as reliable suppliers of quality components.
For manufacturers, obtaining ISO certification standards unlocks numerous advantages that go beyond mere compliance. It establishes a disciplined, process-oriented approach to production, enabling better control over operations and resource allocation. Let’s explore the tangible benefits:
Benefits for Manufacturers:
ISO certifications serve as a blueprint for efficiency and quality. By implementing standards like ISO 9001, you reduce errors and scrap, streamline processes, and achieve consistent product quality. This yields cost savings in the long run. With ISO 14001, you minimize waste and resource usage, improving environmental performance and potentially cutting disposal fees. Similarly, ISO 45001 helps you maintain a safer workplace, reducing accident-related costs. Over time, these improvements enhance your brand reputation, attract new customers seeking reliable suppliers, and increase revenue.
Benefits for Customers:
From the customer’s perspective, ISO certification means assurance. They trust that the CNC machining factory they partner with follows stringent guidelines, ensuring that the precision machining parts delivered meet or exceed expectations. This trust leads to better customer experiences, long-lasting partnerships, and repeat business.
In essence, ISO certification standards foster a win-win scenario. Manufacturers enjoy improved processes, cost reductions, and risk mitigation. Customers receive higher quality products, enjoy better service, and gain confidence in their supply chain. Ultimately, ISO standards drive operational excellence, innovation, and long-term success in an evolving global marketplace.
Partnering with an ISO-certified CNC machining factory streamlines your procurement and product development journey. When you entrust your custom CNC machining projects to a supplier that adheres to ISO certification standards, you gain a reliable partner committed to excellence. You no longer have to worry about inconsistent quality, late deliveries, or inadequate documentation. Instead, you can focus on innovation and strategic growth, knowing that the production foundation is solid.
ISO-certified CNC machining services bring transparency and clear communication channels. From providing thorough documentation and traceability of materials to maintaining rigorous quality checks, these companies operate with efficiency and accountability. For instance, if you need precision machining parts for aerospace applications, working with an ISO 9001-certified shop ensures that every aspect—from machine calibration to operator training—follows established guidelines.
Moreover, an ISO-certified CNC machining factory continuously improves processes, embracing technological advancements and upgrading skills to stay ahead of industry demands. This means your supplier is more likely to adopt cutting-edge machining techniques, better tooling, and advanced metrology equipment, resulting in superior product performance.
In a world where trust and reliability matter, choosing ISO-certified CNC machining services isn’t just a technical decision—it’s a strategic move that helps secure supply chain stability, quality assurance, and customer satisfaction.

What is ISO manufacturing?
ISO manufacturing refers to production processes and supply chains aligned with ISO standards. By following standardized best practices, manufacturers ensure that their CNC machining parts meet global benchmarks for quality, safety, environmental responsibility, and efficiency.
What are the latest ISO standards?
ISO continually updates and releases standards across various domains. Recent focuses include information security (ISO 27001), energy management (ISO 50001), and industry-specific guidelines. Staying updated means regularly checking ISO’s official website or industry publications for new standards relevant to your CNC machining factory.
Why should your rapid prototyping supplier be ISO certified?
A CNC prototype machining supplier with ISO certification standards ensures reliable, consistent quality during the early stages of product development. This reduces iteration cycles, avoids misunderstandings, and accelerates the time-to-market.
Is ISO 9001 only for manufacturing?
No. ISO 9001 applies to organizations in all sectors. While manufacturing benefits significantly from ISO 9001, service providers, software developers, and other entities can also adopt it to improve quality management.
What is ISO 45001 standard?
ISO 45001 outlines requirements for occupational health and safety management systems, helping organizations proactively manage workplace risks, protect employees, and maintain compliance with safety regulations.
Why is ISO important in manufacturing?
ISO standards ensure consistent processes, quality control, customer satisfaction, environmental stewardship, and safety. They facilitate international trade by providing a common framework recognized worldwide.
What is the difference between ISO 9000 and ISO 9001?
ISO 9000 describes the fundamentals and vocabulary of quality management systems, while ISO 9001 specifies the requirements that organizations must meet to achieve certification. ISO 9001 is the standard against which organizations are audited.
What are the 4 ISO standards?
Commonly referenced ISO standards for manufacturing include ISO 9001 (quality), ISO 14001 (environment), ISO 45001 (health and safety), and ISO 50001 (energy). Many others exist, but these four often form a core set.
By clarifying these FAQs, manufacturers, customers, and partners can better understand ISO’s role and its impact on CNC machining services, helping them navigate certification processes and leverage the benefits of standardized operations.
