15 years one-stop China custom CNC machining parts factory
The VMT blog is dedicated to sharing our hard-earned knowledge in prototype manufacturing. We hope these articles will help you optimize your product designs and gain deeper insight into the world of rapid prototyping. Enjoy the read!
Get an Instant Quote VMT
VMT  2025 06 26
2025 06 26 A milling machine is a precision tool used in CNC machining services to cut, shape, and drill solid materials like metal, plastic, and wood. Using rotary cutters, it removes material to achieve complex geometries and tight tolerances, making it vital for industries such as aerospace, automotive, medical, and mold making.
 66
66
 Read more
Read more
 VMT
VMT  2025 06 25
2025 06 25 Tungsten does not rust under normal atmospheric conditions due to its high density, corrosion resistance, and stable chemical structure. It forms a protective oxide layer instead of rusting, making it ideal for CNC machining parts in extreme environments.
 66
66
 Read more
Read more
 VMT
VMT  2025 06 24
2025 06 24 3Cr13 stainless steel is a martensitic stainless steel with 13% chromium and 0.3% carbon, offering good corrosion resistance, moderate hardness, and excellent machinability. It is widely used in CNC machining factories to produce cost-effective components like blades, surgical tools, and industrial machine parts.
 66
66
 Read more
Read more
 VMT
VMT  2025 06 20
2025 06 20 Tungsten metal is a dense, high-strength material known for its exceptional heat resistance, durability, and conductivity. It is widely used in CNC machining parts, aerospace components, medical tools, and electronics. Its high melting point and hardness make it ideal for precision applications, and it’s commonly processed by advanced CNC machining services in modern factories.
 66
66
 Read more
Read more
 VMT
VMT  2025 06 19
2025 06 19 Titanium and tungsten differ in weight, hardness, corrosion resistance, and application suitability. Titanium is lighter and corrosion-resistant, ideal for aerospace and medical use. Tungsten is denser and harder, perfect for high-wear tools and radiation shielding. Choosing the right metal depends on your CNC machining goals and performance requirements.
 66
66
 Read more
Read more
 VMT
VMT  2025 06 18
2025 06 18 CNC machining programming is the process of creating code instructions that direct CNC machines to manufacture parts with precision and efficiency. It includes part design, tool path planning, code generation, and machine setup. This programming is essential for consistent, high-quality results in CNC machining services and manufacturing operations.
 66
66
 Read more
Read more
 VMT
VMT  2025 06 14
2025 06 14 G-code in CNC machining controls the movement of machines. It consists of various commands that guide processes like drilling, turning, and milling. Key commands like G00, G01, and G02 are used to direct rapid movement, linear interpolation, and circular motion. Knowing these commands ensures better efficiency in CNC machining services.
 66
66
 Read more
Read more
 VMT
VMT  2025 06 13
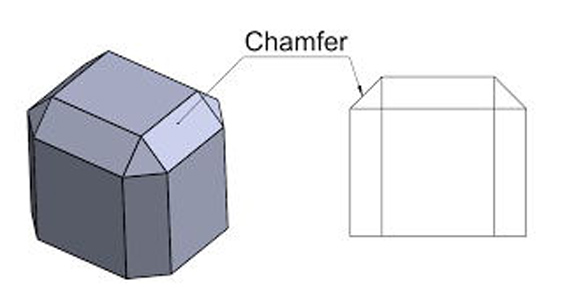
2025 06 13 A chamfer is a beveled edge that replaces a 90-degree corner on a machined part, created to reduce sharp edges, improve assembly, and enhance durability. Chamfering in CNC machining is essential for stress relief, safety, precision, and aesthetics, and it is achieved using specialized tools or multi-axis CNC machining services.
 66
66
 Read more
Read more
Ready To Start Your Next Project?
Get Instant Quote

Request a Free Quote
Send us a message if you have any questions or request a quote. We will get back to you ASAP!