15 years one-stop China custom CNC machining parts factory
 516 |
Published by VMT at Nov 23 2024 | Reading Time:About 4 minutes
516 |
Published by VMT at Nov 23 2024 | Reading Time:About 4 minutes
Are you struggling to achieve precision and efficiency in your CNC machining operations due to improper workpiece holding? Frustrated by the limitations and inefficiencies caused by using the wrong fixtures, leading to wasted time and resources? You're not alone. Many manufacturers face challenges in selecting the appropriate CNC fixtures, which can result in decreased productivity and subpar product quality. But what if you could optimize your machining process by choosing the right CNC fixture types tailored to your specific needs, enhancing both precision and efficiency?
To choose the right CNC fixture for your workpiece, you need to understand the various types of CNC fixtures available—such as modular, universal, and custom fixtures—and consider factors like workpiece geometry, machining operations, and production volume to select the fixture that best suits your specific application.
Now that we've highlighted the importance of selecting the appropriate CNC fixture for your workpiece, let's delve deeper into what CNC fixtures are, their applications, the different types available, and how to make an informed choice. Understanding these aspects will empower you to optimize your CNC machining processes, improve product quality, and maximize efficiency.
Preface
In the competitive world of manufacturing, precision and efficiency are paramount. CNC machining has revolutionized the industry by allowing for high-precision production of complex parts. However, the effectiveness of CNC machining is significantly influenced by the fixtures used to hold workpieces in place during the machining process. Choosing the right CNC fixture is crucial for ensuring product quality, reducing waste, and maximizing spindle time. This comprehensive guide aims to provide an in-depth understanding of CNC fixture types and how to choose the right workpiece fixture for your specific needs.
A CNC fixture is a device used in CNC machining to securely hold a workpiece in place during machining operations. It ensures the precise positioning and stability of the workpiece, allowing for accurate and repeatable machining processes. CNC fixtures are essential components in manufacturing, as they directly impact the quality, efficiency, and safety of machining operations.
Fixtures are designed to align the workpiece in a predetermined position, providing support and rigidity to withstand the forces exerted during machining. They are critical for achieving tight tolerances and complex geometries, especially in custom CNC machining where precision is paramount.

Key characteristics of CNC fixtures include:
Understanding the role and importance of CNC fixtures is the first step toward optimizing your machining processes and achieving high-quality CNC machining parts.
CNC fixtures play a vital role in various machining operations. They are not just simple holders but are integral components that enhance the overall machining process. The applications of CNC fixtures can be broadly categorized into positioning, clamping, and maximizing spindle time.
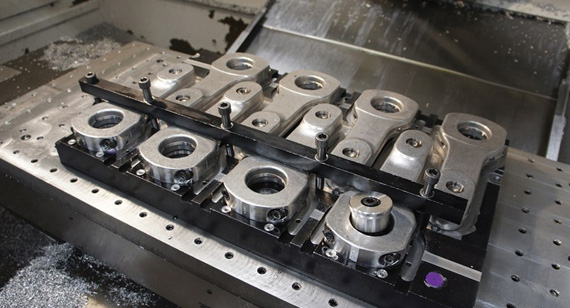
Positioning
One of the primary functions of a CNC fixture is to accurately position the workpiece relative to the cutting tool. Precise positioning is essential for:
Proper positioning reduces errors, enhances product quality, and minimizes waste, which is crucial in industries requiring high-precision components, such as aerospace, automotive, and medical devices.
Clamping
Clamping involves securely holding the workpiece to prevent movement during machining. Effective clamping is critical for:
Different clamping mechanisms, such as mechanical, hydraulic, or pneumatic clamps, can be used depending on the requirements of the machining operation.
Maximizing Spindle Time
Efficient use of spindle time is essential for productivity and cost-effectiveness. CNC fixtures contribute to maximizing spindle time by:
By reducing downtime and streamlining operations, CNC fixtures help manufacturers meet tight deadlines and production targets.
Selecting the right type of CNC fixture is crucial for optimizing machining operations. CNC fixtures can be categorized based on application, power source, and machining options. Understanding the different types allows you to choose the most suitable fixture for your specific needs.
CNC Fixtures by Application
Fixtures can be designed for specific applications, offering tailored solutions to various machining challenges. Here are some common types:
Special Fixtures
Special fixtures are custom-designed for a particular workpiece or operation. They are ideal for:
Custom fixtures can be designed by CNC machining factories to meet specific client requirements.
Universal Fixtures
Universal fixtures are versatile devices that can be adjusted to hold various workpieces. They are suitable for:
Examples include adjustable clamps and vises that can accommodate different sizes and shapes.
Modular Fixtures

Modular fixtures consist of interchangeable components that can be assembled in various configurations. Advantages include:
Modular fixtures are commonly used in industries where product designs frequently change.
Combination Fixtures
Combination fixtures integrate features of different fixture types to provide a versatile solution. They are beneficial for:
Assembly Fixtures
Assembly fixtures are designed to hold components in place during assembly operations. They are essential for:
Used in industries like automotive and electronics, assembly fixtures improve efficiency and product quality.
CNC Vise Fixtures

CNC vise fixtures are common in machining and provide a reliable means of clamping workpieces. Features include:
Vises are often used in milling operations and can be combined with soft jaws customized to the workpiece.
Angle Fixtures

Angle fixtures hold the workpiece at a specific angle relative to the machine table. They are useful for:
Angle fixtures enhance the capability of CNC machines to produce intricate designs.
Jigs
Jigs guide the cutting tool during machining operations. While similar to fixtures, the key difference is that jigs control tool movement, whereas fixtures secure the workpiece. Jigs are important for:
Indexing Fixtures
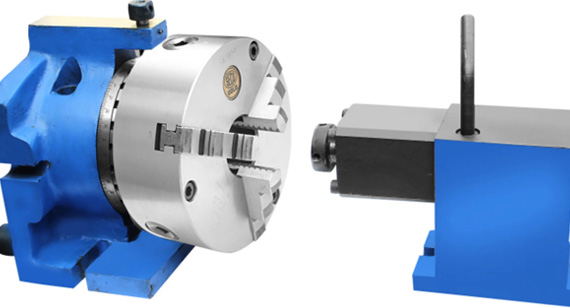
Indexing fixtures allow the workpiece to be rotated or indexed to different positions. They are essential for:
Indexing fixtures are commonly used in custom CNC machining for parts requiring machining on multiple sides.
Clamp Fixtures
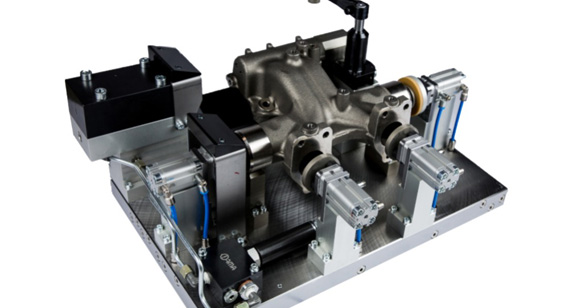
Clamp fixtures use various clamping mechanisms to secure the workpiece. They are characterized by:
Clamp fixtures are widely used due to their simplicity and effectiveness.
Jig Fixtures
Jig fixtures are specialized devices that not only hold the workpiece but also guide the tool during machining. They are essential in operations where precise tool guidance is required.
There Are Many Types of Jigs
Different types of jigs are designed to meet specific machining needs:
Plate Jigs
Plate jigs are flat plates with holes and bushings to guide drills. They are suitable for:
Template Jigs
Template jigs use a template to guide the cutting tool along a predefined path. Applications include:
Angle Jigs
Angle jigs hold the workpiece and guide the tool at a specific angle. Useful for:
Leaf Jigs
Leaf jigs have a hinged leaf to allow easy loading and unloading of the workpiece. Advantages include:
Diameter Jigs
Diameter jigs are designed for cylindrical workpieces, guiding the tool around the circumference. They are used in:
Understanding the various jig types helps in selecting the appropriate one for specific machining tasks.
CNC Fixtures by Power Source
Fixtures can also be classified based on their power source, which influences their clamping force, speed, and suitability for automation.
Electrical Fixtures
Electrical fixtures use electric motors or actuators for clamping and positioning. Benefits include:
Manual Fixtures
Manual fixtures rely on human operators to clamp and release workpieces. Characteristics are:
Suitable for small-scale operations or where automation is not feasible.
Pneumatic Fixtures
Pneumatic fixtures use compressed air to apply clamping force. Advantages include:
Commonly used in high-volume production environments.
Magnetic Fixtures
Magnetic fixtures utilize magnetic force to hold ferrous workpieces. Features include:
Ideal for flat or irregularly shaped ferrous workpieces.
Vacuum Fixtures
Vacuum fixtures hold workpieces using vacuum suction. Benefits are:
Used in industries like aerospace and electronics.
Hydraulic Fixtures
Hydraulic fixtures use hydraulic fluid pressure for clamping. Advantages include:
Ideal for demanding machining operations requiring robust clamping.
CNC Fixtures by CNC Machining Options
Fixtures can be designed specifically for certain machining operations, enhancing efficiency and precision in those processes.
Turning Fixtures
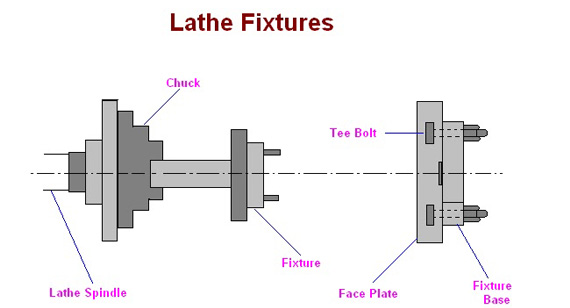
Turning fixtures are used in lathes to hold workpieces for rotational machining. Features include:
Turning fixtures are essential for producing shafts, axles, and other round components.
Milling Fixtures
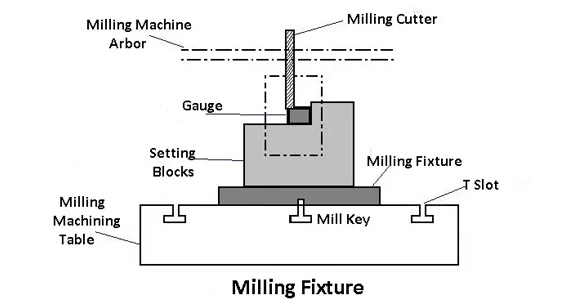
Milling fixtures secure workpieces for milling operations. Characteristics are:
Used extensively in CNC machining services for creating complex geometries.
Boring Fixtures
Boring fixtures hold workpieces during boring operations to enlarge existing holes. They offer:
Boring fixtures are critical for achieving tight tolerances in hole diameters.
Drilling Fixtures
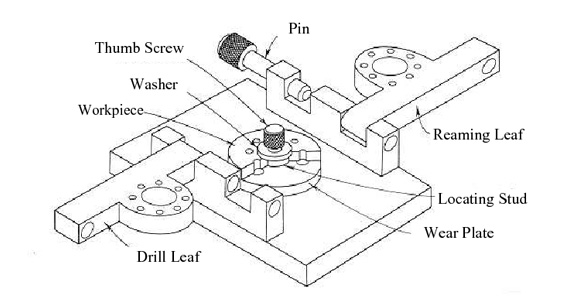
Drilling fixtures are designed to position and hold workpieces for drilling operations. Benefits include:
Widely used in manufacturing industries requiring precise hole patterns.
Grinding Fixtures

Grinding fixtures hold workpieces during grinding operations. They are essential for:
Used in tool making, aerospace, and other precision-demanding sectors.
CNC Fixture Design Considerations
Designing an effective CNC fixture requires careful consideration of various factors to ensure it meets the specific needs of the machining operation. Here are key considerations:

1. Clearly Define the Design Requirements for CNC Fixtures
Understanding the specific requirements of the machining operation is essential. This includes:
Clear requirements guide the design process and ensure the fixture meets operational needs.
2. Gather Relevant Information from the CNC Workshop
Collaboration with the CNC workshop is crucial. Information to gather includes:
This information helps in designing a fixture that is compatible with existing equipment and processes.
3. Prepare Multiple Drafts of CNC Fixture Design
Creating several design iterations allows for:
Using CAD software can aid in visualizing and modifying designs.
4. Select the Best CNC Fixture Solution
Evaluate the drafts based on criteria such as:
Select the design that offers the best balance of these factors.
5. Optimize and Implement the Selected CNC Fixture
Once a design is selected:
Implementing the optimized fixture enhances efficiency and product quality.
6. Workpiece Material
Consider the material properties of the workpiece:
Material considerations ensure the fixture does not damage the workpiece.
7. Improve Tolerance
Design the fixture to maintain or improve tolerance levels:
High-precision fixtures are essential in industries like aerospace and medical devices.
8. Reference Important Surfaces
Use critical surfaces of the workpiece as reference points:
Referencing important surfaces enhances accuracy and consistency.
9. Secure Clamping
Ensure the workpiece is securely clamped:
Secure clamping improves safety and machining quality.
10. Stability and Rigidity
Design the fixture for maximum stability:
A stable fixture leads to better surface finishes and tool life.
11. Alignment and Positioning
Ensure precise alignment:
Proper alignment reduces errors and rework.
12. Material Compatibility
Choose fixture materials compatible with the workpiece and machining environment:
Material compatibility extends fixture life and maintains machining quality.
Advancements in technology have led to innovative fixture solutions that enhance efficiency, precision, and automation in CNC machining.

1. Robotic Fixture Loading
Robotic fixture loading involves using robots to load and unload workpieces onto fixtures. Benefits include:
Integration with CNC machining services allows for continuous, unattended operation.
2. CNC Fixture Monitoring
CNC fixture monitoring uses sensors and software to monitor fixture conditions in real-time. Advantages are:
Monitoring enhances reliability and product quality.
3. Fixture Damping
Fixture damping involves incorporating materials or mechanisms to absorb vibrations. Benefits include:
Damping is especially important in high-speed machining operations.
Determining whether a custom CNC fixture is necessary depends on several factors:
Consulting with experts in custom CNC machining can help assess the need for a custom fixture.
Selecting the appropriate CNC fixture involves evaluating the specific needs of your machining operation and understanding the options available.
Combination Clamps/Building Blocks
Combination clamps and building blocks offer modularity and flexibility. Consider them when:
They are ideal for CNC machining factories with diverse production needs.
Hydraulic/Pneumatic Clamps
Hydraulic and pneumatic clamps provide consistent clamping force and are suitable for:
Evaluate the infrastructure requirements, such as air or hydraulic lines.
Electro-Permanent Magnetic Clamps
Electro-permanent magnetic clamps combine the benefits of electromagnets and permanent magnets. Advantages include:
Suitable for ferrous workpieces with flat surfaces.
Clamp Bases
Clamp bases serve as the foundation for building custom fixture setups. They are useful when:
They offer a balance between custom fixtures and modular systems.
Choosing the right CNC fixture is a critical aspect of optimizing your CNC machining processes. By understanding the different types of CNC fixtures—such as modular, universal, and custom fixtures—and considering factors like workpiece geometry, machining operations, power source, and production volume, you can select the fixture that best suits your specific application. Proper fixture selection enhances precision, efficiency, and safety, ultimately leading to higher quality products and improved productivity in your CNC machining services.
Whether you need standard fixtures or a custom solution, investing time and resources into selecting the right fixture will pay dividends in the long run. Collaboration with experienced CNC machining factories and professionals can provide valuable insights and assistance in making the best choice for your needs.
What Types of Workpieces Can CNC Fixtures Hold?
CNC fixtures can hold a wide variety of workpieces, including flat plates, cylindrical shafts, irregular shapes, and complex geometries. The type of fixture used depends on the workpiece's size, shape, material, and the machining operations required. Custom fixtures can be designed to accommodate unique or challenging workpieces, ensuring secure holding and precise machining.
Are CNC Fixtures Interchangeable Between Different CNC Machines?
While some standard fixtures like vises and clamps may be interchangeable between machines of the same type and size, many fixtures are designed specifically for particular machines or operations. Factors like machine table size, mounting configurations, and the range of motion can affect compatibility. It's essential to verify that a fixture is suitable for use on a specific machine or consider designing fixtures that are adaptable to multiple machines.
How Do I Choose the Right CNC Fixture for My Application?
To choose the right CNC fixture:
How Do CNC Fixtures Differ from Jigs?
The primary difference between fixtures and jigs lies in their function:
Fixtures are generally used in machining processes where the tool path is controlled by the machine (e.g., CNC milling), while jigs are used in operations requiring manual guidance of the tool.
What Are the Common Benefits of Using Workpiece Fixtures?
Benefits of using workpiece fixtures include:
Do All CNC Controls Have Fixture Offset?
Most modern CNC controls offer fixture offset capabilities, allowing the operator to define the location of the workpiece relative to the machine's coordinate system. Fixture offsets are essential for accurate machining, especially when using multiple fixtures or setups. However, the specific features and ease of use can vary between different CNC control systems.
What Are the Three Types of Fixtures?
Fixtures can be broadly classified into three types based on their function and application:
What Are Jigs and Fixtures?
Jigs: Devices that hold the workpiece and guide the cutting tool during machining operations. They control tool movement and are often used in drilling, reaming, or tapping.
Fixtures: Devices that securely hold and position the workpiece but do not guide the tool. They are used in operations where the tool path is controlled by the machine, such as milling or turning.
Both are essential for ensuring precision, efficiency, and safety in manufacturing processes.
What Are Fixtures and Accessories?
Fixtures are devices used to hold and position workpieces during machining. Accessories refer to additional components or tools that enhance the functionality of the machine or fixture. Examples include:
Accessories can extend the capabilities of CNC machines and fixtures, enabling more complex operations and improved efficiency.
By understanding the various CNC fixture types and how to choose the right workpiece fixture, you can optimize your CNC machining parts production, enhance efficiency, and achieve superior product quality. Whether you are involved in custom CNC machining, operating a CNC machining factory, or seeking reliable CNC machining services, selecting the appropriate fixture is a critical step toward success.
