15 years one-stop China custom CNC machining parts factory
 471 |
Published by VMT at Nov 25 2024 | Reading Time:About 5 minutes
471 |
Published by VMT at Nov 25 2024 | Reading Time:About 5 minutes
Are you finding it challenging to produce precise slots and grooves in your CNC milling projects, leading to parts that don't fit together or function as intended? Inaccurate slot milling can result in poor assembly, reduced mechanical performance, and costly rework, leaving you frustrated and behind schedule. By mastering the art of slot milling—understanding its types, technologies, tips, and advantages—you can enhance your CNC machining capabilities, produce high-quality parts, and streamline your manufacturing processes.
Slot milling is a machining process where a milling cutter removes material from a workpiece to create slots, grooves, or pockets. By choosing the right tools and techniques, you can produce accurate slots with the desired dimensions and finishes, improving the functionality and performance of CNC milled parts.
Now that we've identified the critical role of slot milling in achieving precision and efficiency in CNC machining, let's explore what slot milling entails, the various techniques and tools available, and how you can optimize this process. Understanding these aspects will empower you to elevate your custom CNC machining projects and deliver exceptional results.
Preface
In the world of CNC milling and metal machining, slot milling stands out as a fundamental process that enables the creation of slots, grooves, and pockets essential for part functionality. Whether you're involved in producing intricate components for the aerospace industry or crafting prototypes in a CNC machining factory, mastering slot milling is crucial. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of slot milling, covering its definition, applications, key features, step-by-step processes, types of techniques and tools, practical tips, and the advantages and disadvantages associated with it. By the end of this guide, you'll have a thorough understanding of slot milling and how to apply it effectively in your CNC machining services.
Slot milling is a machining process that involves the removal of material from a workpiece using a rotating cutting tool, known as a milling cutter, to create a slot, groove, or pocket. This slot can be of various shapes and sizes, depending on the requirements of the design. Slot milling is performed on CNC milling machines, which provide precise control over the movement of the cutting tool and the workpiece, enabling the production of complex geometries with high accuracy.
In slot milling, the cutter moves along the desired path, cutting into the workpiece to create a slot with specified dimensions. The process can be used on a variety of materials, including metals like aluminum, steel, brass, and titanium, as well as plastics and composites. Slot milling is essential in creating keyways, T-slots, dovetail slots, and other features that are critical for the assembly and functionality of mechanical components.

Key aspects of slot milling include:
Slot milling is integral to various industries, including automotive, aerospace, medical devices, electronics, and general manufacturing, where precise slots are essential for component assembly and operation.
A slot milling cutter is a specialized cutting tool designed specifically for creating slots and grooves in a workpiece during the milling process. The primary purpose of a slot milling cutter is to remove material efficiently and accurately to produce slots with the required dimensions and surface finish. These cutters come in various shapes, sizes, and materials to suit different applications and materials.
Uses of slot milling cutters include:
Slot milling cutters are essential tools in CNC milling operations due to their ability to:
Types of slot milling cutters include:
Selecting the appropriate slot milling cutter is critical for achieving the desired outcome in a milling operation. Factors to consider include the material of the workpiece, the dimensions of the slot, the type of milling machine, and the production volume.
Slot milling is characterized by several key features that distinguish it from other milling processes. Understanding these features is essential for effectively implementing slot milling in CNC machining operations.
1. Direction of Cutting
Slot milling involves both axial and radial cutting motions. The cutter moves horizontally (radially) to create the width of the slot and vertically (axially) to achieve the desired depth. This dual-direction cutting requires careful control of feed rates and speeds to maintain tool integrity and achieve precise dimensions.
2. Tool Selection
The choice of cutting tool is paramount in slot milling. Factors influencing tool selection include:
3. Cutting Parameters
Optimizing cutting parameters such as spindle speed, feed rate, depth of cut, and width of cut is crucial. These parameters depend on the material being machined, the tool used, and the desired surface finish.
4. Chip Evacuation
Effective removal of chips is critical to prevent tool clogging, overheating, and poor surface finish. Slot milling generates significant amounts of chips confined within the slot, necessitating strategies like using tools with fewer flutes, applying coolant, or employing specialized chip evacuation techniques.
5. Tool Path Strategies
The tool path determines the cutter's movement and directly impacts the efficiency and quality of the slot milling process. Strategies include straight-line cutting, ramping, helical interpolation, or trochoidal milling, each with its advantages depending on the application.
6. Machine Stability and Rigidity
Slot milling requires a stable and rigid CNC milling machine to minimize vibrations and deflections that can affect dimensional accuracy and surface finish. Machine maintenance and setup play a significant role in achieving optimal results.
7. Material Considerations
Different materials exhibit varying machinability characteristics. Understanding the material's properties, such as hardness, tensile strength, and thermal conductivity, is essential for selecting the appropriate tools and cutting parameters.
8. Surface Finish Requirements
Depending on the application, the surface finish of the slot may be critical. Achieving the desired finish may involve adjusting cutting parameters, tool selection, or incorporating secondary finishing processes.
By paying attention to these key features, CNC machining professionals can optimize the slot milling process to produce high-quality parts efficiently and consistently.
Executing a successful slot milling operation requires careful planning and adherence to a systematic process. Below are step-by-step instructions that guide you through the slot milling process, ensuring precision, efficiency, and safety.
Step 1: Select a Cutter
Choosing the right cutter is the foundation of a successful slot milling operation.
Step 2: Select Cutting Parameters
Optimizing cutting parameters is critical for tool life and part quality.
Step 3: Secure the Workpiece
Proper fixturing ensures safety and precision.
Step 4: Position the Cutter
Accurate positioning is essential for dimensional accuracy.
Step 5: Start Cutting
Begin the machining operation with caution.
Step 6: Complete Cutting
Ensure the slot is machined to specifications.
Step 7: Release and Inspect Parts
After machining, carefully remove and inspect the workpiece.
By following these steps meticulously, you can achieve precise and high-quality slots in your CNC milling operations, enhancing the overall quality of your CNC milling parts.
Slot milling encompasses various techniques and tools tailored to specific applications and requirements. Understanding the different types allows machinists and engineers to select the most appropriate method for their project, optimizing efficiency and quality in custom CNC machining.
End Milling
End milling is a versatile technique where an end mill cutter removes material to create slots, contours, and profiles.
Tools Used: End mills with flat or ball noses.
Applications:
Advantages:
Considerations:
Face Milling
Face milling involves cutting with the face of the cutter to produce flat surfaces, but it can also be adapted for slot milling in specific situations.
Tools Used: Face mills with multiple cutting edges.
Applications:
Advantages:
Considerations:

Side Milling
Side milling involves using the side of the cutter to remove material, which is particularly useful for creating slots and grooves along the side of a workpiece.
Tools Used: Side milling cutters or slab mills.
Applications:
Advantages:
Considerations:
T-Slots
T-slot milling involves creating T-shaped slots commonly found in machine tool tables and fixtures.
Tools Used: T-slot cutters with a specific profile resembling an inverted 'T'.
Applications:
Advantages:
Considerations:
Slotting Keys
Slotting keys, or keyway milling, involves creating slots for keys used in mechanical power transmission components like shafts and gears.
Tools Used: Woodruff keyseat cutters, end mills.
Applications:
Advantages:
Considerations:
Gang Milling
Gang milling involves the use of multiple cutters mounted on the same arbor to machine several surfaces simultaneously.
Tools Used: Multiple side and face cutters or staggered tooth cutters.
Applications:
Advantages:
Considerations:
By understanding these slot milling techniques and the tools associated with them, machinists can select the optimal approach for their specific application, ensuring high-quality results in CNC machining services.
Groove milling, a subset of slot milling, involves creating grooves or channels in a workpiece. These features are essential in various industries and applications, contributing to the functionality and assembly of components. Below are some common applications of groove milling in different sectors.
Groove milling is critical in the manufacturing of gears, where precise slots and grooves are required for proper meshing and torque transmission.
Applications:
Importance:

Tools and Fixtures
In the creation of tools and fixtures, groove milling enables the production of features that facilitate assembly and functionality.
Applications:
Importance:
The electronics industry relies on groove milling for producing components that require precise channels and slots.
Applications:
Importance:

Medical device manufacturing demands high precision and quality, where groove milling plays a vital role.
Applications:
Importance:

Aircraft Parts
The aerospace industry utilizes groove milling for components that require lightweight and robust designs.
Applications:
Importance:
In automotive manufacturing, groove milling contributes to the production of parts essential for vehicle operation.
Applications:
Importance:

General Manufacturing
Beyond specialized industries, groove milling is fundamental in general manufacturing for creating functional features.
Applications:
Importance:
Groove milling's wide-ranging applications highlight its significance in modern manufacturing. Mastery of groove milling techniques enables CNC machining services to meet the varied demands of different industries, delivering precise and functional components.
Achieving optimal results in slot milling requires not only the right tools and equipment but also adherence to best practices and techniques. Below are valuable tips and practices that can enhance the efficiency, quality, and longevity of your slot milling operations.
Ramp Down Entry
Entering the material gradually can reduce stress on the tool and improve surface finish.
Technique:
Benefits:
Implementation:
Chip Evacuation is Key
Efficient removal of chips is critical in slot milling to prevent tool damage and ensure quality.
Challenges:
Solutions:
Maintain Spindle Load
Keeping the spindle load consistent ensures stable cutting conditions.
Importance:
Strategies:
Climb Milling
Choosing the right milling direction can impact tool life and finish.
Climb Milling:
Advantages:
Considerations:
Select a Larger Tool Diameter
Using a larger diameter tool can enhance machining performance.
Benefits:
Limitations:
Optimize Feed Rates
Adjusting feed rates according to cutting conditions can improve efficiency and quality.
Factors to Consider:
Techniques:
By incorporating these tips and practices into your slot milling operations, you can enhance productivity, reduce costs, and achieve superior results in your CNC milling parts.
The cutter path in slot milling significantly influences machining efficiency, tool life, and part quality. Different techniques can be employed depending on the material, machine capabilities, and desired outcomes. Below are common cutter path strategies used in slot milling.
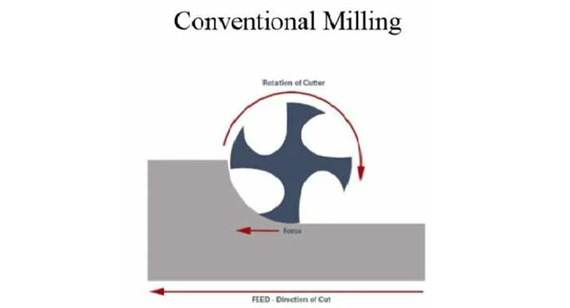
Conventional Milling
Conventional milling, also known as up milling, involves feeding the workpiece against the rotation of the cutter.
Characteristics:
Advantages:
Disadvantages:
Trochoidal Milling
Trochoidal milling is an advanced technique where the cutter moves in a series of circular arcs, allowing for constant engagement with the material.
Characteristics:
Advantages:
Disadvantages:
Plunge Milling
Plunge milling, or zig-zag milling, involves plunging the cutter vertically into the material and then moving laterally to remove material.
Characteristics:
Advantages:
Disadvantages:
By selecting the appropriate cutter path technique, machinists can optimize the slot milling process for their specific application, balancing factors like efficiency, tool life, and surface quality in custom CNC machining.
Understanding the advantages and disadvantages of slot milling helps manufacturers make informed decisions about employing this process in their CNC machining services. While slot milling offers numerous benefits, it also presents certain challenges that must be managed effectively.
Advantages of Slot Milling
1. Versatility
2. Precision and Accuracy
3. Efficiency
4. Surface Finish
5. Cost-Effectiveness
Disadvantages of Slot Milling
1. Tool Wear and Breakage
2. Chip Evacuation Challenges
3. Machine Requirements
4. Complexity of Setup
5. Limitations on Slot Dimensions
Conclusion on Advantages and Disadvantages
While slot milling offers significant benefits in terms of versatility, precision, and efficiency, it requires careful consideration of tooling, machine capabilities, and process parameters. By understanding and addressing the potential disadvantages, manufacturers can effectively leverage slot milling in their CNC machining factories to produce high-quality components.
Slot milling is a fundamental and versatile process in CNC milling that enables the creation of precise slots, grooves, and pockets essential for the functionality of countless components across various industries. By comprehending the types of slot milling techniques and tools, following systematic step-by-step procedures, and applying best practices and tips, manufacturers can enhance the quality and efficiency of their CNC milling parts.
The advantages of slot milling, such as precision, versatility, and efficiency, make it an indispensable process in custom CNC machining and CNC machining services. However, it's crucial to be mindful of the potential challenges, including tool wear and chip evacuation issues, to mitigate risks and optimize operations.
By integrating the knowledge and insights from this comprehensive guide into your machining practices, you can improve your slot milling operations, deliver superior products, and maintain a competitive edge in the field of CNC metal machining.
What Is the Difference Between Face Milling and Slot Milling?
Face milling and slot milling are two distinct milling operations with different objectives:
Face Milling:
Slot Milling:
The main difference lies in the direction of the cut and the type of surface being machined. Face milling targets external surfaces, while slot milling focuses on internal features.
What Is the Difference Between Slot Milling and Perimeter Milling?
Slot milling and perimeter milling are both used to shape workpieces but serve different purposes:
Slot Milling:
Perimeter Milling:
The key difference is that slot milling removes material from within the workpiece, whereas perimeter milling defines the outer shape.
What Are the Common Materials Compatible with Slot Milling?
Slot milling is compatible with a wide range of materials, including:
Metals:
Plastics:
Composites:
Material selection impacts tool choice, cutting parameters, and machining strategies.
What Machines Can Be Used for Slot Milling?
Slot milling can be performed on various milling machines, including:
The choice of machine depends on factors like the size of the workpiece, complexity of the slot, and production volume.
What Materials Can Be Slot Milled?
Materials that can be slot milled include:
The machinability of the material influences the selection of tools and cutting parameters.
What Types of Tools Are Used for Slot Milling?
Various tools are used in slot milling, including:
Tool selection depends on the slot geometry, material, and desired surface finish.
What Are the Common Tools for Slotting Operations?
Common tools for slotting include:
Choosing the right tool is critical for efficiency and quality in slot milling operations.
Are CNC Machines Suitable for Slot Milling?
Yes, CNC machines are highly suitable for slot milling due to:
CNC milling machines are widely used in custom CNC machining and CNC machining factories for slot milling applications.
By mastering slot milling and leveraging the right tools, techniques, and knowledge, you can enhance your CNC milling operations, produce high-quality parts, and meet the diverse needs of industries relying on precise and functional components.
