15 years one-stop China custom CNC machining parts factory
 3216 |
Published by VMT at Feb 23 2025 | Reading Time:About 2 minutes
3216 |
Published by VMT at Feb 23 2025 | Reading Time:About 2 minutes
Casting defects can significantly impact the quality and functionality of manufactured parts, leading to costly delays and product failure. Understanding the causes behind these defects is crucial for optimizing production efficiency. Whether you are working with metal casting CNC machining parts or other types of casting processes, identifying and addressing casting defects can improve the final product's durability and precision. In this guide, we will explore 17 common casting defects, their causes, and solutions to help ensure your casting process runs smoothly and produces high-quality components.
Metal casting defects, such as porosity, shrinkage, and slag inclusions, can compromise the quality of your parts. These issues arise from various factors, including mold material, heat, and metal flow. By identifying the defect types and their causes, manufacturers can implement effective remedies to prevent them, improving the overall production process. Regular inspections and precision techniques can minimize casting defects, leading to more efficient and cost-effective manufacturing.
Now that we have an overview of the importance of casting defect management, let’s dive deeper into the types of defects that commonly occur in the casting process, their causes, and the solutions available to address these challenges. By understanding these issues, you can take proactive steps to ensure high-quality output from your casting operations.
Metal casting is a manufacturing process where molten metal is poured into a mold to take the shape of the mold cavity. Once the metal cools and solidifies, it forms a part with a precise shape and size. This technique is widely used in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and construction to create durable parts, from engine components to structural elements. In metal casting, CNC machining parts may be post-processed to ensure the final product meets the exact specifications required.

Casting defects refer to imperfections or flaws that occur during the casting process. These defects can manifest as holes, cracks, or surface irregularities, potentially compromising the structural integrity and function of the part. Defects in casting CNC machining parts can lead to costly repairs, production delays, and product rejections. It’s critical for manufacturers to identify these defects early in the process and implement preventive measures to minimize their occurrence.

In the world of casting, defects are an inevitable part of the process. These defects can compromise the integrity, appearance, and functionality of the final casting. Understanding the different types of defects and their causes is essential for improving the casting process and ensuring high-quality products. This guide covers the various casting defects, including metallurgical defects, defects due to heat, issues with mold materials, and casting shape defects. Let’s explore the most common defects in detail, how they occur, and how they can be addressed.

Metallurgical Defects
Metallurgical defects arise from issues related to the metal itself during the casting process. These include voids, inclusions, and other structural weaknesses that can affect the quality and mechanical properties of the final casting. Below are some of the most common metallurgical defects.
1. Porosity Defects
Porosity defects occur when gas pockets or voids form inside the casting, weakening the structure and affecting its mechanical properties.
Gas Porosity
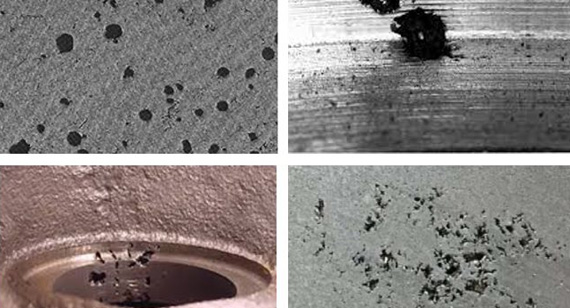
Gas porosity defects are air bubbles trapped in the casting during solidification. These voids can form on the surface or within the body of the casting.
Causes:
Remedies:
Shrinkage Porosity
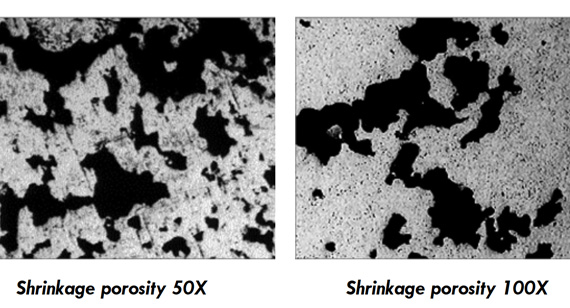
What is Shrinkage Porosity? Shrinkage porosity is a type of defect caused by the solidification of the casting. As the metal cools, it contracts, which can lead to voids if the mold does not compensate for the shrinkage.
Causes:
Remedies:
2. Sinks

What are Sinks? Sinks are surface depressions that appear on castings due to the insufficient flow of molten metal during solidification. These depressions are a result of improper metal distribution in thick sections.
Causes:
Remedies:
3. Slag Inclusions

What Are Slag Inclusions? Slag inclusions occur when impurities from the mold material or molten metal get trapped within the casting.
Causes:
Remedies:
4. Dross

What Is Dross? Dross is the oxide or non-metallic debris that forms on the surface of molten metal. It can become embedded in the casting, compromising its strength and surface finish.
Causes:
Remedies:
5. Welding

What Is Welding? Welding defects occur when sections of the casting are unintentionally fused together during solidification.
Causes:
Remedies:
Defects Caused by Heat
Heat-related defects occur when the metal's temperature is not properly controlled during the casting process. These defects are related to stresses, cooling rates, and temperature variations within the mold.
1. Hot Cracks

What Are Hot Cracks? Hot cracks occur when thermal stresses exceed the metal's strength during the solidification process. These cracks can form during or after casting as the metal cools.
Causes:
Remedies:
2. Cold Shuts
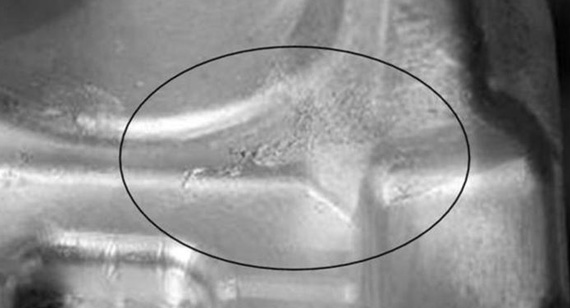
What Are Cold Shuts? Cold shuts occur when two streams of molten metal fail to fuse properly, creating a weak spot on the surface of the casting.
Causes:
Remedies:
3. Thermal Fatigue

What Is Thermal Fatigue? Thermal fatigue occurs when repeated heating and cooling cycles cause cracks to form in the casting material.
Causes:
Remedies:
Defects in Mold Material
Mold material defects occur when the material used for the mold does not properly withstand the conditions during the casting process, resulting in defects in the final part.
1. Cut and Wash
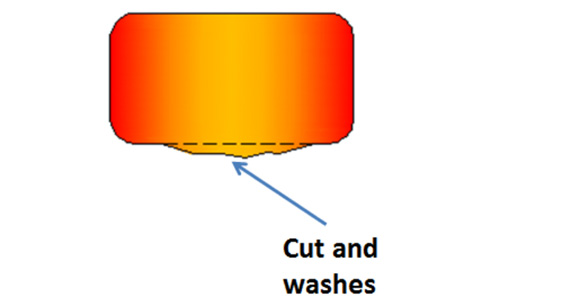
What Are Cut and Wash Defects? Cut and wash defects occur when the molten metal erodes the mold surface during the pouring process, causing rough spots on the casting.
Causes:
Remedies:
2. Fusion

What Is Fusion? Fusion occurs when molten metal bonds with the mold material, creating a problematic bond that can weaken the casting.
Causes:
Remedies:
3. Runout

What Is Runout? Runout occurs when molten metal leaks out of the mold cavity, resulting in defects along the edges of the casting.
Causes:
Remedies:
4. Swells
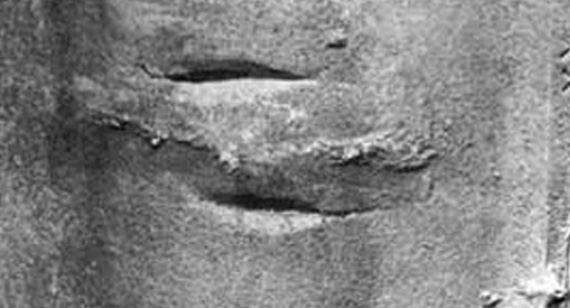
What are Swells?
Swells are defects in castings characterized by bulges or irregular growths in the surface of the casting, typically near the edges or thin sections. These deformations often affect the dimensional accuracy and appearance of the final part. Swells can lead to rework or material wastage, increasing production costs.
Causes:
Swells can occur due to several factors, including:
Remedies:
5. Drops

What are Drops?
Drops refer to small pieces of metal that detach from the main casting and fall into the mold cavity. These unwanted fragments can become part of the casting, causing defects like surface irregularities or cracks.
Causes:
Remedies:
6. Metal Penetration

What is Metal Penetration?
Metal penetration occurs when molten metal infiltrates the mold material, causing the surface of the casting to become rough or porous. This defect is often found in sand casting when molten metal seeps into the sand mold, leading to weakened casting surfaces.
Causes:
Remedies:
7. Rat Tails
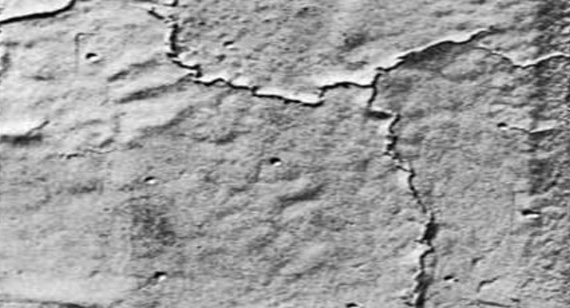
What are Rat Tails?
Rat tails are defects that appear as thin, elongated ridges or fins of metal, typically on the surface of the casting. These defects often resemble the tail of a rat and occur when the metal solidifies unevenly. Rat tails can weaken the overall structural integrity of the casting.
Causes:
Remedies:
Defects in Casting Shape
Defects in casting shape occur when the final casting does not meet the required dimensions or shape due to errors in mold alignment, temperature, or cooling.
1. Misalignment

What Is Misalignment? Misalignment occurs when the mold sections do not align properly during the pouring process, leading to dimensional inaccuracies in the final casting.
Causes:
Remedies:
2. Flash

What Is Flash? Flash is the excess material that overflows from the mold cavity, creating thin, unwanted layers on the casting.
Causes:
Remedies:
By identifying these common defects and understanding their causes, manufacturers can improve their casting processes and produce higher-quality, more reliable parts. Proper attention to detail, process control, and material selection are key to reducing casting defects and achieving optimal results.
At VMT, we understand the critical importance of high-quality metal casting in achieving superior performance and reliability in your products. As a trusted CNC machining factory, we offer comprehensive metal casting services that ensure precise, defect-free castings tailored to your specific needs. Whether you're working with aluminum, steel, or other metals, we have the expertise, advanced technology, and quality control processes in place to deliver exceptional results.
Our team is committed to addressing and preventing common casting defects, such as porosity, shrinkage, slag inclusions, and more, by employing state-of-the-art casting techniques and meticulous attention to detail. With VMT as your partner, you can be confident that your casting projects will be executed efficiently, accurately, and with the highest standards of quality.
From custom CNC machining parts to specialized casting for diverse industries, VMT provides end-to-end solutions that enhance your production process. Our commitment to innovation and excellence makes us the ideal partner for all your metal casting needs.

Casting defects are a challenge faced by manufacturers worldwide, but with the right knowledge and solutions, they can be effectively minimized. Understanding the various types of casting defects, their causes, and remedies is essential to improving the quality and efficiency of your casting processes. By partnering with VMT, you gain access to not only high-quality casting services but also a dedicated team focused on delivering precise and reliable results.
Whether you need assistance with shrinkage porosity, slag inclusions, or mold material defects, VMT’s metal casting solutions are designed to meet the demands of modern manufacturing. Our expertise, combined with advanced CNC machining services, ensures that your projects will achieve the highest standards of quality and precision.
Let VMT be your trusted partner in overcoming casting challenges and delivering exceptional results, every time.
1. What are the 5 types of casting defects?
The five main types of casting defects include porosity, shrinkage, sinks, slag inclusions, and dross. These defects can compromise the quality, strength, and functionality of cast parts, making it essential to address them during the casting process.
2. How to identify casting defects?
Casting defects can be identified through various inspection techniques such as visual inspection, dimensional checks, and non-destructive testing (NDT) methods like X-ray, ultrasonic testing, and dye penetrant testing. These techniques help detect surface and internal defects such as cracks, porosity, and inclusions.
3. How to control casting defects?
Casting defects can be controlled by implementing process optimization, such as maintaining consistent pouring temperatures, adjusting cooling rates, ensuring mold quality, and proper ventilation. Additionally, the use of simulation software and regular inspections during production can help detect and correct defects early in the process.
4. What are the discontinuities in castings?
Discontinuities in castings refer to structural imperfections in the material that can affect the performance of the cast part. These can include voids, cracks, and inclusions, often caused by issues during the casting process like improper cooling or contamination.
5. What are the 5 discontinuities?
The five types of discontinuities in castings typically include porosity, shrinkage, cracks, inclusions, and misalignment. These discontinuities can weaken the casting and lead to failure in end-use applications if not properly addressed.
6. What is the difference between discontinuities and defects?
Discontinuities are imperfections within the material's structure, while defects are flaws in the casting process that impact the part's functionality or quality. All defects are discontinuities, but not all discontinuities are considered defects if they don’t affect the part’s performance.
7. What causes pinholes in castings?
Pinhole defects are typically caused by trapped gas bubbles during the solidification process. These gases may be released by the molten metal, mold materials, or atmospheric contaminants. Improper venting, excessive moisture in the mold, or incorrect pouring temperatures can contribute to this issue.
8. What are the different types of discontinuities?
Different types of discontinuities in castings include porosity, cracks, inclusions, misalignment, and cold shuts. These defects can arise from issues such as gas entrapment, rapid cooling, improper mold preparation, or poor alloy composition.
9. What are the names of discontinuities?
The primary names of discontinuities in casting are porosity (gas or shrinkage), cracks (hot cracks or cold cracks), inclusions (slag or dross), misalignment, and flash. These names reflect the specific imperfections in the material or shape of the casting.
10. What are the 4 types of discontinuities in welding?
The four main types of discontinuities in welding are cracks, porosity, inclusions, and lack of fusion. These can occur during the welding process due to improper technique, contamination, or environmental factors affecting the weld joint.
11. What are the different types of geological discontinuities?
Geological discontinuities refer to natural defects in the earth’s crust and include faults, fractures, bedding planes, joints, and folds. These discontinuities can influence the physical properties of rocks and soils and are critical to understanding geological formations.
12. What are the 4 main types of castings?
The four main types of casting include sand casting, die casting, investment casting, and permanent mold casting. Each process has unique characteristics and is selected based on the part’s material, size, and application requirements.
13. How to check for casting defects?
Casting defects can be checked using visual inspections, dimensional measurements, and non-destructive testing (NDT) methods such as X-ray, ultrasonic testing, and dye penetrant testing. Regular monitoring of the casting process and in-process quality checks help detect defects early.
14. How many types of defects are there?
There are numerous types of defects that can occur in the casting process, often categorized into metallurgical defects, heat-related defects, mold material defects, and shape-related defects. Each category has several specific defects such as porosity, cracks, and misalignment that need to be managed for optimal casting quality.
These FAQs provide a comprehensive understanding of casting defects and discontinuities, ensuring that manufacturers and engineers can effectively detect, control, and prevent these issues during the casting process. At VMT, we provide expert metal casting and CNC machining services to help ensure high-quality parts with minimal defects.
