15 years one-stop China custom CNC machining parts factory
 320 |
Published by VMT at Dec 17 2024 | Reading Time:About 4 minutes
320 |
Published by VMT at Dec 17 2024 | Reading Time:About 4 minutes
Are you struggling to find a finishing method that enhances both the appearance and durability of your CNC machining parts, ensuring they stand out in a competitive market? Perhaps you’ve tried conventional paints or coatings, only to be disappointed by peeling layers, uneven coverage, or subpar corrosion resistance. This can be frustrating, as it not only affects the longevity of your precision machining parts but also tarnishes your reputation with customers who expect top-notch quality. For those who rely heavily on custom CNC machining and CNC machining services, delivering components with inferior finishes can quickly erode trust and repeat business.
The aggravation intensifies when you consider that each flawed finish or reworked part costs time, materials, and money. With higher expectations for environmental compliance, greater durability, and aesthetic appeal, traditional finishing methods might leave you feeling trapped in a cycle of continuous trial and error. It’s stressful, time-consuming, and puts unnecessary strain on your CNC machining factory’s resources.
Thankfully, there’s a proven solution: powder coating finish. By embracing powder coating—a process that involves electrostatically applying dry powder to parts and curing it into a strong, uniform layer—you can significantly enhance the performance and appearance of your CNC machined parts. Powder coating is known for its exceptional durability, corrosion resistance, and consistent color quality. It’s more environmentally friendly than many liquid paints, and it can produce a wide variety of finishes, from matte to glossy, textured to smooth. By understanding how powder coating works, its advantages, its suitable applications, and its role in precision machining parts production, you can deliver consistently superior results and confidently meet the evolving demands of your customers.
For a superior finish on CNC machining parts, apply a powder coating finish. First, thoroughly clean and pretreat the part. Then, apply the powder via electrostatic spray or fluidized bed dipping. Finally, cure it in an oven. This process ensures uniform coverage, enhanced durability, improved corrosion resistance, and a visually appealing result, all while reducing environmental impact.
Now that you understand powder coating’s promise as a reliable, high-quality finishing method for precision machining parts, it’s time to dive deeper. In the following sections, we’ll explore every facet of powder coating finish—what it is, why it’s beneficial, the types of powders available, and how it compares to other finishing processes. We’ll walk through the entire workflow, from pretreatment to curing, so you can fully grasp each step’s importance and how it contributes to achieving a flawless, long-lasting result.
We’ll also examine industry-specific applications, practical tips for achieving consistent results, and how powder coating integrates seamlessly with custom CNC machining operations. As you read on, you’ll discover how powder coating promotes not only aesthetics but also corrosion resistance, environmental responsibility, and improved mechanical performance. We’ll delve into various thermoplastic and thermosetting powders and discuss how each choice can influence the final look and feel of your CNC prototype machining projects.
By understanding these fundamentals, you’ll be better equipped to decide whether powder coating is the right surface treatment for your CNC machining services. So, let’s begin by exploring what powder coating truly is and why it’s become an indispensable tool in modern manufacturing settings around the world.
Preface
In an industry driven by efficiency, quality, and innovation, the finishing process you select for your CNC machining parts can profoundly influence the final product’s success. Powder coating finish stands out as a robust, versatile solution, enabling manufacturers to deliver high-performance parts tailored to diverse applications—from automotive and aerospace components to consumer electronics enclosures and architectural fixtures. The journey to understanding powder coating begins by recognizing its fundamental principles: it’s a dry finishing method that relies on resin powders, curing processes, and electrostatics to produce uniform, durable finishes.
Powder coating differs significantly from traditional liquid paints. Instead of solvents, it uses finely ground particles of pigment and resin that adhere to the part’s surface through an electrostatic charge. Once baked, these particles melt, flow, and harden into a continuous, protective layer. This approach reduces volatile organic compounds (VOCs), making it more eco-friendly. Moreover, powder coating integrates smoothly with CNC machining services and custom CNC machining workflows, allowing for precise application on complex geometries with minimal waste.
As you explore the following sections, keep in mind that powder coating isn’t just about aesthetics—it’s about building trust with customers, enhancing product longevity, and meeting global standards for quality and environmental stewardship. With an in-depth understanding, you’ll be ready to incorporate powder coating into your CNC machining factory’s capabilities, ensuring that each part you produce meets the highest benchmarks for performance and reliability.
Powder coating is a dry finishing process widely used across manufacturing industries to protect and enhance metal (and sometimes plastic) components. Instead of relying on liquid paints that contain solvents, powder coating uses a fine blend of resin, pigments, and other additives. This mixture is applied as a free-flowing, dry powder, typically charged electrostatically, and then cured under heat. The result is a uniform, durable finish that surpasses many conventional coatings in terms of longevity, environmental friendliness, and aesthetic versatility.
For CNC machining parts, powder coating offers a robust layer of defense against corrosion, chemicals, and mechanical wear. It works well on components produced through custom CNC machining—such as brackets, housings, and structural frames—ensuring that their underlying precision isn’t compromised by inferior finishes. Moreover, because powder coating finish doesn’t rely on solvents, it releases fewer harmful emissions, making it a more sustainable choice. This method also reduces overspray waste, as unused powder can often be recovered and reused, bolstering cost-effectiveness.
In practice, powder coating aligns seamlessly with modern CNC machining services. After parts are milled, turned, or otherwise shaped, they undergo pretreatment to remove contaminants. Then, the electrostatic application of powder and controlled curing ensure a stable, high-quality surface. The flexibility to choose from various colors, textures, and gloss levels empowers manufacturers to meet specific design criteria. Ultimately, powder coating elevates product quality, environmental stewardship, and brand reputation—all essential ingredients in a competitive manufacturing landscape.

Powder coatings come in two main categories: thermoplastic and thermosetting. Each category offers distinct properties, making them suitable for different applications. For CNC machining factory operations, understanding these types ensures that you can select the perfect powder coating to complement your precision machining parts and product performance targets.
Thermoplastic coatings are composed of materials that melt and flow when heated, solidifying upon cooling without undergoing a chemical change. In contrast, thermosetting coatings involve a cross-linking reaction during curing, resulting in a stable, irreversible chemical bond that enhances durability, chemical resistance, and temperature tolerance.
Within these categories, multiple formulations exist, from nylon-based thermoplastics to epoxy-based thermosets. The choice of powder depends on factors such as desired finish quality, operating environment, and mechanical stress. For example, if your CNC prototype machining project demands a durable coating for outdoor exposure, a polyester-based thermoset might excel. If abrasion resistance is key for moving mechanical parts, a nylon-based thermoplastic could be ideal.
Ultimately, selecting the right powder type involves balancing cost, performance attributes, and application techniques. As you explore the following sections, you’ll learn about specific materials—like nylon, PVC, epoxy, polyester, and UV-cured powders—and discover how they align with various use cases in CNC machining services. This knowledge allows you to tailor your finishing approach, ensuring every coated component meets the rigorous expectations of modern industry demands.

Thermoplastic Powder Coating Finishes
Thermoplastic powder coatings melt at elevated temperatures and re-harden upon cooling, without undergoing chemical changes. This characteristic allows these coatings to be remelted and reshaped if necessary, making them versatile and, in some instances, reusable. Thermoplastics generally offer good toughness and impact resistance, making them suitable for applications where mechanical stress and wear are factors.
Nylon Powder Coatings:
Nylon, a popular thermoplastic coating material, is prized for its excellent impact resistance, low friction, and ability to reduce noise in mechanical assemblies. When applied to CNC machining parts—such as gears, rollers, or bearings—nylon coatings help diminish wear and prolong service life. Their chemical resistance and flexibility also make them suitable for parts exposed to aggressive environments.
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Powder Coatings:
PVC coatings provide a soft, pliable protective layer with strong chemical and moisture resistance. These properties make PVC coatings suitable for parts needing cushioning, insulation, or protection from outdoor conditions, such as handles, grips, or protective covers.
Polyester Powder Coatings:
Polyester coatings excel in UV resistance and color retention. They’re often used for outdoor applications, from railing systems to automotive trim. Their stability under sunlight helps maintain appearance and performance over time.
Polyolefin Powder Coatings:
Polyolefins like polyethylene offer excellent moisture resistance and flexibility. Though less common in precision machining parts, they can serve specialized roles where environmental exposure is a concern.
For CNC machining services, choosing a thermoplastic powder means considering factors like operating temperature, mechanical loads, and chemical exposure. Each thermoplastic offers a unique balance of properties, enabling you to align the coating choice with your application’s performance criteria.
Thermosetting Powder Coating Finishes
Thermosetting powders, once heated, cross-link to form a chemically bonded network. Unlike thermoplastics, this reaction is irreversible, resulting in a harder, more chemically resistant coating that maintains its form under higher temperatures. Such coatings are popular in applications demanding long-term durability, stability, and attractive finishes—qualities often essential for CNC machining parts serving in harsh conditions.
Epoxy Resins:
Epoxy powders deliver excellent adhesion, corrosion resistance, and mechanical strength. They’re commonly used on parts needing robust protection against chemicals or moisture, like automotive components or pipeline fittings. Epoxy coatings excel in providing a smooth, uniform finish that enhances precision machining parts without compromising tolerances.
Epoxy Polyester Blends:
Combining the best of epoxy and polyester resins, these blends strike a balance between durability, weatherability, and aesthetics. They are often employed in situations where outdoor exposure and mechanical demands coexist. For custom CNC machining products that must retain their appearance despite environmental stresses, epoxy-polyester blends offer an attractive solution.
Acrylic Fibers:
Acrylic-based thermosets provide excellent gloss retention and color stability. While not as mechanically robust as epoxies, they shine in decorative and UV-stable applications, making them suitable for consumer electronics enclosures or signage parts produced by CNC machining services.
Ultraviolet (UV) Cured Powder Coatings
UV-curable powders cure rapidly under UV light, speeding up production cycles and reducing energy costs. They deliver consistent thickness and smooth finishes, suitable for smaller precision machining parts or rapid turnarounds, as in CNC prototype machining.
Overall, thermosetting powders offer long-lasting finishes that stand up to demanding operational conditions. Their chemical cross-linking ensures that once cured, these coatings remain stable, even under load, heat, or chemical attack—ideal traits for parts where reliability is paramount.
Powder coating is extremely versatile, applying to a range of materials beyond conventional metals. While it’s most commonly used on steel, aluminum, and other metal alloys, advancements have expanded its reach. For CNC machining parts made from aluminum alloys, powder coating finish provides a robust, attractive protective layer. Steel components, including structural frames or brackets, similarly benefit from increased corrosion resistance and durability.
While metal is the primary candidate, some heat-stable plastics and composites can also be powder coated, provided they withstand the curing temperatures (generally around 160°C to 200°C). However, these non-metallic substrates require specialized pretreatment and careful handling to ensure proper adhesion. In the context of CNC machining services, focusing on metal substrates remains the norm since metals handle the thermal curing step without warping or losing integrity.
Additionally, certain conductive coatings or primers enable the electrostatic application of powder onto materials that don’t naturally hold a charge, expanding possibilities for innovative designs. For instance, if a custom CNC machining project involves hybrid assemblies of metal and certain composites, powder coating parts of the assembly can unify the product’s appearance and performance.
In short, powder coating’s adaptability makes it a practical choice for diverse components. Whether dealing with precision machining parts in aerospace, automotive housings, or architectural fixtures, if the substrate tolerates curing conditions and can achieve proper surface preparation, powder coating is a reliable and effective finishing solution.
Powder coating finish has gained widespread acclaim due to the multitude of benefits it brings to manufacturing processes, especially in producing CNC machining parts:
Durability:
Powder coatings form a tough, resilient surface that resists chipping, scratching, and corrosion. This ensures that precision machining parts maintain their aesthetic and functional integrity over extended service life. In applications like automotive components or industrial equipment, durability translates into reduced maintenance and longer product lifespan.
Variety:
Powder coatings offer an extensive palette of colors, gloss levels, textures, and special effects. Manufacturers can choose from smooth or textured finishes, matte or glossy appearances, and even specialty coatings like metallic or wrinkle finishes. This variety empowers custom CNC machining projects to align the part’s final look with branding, aesthetic preferences, or environmental conditions.
Less Toxicity:
Because powder coatings contain no solvents and emit minimal volatile organic compounds (VOCs), they’re more environmentally friendly and safer for workers in a CNC machining factory. Reduced exposure to harmful chemicals fosters a healthier work environment and aligns with modern sustainability goals.
Cost-Effectiveness:
Powder coating’s efficiency reduces waste and rework, enabling recapture of overspray powder and yielding consistent thickness. Over time, these advantages trim costs, enhance productivity, and improve profit margins for CNC machining services. Combined with the improved durability, the reduced need for touch-ups and maintenance ensures a better return on investment.
In essence, powder coating’s durability, variety, environmental benefits, and cost savings make it a compelling choice for enhancing CNC machined parts, strengthening brand credibility, and maintaining competitiveness in a demanding global market.
The powder coating process can be understood in three core steps: pretreatment, powder application, and curing. Each phase plays a crucial role in achieving a high-quality, enduring finish that meets the stringent requirements for CNC machining parts.
Pretreatment:
Before applying powder, the part must be thoroughly cleaned to remove oils, grease, dust, and oxidation. Depending on the substrate (often metal in custom CNC machining), pretreatment may include degreasing, pickling, phosphating, or applying a conversion coating. This ensures the powder adheres effectively, reducing the likelihood of defects like bubbles, peeling, or uneven thickness. Good pretreatment sets the stage for a flawless finish and long-term performance.

Application of Powder Coating Methods (Fluidized Bed and Electrostatic Spraying):
Two main application techniques exist. Fluidized bed coating involves heating the part and dipping it into a bed of fluidized powder, which melts onto the surface. Electrostatic spraying, more common in industrial settings, charges the powder particles so they adhere to the grounded part’s surface. In a CNC machining factory, electrostatic spraying offers versatility and control, allowing for uniform coverage and effective coating of complex geometries.
Curing Process:
After the powder is applied, the coated part is placed in an oven. The high temperature melts the powder, causing it to flow and chemically bond, forming a durable, continuous film. Once cooled, the part emerges with a robust, attractive finish that provides lasting protection. By mastering these steps, CNC machining services can integrate powder coating seamlessly, delivering superior product quality and reliability.
Powder coating surface treatment builds on the principles described above, focusing on the specific workflows tailored for mechanical parts. This involves meticulous preparation to ensure that the powder adheres well, followed by controlled application and curing stages.
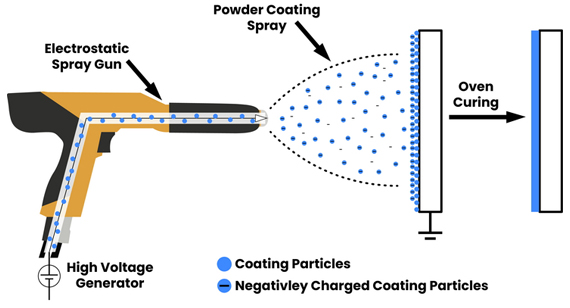
We will discuss the three main stages of powder coating treatment for mechanical parts:
Surface preparation stage:
This crucial preliminary step involves cleaning the part and possibly roughening it to improve adhesion. For precision machining parts, attention to detail matters—the surface must be pristine, ensuring uniform adhesion and reducing the risk of coating defects.

Application stage of powder spraying method:
Two primary techniques emerge here:
Electrostatic Deposition:
In electrostatic spraying, a powder spray gun imparts an electrostatic charge to the powder particles. The grounded part attracts these charged particles, forming a uniform layer. This is the most common method used by CNC machining services, providing excellent control over thickness and coverage.
Fluidized Bed Powder Coating:
Parts heated above the powder’s melting point can be dipped into a fluidized bed of powder. The powder melts instantly, coating the part. While less common for intricate CNC machined parts, it works well for simple shapes requiring thick, even coatings.

Coated part curing stage:
Curing the coated part in an oven solidifies the film, ensuring it’s fully cross-linked and stable. Proper curing enhances durability, adhesion, and finish quality. Once cooled, the result is a tough, long-lasting coating that boosts the part’s aesthetic and functional attributes, essential for products delivered by custom CNC machining operations.
Like any finishing method, powder coating presents both strengths and shortcomings. Understanding these advantages and disadvantages helps you decide when and why to choose it for your CNC machining parts.
Advantages of Powder Coating:
Disadvantages of Powder Coating:
Overall, the advantages often outweigh the disadvantages, making powder coating a favorite choice in CNC machining services to enhance product performance and longevity.
Powder coating’s adaptability and robust properties have secured its role in numerous sectors, from automotive to medical devices. For CNC machining factories producing a wide array of precision machining parts, powder coating finish ensures that these components meet the stringent requirements of diverse markets.

Car frames, suspension components, engine brackets, and wheel rims benefit from powder coating’s exceptional durability and corrosion resistance. By selecting a suitable powder and applying it uniformly, automotive suppliers ensure their CNC machined parts last longer, resisting road salt, moisture, and heat.
Construction and Steel Industry:
Structural beams, fencing, architectural metalwork, and building façades gain aesthetic and protective advantages. Powder coating prevents rust, fading, and chipping, maintaining visual appeal and integrity in harsh outdoor environments.
Outdoor Applications:
Patio furniture, playground equipment, and agricultural machinery face changing weather, UV rays, and moisture. Powder coating reduces maintenance costs, extends product life, and keeps colors vibrant.
Housings, enclosures, and heatsinks for electronics benefit from electrostatically applied powder coatings that provide insulation, reduce static, and improve durability. CNC machining services can produce complex aluminum housings that, after powder coating, protect sensitive circuitry.
Medical devices require surfaces that resist chemicals, frequent cleaning, and sterilization. Powder coating can offer smooth, easy-to-clean finishes that reduce contamination risks and enhance patient safety.
By tailoring powder coating techniques and materials to each industry’s demands, manufacturers can consistently deliver high-quality products. The result is a more competitive business, where CNC prototype machining and large-scale production alike yield parts that excel in function and aesthetics.
Producing a flawless powder coating finish involves more than simply applying powder and curing it. Attention to detail throughout the process ensures that your CNC machining parts stand out in quality and durability. Consider these practical tips:

Prepare the Surface:
Cleanliness is crucial. Remove oils, greases, and contaminants. For challenging parts, consider abrasive blasting or chemical pretreatments. Proper surface preparation ensures the powder bonds effectively, preventing flaking or peeling.
Choose the Right Powder Material:
Select powder type and chemistry (thermoplastic or thermoset) based on the part’s end-use conditions. Consider corrosion exposure, temperature range, and mechanical stress. Aligning powder characteristics with application demands is key to long-term success.
Avoid Using Frames:
Minimizing obstructions and ensuring parts hang freely during spraying prevents uneven coverage. This improves consistency, reduces defects, and avoids uncoated “shadow” areas.
Use the Spray Gun Correctly:
Calibrate gun settings and maintain proper distance to ensure uniform thickness. Mastering the correct spray technique prevents excessive buildup and orange-peel textures.
Ensure Powder Cures:
Monitor oven temperature and curing time meticulously. Under-curing leads to weak adhesion; over-curing may affect color or gloss. Achieving the right curing conditions solidifies the coating’s protective qualities.
Understand Powder Types and 7. Keep Pumps in Good Condition:
Familiarize yourself with various powders and their application parameters. Regularly maintain pumping and spraying equipment to ensure a steady powder flow and optimal deposition.
By implementing these tips, CNC machining services can achieve consistently high-quality finishes, delighting customers and reinforcing their reputation as providers of top-notch, powder-coated precision machining parts.
At VMT, we take pride in offering not only top-tier CNC machining services but also premium finishing solutions that complement your custom CNC machining projects. Our powder coating finish services highlight our commitment to delivering excellence at every step, from initial design consultation to final product dispatch.
Our team of experts understands the intricacies of powder coating. We meticulously prepare each precision machining part by ensuring it’s thoroughly cleaned and free of contaminants, then apply the chosen powder with precise control. Whether you need a glossy black finish for an automotive component, a textured green for an architectural fixture, or a durable matte coating for industrial machinery, we can tailor the process to match your aesthetic and functional requirements.
At VMT, we invest in advanced equipment, quality powders, and continuous training to maintain the highest standards. We consistently audit our processes, track performance metrics, and fine-tune techniques to ensure each batch meets client specifications. This dedication to excellence is what sets us apart. We believe that combining custom CNC machining and powder coating under one roof not only streamlines workflows but also provides our clients with a single point of accountability. Ultimately, choosing VMT means receiving not just parts, but solutions engineered to excel in challenging real-world applications.

Powder coating finish stands as a robust and versatile solution that enhances the quality, durability, and visual appeal of CNC machining parts. By embracing this finishing technique, manufacturers unlock numerous benefits: improved corrosion resistance, a wide range of achievable textures and colors, reduced environmental impact, and cost efficiencies. The method’s adaptability to various materials, from steel and aluminum to certain engineered plastics, ensures that your custom CNC machining projects can yield products that excel in diverse applications.
Moreover, the synergy between powder coating and CNC machining services empowers manufacturers to deliver consistently high-quality results. By integrating best practices—rigorous pretreatment, careful powder selection, and precise curing controls—producers can achieve repeatable, flawless finishes that delight customers and enhance brand credibility. Adopting industry standards and certifications further reinforces your commitment to quality, sustainability, and innovation.
As markets continue to evolve, staying ahead means investing in processes that offer long-lasting, high-value solutions. Powder coating’s proven track record, combined with a steady stream of technological advancements, ensures it remains a trusted finishing method for years to come. Ultimately, integrating powder coating into your CNC machining factory’s capabilities ensures you remain competitive, responsive to changing demands, and poised to meet the highest customer expectations.
What is the difference between powder coating and wet paint?
Powder coating uses dry, electrostatically charged powders that are cured under heat, creating a durable, solvent-free film. Wet paint relies on liquid solvents and may require multiple coats. Powder coatings generally produce thicker, more uniform finishes and emit fewer volatile organic compounds (VOCs), making them more eco-friendly.
What is the price of powder coating?
Costs vary depending on factors like part size, powder type, and complexity. While initial equipment and setup expenses can be higher, long-term savings stem from reduced waste, reusable overspray, and improved efficiency. Over time, powder coating proves cost-effective for both small and large-scale CNC machining services.
Why is powder coating better than traditional regular paint?
Powder coating often provides superior durability, corrosion resistance, and color consistency. It’s also environmentally friendly, releasing minimal VOCs. These attributes make it a more reliable, stable choice for finishing CNC machining parts, especially those exposed to harsh conditions.
Why is industrial powder coating green and environmentally friendly?
Powder coatings contain no solvents, drastically cutting down VOC emissions. Additionally, overspray powder can be reclaimed, reducing waste. These environmental benefits align with global sustainability goals, appealing to clients who prioritize eco-conscious suppliers.
How durable is powder coating?
Powder coatings form a robust barrier against scratches, chemicals, and UV rays. Properly applied and cured, they can outlast many liquid paints, maintaining their protective function and appearance for years, even in demanding settings.
How long does powder coating last?
Lifespan varies, but well-applied coatings can endure a decade or more, depending on environmental exposure and mechanical wear. Regular maintenance and proper handling further extend service life.
Is powder coating better than liquid paint?
Often, yes. Powder coatings offer thicker, more uniform layers without drips, improved durability, and fewer environmental concerns. While liquid paint may still be suitable for specific applications, powder coating often delivers superior overall performance and cost savings.
What types of materials can you powder coat?
Primarily metals (steel, aluminum), but also some heat-tolerant plastics and composites. The key requirement is that the substrate withstands curing temperatures without deforming or degrading.
What industries use powder coating?
Automotive, aerospace, construction, electronics, and medical fields all rely on powder coatings. The technique’s versatility and robust protective qualities make it ideal for diverse applications.
What metals cannot be powder coated?
Most metals can be powder coated if they handle curing temperatures well. Soft, low-melting metals or surfaces without proper pretreatment may be unsuitable, but in general, steel and aluminum are prime candidates.
Is powder coating matte or glossy?
Powder coatings can achieve various finishes: matte, glossy, satin, or textured. The final appearance depends on powder formulation and cure parameters, granting flexibility to match design preferences.
What is the difference between matte and glossy coatings?
Matte coatings diffuse light, reducing glare and providing a subdued look. Glossy coatings reflect more light, delivering a bright, shiny surface. The choice depends on aesthetic goals, branding, and application requirements.
