15 years one-stop China custom CNC machining parts factory
 139 |
Published by VMT at Mar 11 2025 | Reading Time:About 6 minutes
139 |
Published by VMT at Mar 11 2025 | Reading Time:About 6 minutes
In today's advanced manufacturing industries, achieving high-precision, strong, and reliable welds is essential. Traditional welding methods often lead to excessive heat input, material distortion, and a need for post-processing. These challenges make laser welding a game-changer, offering unmatched speed, accuracy, and efficiency for a wide range of materials.
But what exactly is laser welding, and how does it compare to traditional techniques? Whether you're a manufacturer, engineer, or CNC machining expert, understanding the laser welding process, materials, and benefits is key to achieving superior results.
Laser welding is a high-precision process that delivers strong, clean welds with minimal heat input and distortion, making it ideal for industries like aerospace, medical, and automotive manufacturing.
Now, let’s explore how laser welding works, its advantages, suitable materials, and its growing applications in CNC machining and industrial production.
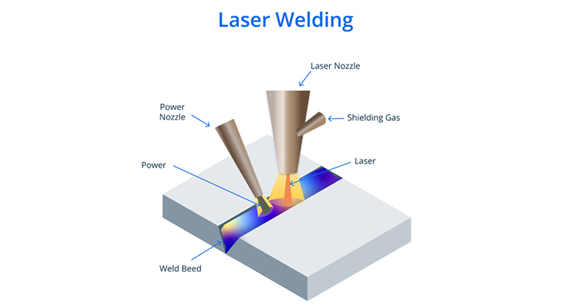
Laser welding is a high-precision joining process that uses a focused laser beam to melt and fuse materials together. Unlike traditional welding methods that require an electrode or filler material, laser welding relies on intense heat concentration to create a seamless bond.

How It Works:
Laser welding is known for its high precision, minimal heat-affected zones, and ability to weld delicate or complex components.
In the ever-evolving world of manufacturing and CNC machining, industries demand faster, more precise, and highly efficient welding techniques. Traditional welding methods, while effective, often lead to excessive heat input, material distortion, and longer production times.
This is where laser welding revolutionizes the industry—offering exceptional precision, high-speed processing, and minimal heat-affected zones. It is widely adopted in aerospace, automotive, medical, and electronic industries due to its ability to produce clean, reliable, and repeatable welds.
Laser welding surpasses traditional methods by delivering high-speed, precision welds with minimal heat distortion, making it ideal for advanced manufacturing.
Let’s explore the key advantages of laser welding and how it has transformed modern manufacturing.
1. High Precision and High Repeatability
Laser welding delivers ultra-precise welds, ensuring consistent results in high-tech industries.
2. Fast Welding Speed
Laser welding enhances production speed, making it perfect for high-volume manufacturing.
3. Low Heat Input and Minimal Distortion
Laser welding ensures minimal heat distortion, preserving material integrity.
4. High Welding Quality
Laser welding produces high-quality, clean welds with minimal finishing required.
5. Less Maintenance Required
Laser welding reduces maintenance costs, improving overall operational efficiency.
6. Easy to Automate
Laser welding supports full automation, making it the future of precision manufacturing.
Early Development of Laser Technology
The concept of laser welding can be traced back to the 1960s, following the invention of the first functional laser by Theodore Maiman in 1960. As scientists explored industrial applications for lasers, they discovered that high-intensity laser beams could melt and fuse materials together.
Key Milestones in Laser Welding Technology
1960s – Early Laser Research
1970s – Laser Welding for Aerospace and Automotive
1980s – Advancements in CO₂ and Fiber Lasers
1990s – Adoption of Automated Laser Welding
2000s–2020s – Modern Fiber Laser Welding
Laser welding has evolved into a highly advanced, automated, and efficient process, transforming modern manufacturing.
Laser welding is a versatile and highly efficient joining process used across various industries. However, not all materials respond the same way to laser welding. Factors such as reflectivity, thermal conductivity, and absorption rate influence how well a material can be welded.
By selecting the right material and laser parameters, manufacturers can achieve strong, precise, and defect-free welds.
Metallic Materials Suitable for Laser Welding
Laser welding is widely used for metal CNC machining parts due to its ability to create strong, clean welds with minimal distortion. However, each metal has different properties that affect its weldability.
1. Aluminum
Challenges:
Solutions:
Common Applications:
Aluminum can be successfully laser welded using high-power fiber lasers and optimized welding parameters.

2. Copper
Challenges:
Solutions:
Common Applications:
Copper requires specialized laser settings but can be effectively welded using advanced laser technologies.

3. Brass
Challenges:
Solutions:
Common Applications:
Brass can be laser welded with controlled parameters and proper laser beam adjustments.

4. Steel (Carbon & Stainless Steel)
Advantages:
Common Applications:
Steel is highly suitable for laser welding and widely used in various industries.

5. Titanium
Advantages:
Challenges:
Common Applications:
Titanium welds exceptionally well with laser welding, provided it is properly shielded from oxygen exposure.

6. Nickel and Nickel Alloys
Advantages:
Common Applications:
Nickel-based materials are well-suited for laser welding in high-temperature applications.
Plastic Materials Suitable for Laser Welding
Laser welding is not limited to metals—it is also used for plastic joining in industries like medical devices, electronics, and automotive manufacturing.
Unlike metals, plastics require specialized transmission welding techniques, where the laser beam passes through a transparent layer to heat and bond the underlying plastic layer.
1. Polycarbonate (PC)
Advantages:
Common Applications:
Polycarbonate is widely used in laser welding due to its strength and transparency to certain laser wavelengths.

2. Nylon (Polyamide, PA)
Advantages:
Common Applications:
Nylon is well-suited for laser welding in high-performance applications.

3. ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene)
Advantages:
Common Applications:
ABS is a popular choice for laser-welded plastic components in mass production.

Conclusion: Selecting the Right Materials for Laser Welding
With the right laser type and welding parameters, manufacturers can achieve high-quality, defect-free welds across various materials.
Need expert CNC machining or laser welding services? Contact us for high-precision solutions!
Laser welding is a high-precision process that offers fast, clean, and strong welds in various industries, from aerospace and automotive to medical and CNC machining. However, the success of laser welding depends on multiple factors, including material properties, heat management, and operator expertise.
Understanding these factors is essential for optimizing weld quality, preventing defects, and ensuring a reliable, long-lasting joint.
The effectiveness of laser welding is influenced by material properties, thermal behavior, operator experience, and the choice of laser type. Properly managing these factors ensures high-quality welds with minimal defects.
Let’s explore these factors in detail and how they impact the performance and efficiency of laser welding.
Material Properties Affecting Laser Welding
Not all materials respond to laser welding the same way. The chemical composition, thermal behavior, and surface characteristics of a material determine how well it absorbs laser energy and forms a strong weld.
1. Melt Temperature
Choosing the correct laser power for the material's melting temperature ensures optimal fusion without defects.
2. Albedo (Reflectivity of the Material)
Highly reflective metals, like aluminum, copper, and brass, pose challenges in laser welding because they reflect much of the laser energy instead of absorbing it.
Solutions to improve laser absorption include:
Materials with high reflectivity require specialized laser sources and optimized process parameters to improve absorption.
3. Thermal Conductivity
Materials with high thermal conductivity need precise energy control to prevent heat loss and ensure deep penetration.
Operator Experience and Process Control
Even with advanced laser welding technology, operator expertise plays a crucial role in determining weld quality.
1. Laser Welding Parameters and Setup
Operators must carefully adjust:
Incorrect parameter settings can lead to:
Skilled operators fine-tune laser settings to achieve defect-free welds with strong joint integrity.
2. Joint Design and Fit-Up Precision
Proper joint preparation ensures even heat distribution and strong weld integrity.
3. Shielding Gas Selection
Shielding gas (like argon, helium, or nitrogen) is essential for preventing oxidation and contamination in laser welding.
Choosing the right gas depends on the material:
Proper shielding gas selection prevents oxidation, porosity, and weld contamination.
Conclusion: Optimizing Laser Welding for Superior Results
By optimizing these factors, manufacturers can achieve stronger, cleaner, and more reliable laser welds, enhancing productivity and product performance.
Looking for precision CNC machining and laser welding services? Contact us today for expert solutions!
Laser welding is a high-precision process that relies on advanced welding equipment, automation, and Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM) systems to achieve consistent, high-quality welds. Unlike traditional welding methods, laser welding requires specialized machinery capable of focusing high-intensity beams with pinpoint accuracy.
With the rise of automation in CNC machining and manufacturing, robotic laser welding systems have become increasingly popular. The selection of laser types (solid-state, gas, fiber lasers), automation tools, and control systems plays a critical role in determining weld quality, efficiency, and repeatability.
Choosing the right laser welding equipment ensures strong, precise, and defect-free welds while optimizing production efficiency.
Now, let’s dive into the key components of laser welding equipment and their significance.
Automation and CAM in Laser Welding
Automation and Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM) have revolutionized laser welding by reducing human error, improving consistency, and increasing production speed.
1. Robotic Welding Systems
2. CNC-Integrated Laser Welding
3. Automated Quality Control
Automation and CAM ensure precision, consistency, and higher productivity in laser welding.
Lasers Used in Welding: Key Technologies
Laser welding systems rely on various types of lasers, each suited for different materials and applications.
1. Solid-State Lasers
What Are Solid-State Lasers?
Types of Solid-State Lasers Used in Welding:
Nd:YAG (Neodymium-doped Yttrium Aluminum Garnet) Lasers:
Disk Lasers:
Solid-state lasers are powerful and precise, making them ideal for deep-penetration welding.

2. Gas Lasers
What Are Gas Lasers?
Types of Gas Lasers Used in Welding:
CO₂ (Carbon Dioxide) Lasers:
Gas lasers, especially CO₂ lasers, are excellent for welding metals but require proper energy control.
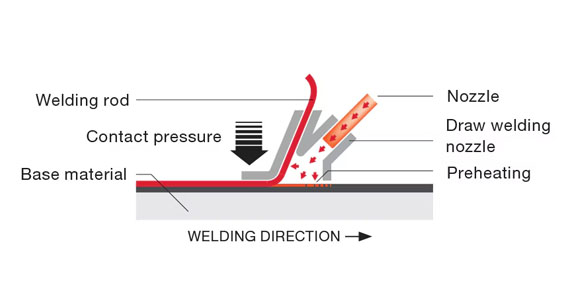
3. Fiber Lasers
What Are Fiber Lasers?
Advantages of Fiber Lasers for Welding:
Fiber lasers are the most advanced and widely used laser welding technology due to their efficiency and precision.

Conclusion: Selecting the Right Laser Welding Equipment
By selecting the right laser technology and automation tools, manufacturers can achieve highly precise, strong, and defect-free welds for a wide range of materials and applications.
Need expert CNC machining and laser welding services? Contact us for high-precision manufacturing solutions!
Laser welding is an advanced high-precision welding method, but it also poses serious safety risks if proper precautions are not taken. The high-intensity laser beam, UV radiation, and hot metal splatter can cause eye injuries, skin burns, and respiratory hazards.
Wearing the correct safety gear is crucial for protecting workers from potential hazards associated with laser welding.
Here’s a breakdown of the essential personal protective equipment (PPE) for laser welding operators.
Essential Safety Gear for Laser Welding
1. Laser Safety Glasses
2. Heat-Resistant Gloves
3. Flame-Resistant Welding Clothing
4. Respiratory Protection (If Necessary)
Proper PPE ensures laser welding operators stay protected from eye damage, burns, and inhalation hazards.
Laser welding relies on different laser sources, each suited for specific materials and applications. The three most commonly used laser types are CO₂ lasers, Nd:YAG lasers, and fiber lasers.
1. CO₂ (Carbon Dioxide) Lasers
What Are CO₂ Lasers?
Advantages of CO₂ Lasers:
Disadvantages of CO₂ Lasers:
CO₂ lasers are excellent for deep-penetration welding but are gradually being replaced by fiber lasers due to efficiency.
2. Nd:YAG (Neodymium-Doped Yttrium Aluminum Garnet) Lasers
What Are Nd:YAG Lasers?
Advantages of Nd:YAG Lasers:
Disadvantages of Nd:YAG Lasers:
Nd:YAG lasers are widely used in precision applications but are being replaced by fiber lasers for higher efficiency.
3. Fiber Lasers
What Are Fiber Lasers?
Advantages of Fiber Lasers:
Disadvantages of Fiber Lasers:
Fiber lasers are the most advanced and efficient laser welding technology, making them the preferred choice for precision CNC machining.
4. Disk Lasers
What Are Disk Lasers?
Advantages of Disk Lasers:
Disadvantages of Disk Lasers:
Disk lasers are ideal for high-precision, high-power applications but remain less common than fiber lasers.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Laser for Welding
Choosing the right laser type depends on the material, application, and precision requirements in CNC machining and manufacturing.
Looking for high-quality CNC machining and laser welding solutions? Contact us today for expert guidance!
Laser welding is a high-precision process used across industries like aerospace, automotive, medical, and CNC machining. Unlike traditional welding, laser welding focuses a high-energy beam to create strong, clean, and precise welds with minimal heat distortion.
However, achieving a defect-free laser weld requires careful preparation, correct beam adjustments, and post-weld cooling. By following a structured step-by-step approach, manufacturers can ensure strong weld integrity and repeatability in production.
To achieve a high-quality laser weld, proper part cleaning, fixture setup, beam focusing, power adjustment, and controlled cooling are essential.
Let’s go through each step of the laser welding process in detail.
1. Cleaning the Parts to Be Welded
Why is Cleaning Important?
How to Clean the Parts?
Proper cleaning ensures optimal laser energy absorption and strong weld formation.
2. Manual and Automatic Fixtures to Hold the Parts
Why Are Fixtures Necessary?
Types of Fixtures for Laser Welding
Best Practices for Fixturing:
Using precision fixtures improves welding accuracy, consistency, and repeatability.
3. Focus the Beam on the Weld Area
Why Is Beam Focus Important?
How to Adjust Beam Focus?
Precise beam focusing ensures proper weld depth and strength.
4. Adjust the Power of the Beam
Why Is Power Adjustment Important?
Factors Affecting Power Settings:
Optimizing laser power ensures a balance between strong weld penetration and minimal heat distortion.
5. Aim the Beam at the Starting Point of the Weld Area
Why Is the Starting Point Important?
How to Ensure Proper Beam Alignment?
Proper beam aiming prevents irregular welds and ensures a clean start.
6. After Welding, Let the Parts Cool Naturally
Why Is Controlled Cooling Important?
Best Practices for Post-Weld Cooling:
Gradual cooling preserves weld strength and prevents thermal cracking.
Conclusion: Following the Correct Laser Welding Steps Ensures High-Quality Welds
By following these laser welding steps, manufacturers can achieve precise, reliable, and defect-free welds in CNC machining and industrial applications.
Need high-quality CNC machining and laser welding services? Contact us today for expert solutions!
Laser welding has become a cornerstone of modern manufacturing, offering high precision, minimal heat distortion, and automation compatibility. Due to its ability to weld metals and plastics with micron-level accuracy, it is widely used across high-tech industries such as aerospace, medical, automotive, and electronics.
Industries that require strong, lightweight, and defect-free welds rely on laser welding to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance product quality.
Laser welding is widely used in aerospace, medical, industrial, optical, and electronic manufacturing, thanks to its high precision and automation capabilities.
Let’s explore the key industries that benefit from laser welding and how it transforms production.
1. Aerospace Industry
Why Laser Welding Is Essential for Aerospace Manufacturing:
Common Aerospace Applications of Laser Welding:
Laser welding in aerospace improves fuel efficiency, component longevity, and overall flight safety.
Why Laser Welding Is Used in Medical Devices:
Common Medical Applications of Laser Welding:
Laser welding provides high precision and biocompatibility, making it ideal for medical device manufacturing.
3. Optical Industry
Why Laser Welding Is Used in Optical Manufacturing:
Common Optical Applications of Laser Welding:
Laser welding enables high-precision, contamination-free optical component manufacturing.
4. Industrial and Heavy Machinery Manufacturing
Why Laser Welding Is Used in Industrial Machinery:
Common Industrial Applications of Laser Welding:
Laser welding increases efficiency and durability in industrial machinery production.
Why Laser Welding Is Critical in Electronics Manufacturing:
Common Electronics Applications of Laser Welding:
Laser welding is indispensable in the miniaturization and precision manufacturing of electronics.
Why Laser Welding Is a Game-Changer for Automotive Manufacturing:
Common Automotive Applications of Laser Welding:
Laser welding improves vehicle safety, fuel efficiency, and production speed.
7. Other Industries Benefiting from Laser Welding
Defense and Military Applications
Jewelry and Luxury Goods
Watchmaking and Precision Mechanics
Laser welding is a transformative technology used in diverse industries, from luxury goods to military defense.
Conclusion: Why Laser Welding Is the Future of Manufacturing
Looking for expert CNC machining and laser welding solutions? Contact us today for precision manufacturing!
Laser welding has emerged as a game-changing technology across industries, offering unmatched precision, speed, and efficiency. Unlike traditional welding methods, which can introduce excessive heat, distortion, and inconsistencies, laser welding provides clean, strong, and defect-free welds with minimal thermal impact.
Key Takeaways from Laser Welding
Seamless Integration with CNC Machining – Laser welding can be fully automated and integrated into CNC machining systems, further enhancing repeatability and efficiency.
The Future of Laser Welding
As manufacturers continue to prioritize automation, lightweight materials, and high-precision fabrication, laser welding will play an even bigger role in next-generation industries. From electric vehicles and renewable energy to advanced robotics and aerospace exploration, laser welding is paving the way for smarter, faster, and more sustainable production methods.
Whether in aerospace, medical, automotive, or industrial CNC machining, laser welding is the future of high-quality manufacturing.
Looking for expert CNC machining and laser welding solutions? Contact us today for custom precision manufacturing!
Here are answers to the most frequently asked questions about laser welding, covering strength, cost, applications, safety, and technology.
1. Is laser welding as strong as MIG?
Yes, laser welding can be as strong or even stronger than MIG (Metal Inert Gas) welding in many applications. Laser welding creates deep penetration welds with minimal heat distortion, making it ideal for thin materials, precision components, and high-strength joints. However, MIG welding is better suited for thicker materials and structural applications.
2. Does laser welding really work?
Yes! Laser welding is widely used across industries, including aerospace, automotive, electronics, and medical devices. The process produces high-strength, defect-free welds with minimal heat input, reducing warping and improving product longevity.
3. What is the laser welding process?
The laser welding process involves:
Laser welding is a fast, precise, and automated process for joining materials with minimal distortion.
4. Are laser welds stronger than stick welds?
Yes, in many cases, laser welds can be stronger than traditional stick welding (SMAW – Shielded Metal Arc Welding). Laser welding:
For precision applications, laser welding can offer stronger and cleaner welds than stick welding.
5. Will laser welding replace TIG welding?
Not entirely. TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) welding is still preferred for manual welding of thin metals, but laser welding is increasingly replacing TIG welding in automated and precision applications.
Advantages of Laser Welding over TIG Welding:
Laser welding is becoming the preferred choice for high-precision manufacturing, but TIG welding remains useful for manual and artistic applications.
6. What are the problems with laser welding?
While laser welding offers many benefits, it also has challenges:
Despite these challenges, laser welding is the best option for high-precision, automated manufacturing.
7. Is laser welding expensive?
Yes, laser welding can be costly, mainly due to:
However, long-term savings on labor, material efficiency, and defect reduction make it cost-effective for mass production.
For high-precision, high-volume production, laser welding offers excellent ROI despite its initial cost.
8. What are the dangers of laser welding?
Laser welding poses several safety risks, including:
Solution: Operators must use laser safety glasses, protective clothing, fume extraction, and proper shielding.
With the right safety precautions, laser welding is safe for industrial use.
9. What is the service life of a laser welding machine?
A well-maintained fiber laser welding machine lasts 50,000 – 100,000 hours, while CO₂ lasers last about 10,000 – 20,000 hours.
Regular maintenance ensures long service life and optimal performance.
10. Does a laser welder require gas?
Yes, most laser welding processes use shielding gases (argon, helium, or nitrogen) to:
Gas selection depends on the material and welding process.
11. How thick steel can a laser welder weld?
Laser welding works best on thin to medium-thickness metals (up to 10mm).
Laser welding is ideal for thin and precision components but has limitations with very thick steel.
12. What is the price of a laser welding machine?
Laser welding machines range from $20,000 to $500,000+, depending on power, automation, and brand.
Investment in laser welding depends on production needs and material types.
13. Which weld has the highest strength?
Electron beam welding (EBW) produces the highest-strength welds, followed by laser welding and friction stir welding.
Laser welding offers excellent strength with minimal defects.
14. What are the advantages of laser welding?
Laser welding is the future of high-efficiency, high-precision manufacturing.
15. What is the most advanced type of welding?
The most advanced welding methods include:
Laser welding is one of the most advanced and widely used precision welding technologies.
Conclusion: Laser Welding Is the Future of Precision Welding
Laser welding is transforming CNC machining, aerospace, medical, and electronics industries with its high-speed, high-precision, and automation capabilities. While it has higher initial costs, the benefits of stronger, cleaner, and faster welds make it a preferred choice for modern manufacturing.
Looking for expert CNC machining and laser welding solutions? Contact us today!
