15 years one-stop China custom CNC machining parts factory

Hey there I’m VMT Sam!
With 25 years of CNC machining experience we are committed to helping clients overcome 10000 complex part-processing challenges all to contribute to a better life through intelligent manufacturing. Contact us now
 799 |
Published by VMT at Oct 31 2024 | Reading Time:About 2 minutes
799 |
Published by VMT at Oct 31 2024 | Reading Time:About 2 minutes
Struggling to print intricate logos or designs on complex shapes? Pad printing technology offers a precise solution to transfer detailed artwork onto curved or irregular surfaces—perfect for industries like electronics and cosmetics.
Pad printing is a specialized printing process that transfers ink from an etched plate to a product surface using a silicone pad. This method allows printing on irregular shapes, making it essential in producing CNC machining parts with custom designs, logos, and markings.
Now, let’s dive deeper into how pad printing works, its components, and the industries it serves.
Pad printing is an indirect offset printing process that transfers ink from a flat plate (cliché) to a 3D object using a flexible silicone pad. The silicone pad's adaptability allows it to transfer precise images onto flat, curved, or textured surfaces, making it ideal for applications like CNC machining parts or consumer products that require branding or functional labels. This versatile method is used across various industries, including automotive, electronics, medical devices, and sporting goods.

The pad printing process relies on several key elements working in harmony: an etched plate (to hold the design), silicone pad, ink, and the part being printed. The pad compresses onto the inked plate, picks up the design, and transfers it to the substrate with high precision. Silicone’s non-stick nature ensures the ink releases easily from the pad, enabling detailed prints even on curved or irregular shapes.
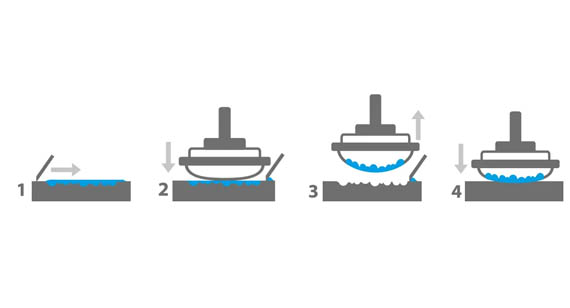
Pad Printing Steps
The pad printing process follows a series of precise steps. Using a closed-cup pad printing machine, here’s how it works:
Step 1: In situ (Ink Application)
The ink cup, containing the printing ink, slides across the plate, filling the etched design with ink. Excess ink is scraped away by the ink cup’s doctoring edge to ensure only the etched areas contain ink.
Step 2: Expose to Air (Ink Tack Formation)
The ink in the etched design briefly air-dries, becoming tacky. This stage ensures the ink will adhere to the silicone pad during transfer without smudging.
Step 3: Printing (Pad Transfer)
The silicone pad compresses onto the inked plate, picking up the tacky ink. It then moves to the product and presses down, transferring the ink to the substrate’s surface.
Step 4: Next Cycle
The process repeats for each print, with machines capable of handling rapid cycles for production efficiency.
Basic Components of Pad Printing Machine
A reliable pad printing machine consists of several essential components that work together to ensure precision and consistency.
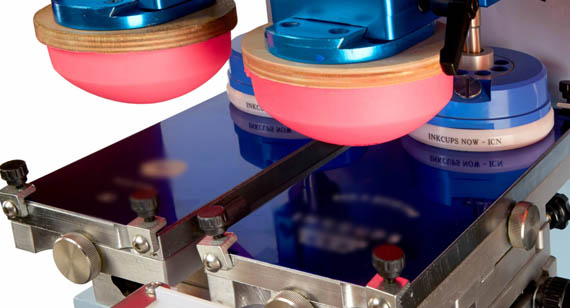
2.1 Pad Printing Machine
The printing machine houses the control system, printer bed, and pneumatic or motor-driven mechanisms that control the pad’s movements and the ink cup’s operation.
2.2 Pad Printing Ink Cup
The ink cup serves two functions: containing the ink and scraping excess ink off the printing plate to ensure crisp design prints.
2.3 Pad Printing Ink
Pad printing inks vary based on the material being printed. They must adhere well and provide long-lasting results on surfaces like plastics, metals, glass, or painted parts.
2.4 Printing Pad
Made of silicone, the pad’s flexibility allows it to conform to irregular surfaces, ensuring complete ink transfer. Pads come in different shapes and hardness levels to suit various applications.
2.5 Pad Printing Plate
The plate holds the design or logo to be printed. Plates are made using either photopolymer platemaking or laser etching.
Photopolymer Platemaking: This involves exposing light-sensitive plates to UV light through a film of the design. It’s cost-effective but limited in durability.
Laser Platemaking: A high-precision laser engraves the design directly into the plate, providing greater detail and longevity.
Pad printing is superior to screen printing for irregular shapes, while screen printing excels at printing large designs on flat surfaces. Both techniques have their place in CNC machining factories, but pad printing is preferred for high-detail logos on complex parts.

Advantages of Pad Printing
Compatible with Different Surfaces
Pad printing works on surfaces of varying shapes—flat, cylindrical, or curved—making it indispensable for CNC machining parts.
Compatible with Various Materials
The process supports a wide range of materials, such as plastics, metals, glass, and silicone.
Economical and Efficient
Pad printing offers low setup costs for small-batch production, which is essential for CNC prototype machining and custom manufacturing projects.
Provides High-Quality Printing
The silicone pad delivers sharp, high-resolution prints, even on textured surfaces.
Supports a Wide Range of Color Options
Pad printing accommodates multi-color designs by using separate pads for each color layer.
Disadvantages of Pad Printing
Slow Speed
Compared to other printing processes, pad printing can be slower since each design layer requires individual printing cycles.
Small Printing Area
Pad printing is best suited for small logos and designs, limiting its use on large surfaces.
Color Variability Issues
Improper mixing of inks or environmental factors can cause inconsistencies in color matching.
Cosmetics
Pad printing is ideal for printing brand logos and product details on cosmetic containers like lipstick tubes or perfume bottles.
Automotive
In automotive manufacturing, pad printing applies functional markings, such as control symbols on buttons and knobs.
Consumer Appliances
Pad printing offers high-resolution branding on electronic devices like remote controls, coffee machines, and kitchen gadgets.
Electronics
Precision is key when printing on circuit boards or small components like connectors, making pad printing the preferred method.
Medical Devices
Pad printing ensures accurate, long-lasting marks on surgical tools and devices, which need high precision for compliance purposes.
Sporting Goods
Logos on golf balls, helmets, and water bottles are often applied using pad printing due to its durability and ability to print on curved surfaces.
Choose High-Quality Equipment
Invest in reliable pad printing machines to ensure consistent quality across production runs.
Mix Inks Carefully
Proper ink mixing prevents color inconsistencies and ensures durability on different materials.
Select the Right Pad Type
Match pad hardness and shape to the substrate for optimal ink transfer.
Avoid Excessive Pad Pressure
Overly high pressure can damage parts or cause misaligned prints, leading to production errors.
Pad printing can be complemented with additional finishing techniques such as anodizing, powder coating, or laser engraving. These services ensure the printed product aligns with functional and aesthetic standards required in custom CNC machining services.
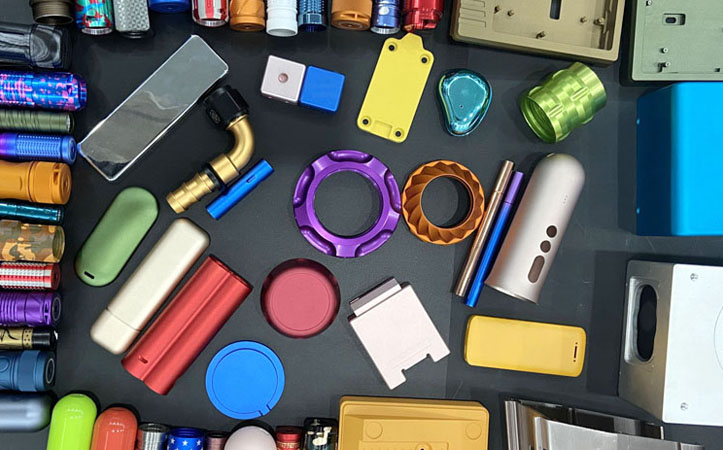

Pad printing offers unmatched versatility for printing intricate designs on irregular surfaces, making it a go-to solution for many industries. Its compatibility with different materials and economical setup makes it ideal for both CNC prototype machining and large-scale production.
FAQs
Can you pad print on paper?
Yes, although pad printing is more commonly used on non-porous materials like plastic or metal.
Is pad printing better than screen printing?
Pad printing is ideal for small, intricate designs on irregular surfaces, whereas screen printing is better for large, flat surfaces.
How long can pad printing last?
With proper ink selection, pad prints can last for years without fading or peeling.
What factors affect the life of pad printing rubber tips?
Exposure to harsh chemicals and excessive use can reduce pad life.
What is the accuracy level of pad printing machines?
Modern pad printing machines offer accuracy within microns, ensuring precision for detailed designs.
What is the ink thickness of pad printing?
The typical ink layer ranges from 4 to 20 microns, depending on the substrate and ink type.
What is the PAD process?
The PAD process involves picking up ink from the plate and transferring it to the product using a silicone pad.
Is pad printing durable?
Yes, especially with the right ink and curing processes, pad prints can withstand wear and tear.
How long does pad printing take to dry?
Drying time depends on the ink type, but it typically takes a few seconds to a few minutes.
Does pad printing heat up?
Some processes may involve heat curing, but pad printing itself does not generate significant heat.
What is the depth of pad printing?
The etched plate depth typically ranges from 25 to 75 microns, depending on the design complexity.
Ready To Start Your Next Project?
Get Instant Quote

Request a Free Quote
Send us a message if you have any questions or request a quote. We will get back to you ASAP!
