15 years one-stop China custom CNC machining parts factory
 1318 |
Published by VMT at Feb 27 2025 | Reading Time:About 6 minutes
1318 |
Published by VMT at Feb 27 2025 | Reading Time:About 6 minutes
Plastic welding is one of the most effective methods used to join plastic materials together. But with so many different techniques available, it can be difficult to choose the best one for your project. Are you struggling to find the most suitable welding method for your plastic welding CNC machining parts? Whether you are working on custom CNC machining parts, prototypes, or even large-scale manufacturing, understanding the different plastic welding methods can significantly improve your results. In this article, we’ll explore 10 welding technologies and their advantages, so you can make an informed decision based on your specific needs. Read on to learn more about the techniques that can make your next project a success.
There are 10 major methods for plastic welding, each with its own set of advantages. These techniques include ultrasonic welding, laser welding, friction welding, and more. Understanding which welding method is best suited for your application—whether for plastic welding CNC machining parts or custom CNC machining projects—can help streamline the process and improve the final result. Continue reading to discover each method and how it can benefit your projects.
Now that we've introduced the various methods of plastic welding, let’s dive deeper into each technique, explaining their unique advantages and how they work. Whether you need to weld large plastic components for automotive use or are producing smaller, more intricate plastic parts, this guide will help you navigate the different options available. Let’s start with one of the most common methods: ultrasonic welding.
Plastic welding is the process of joining plastic materials by applying heat or pressure to form a bond between the pieces. It is used in a variety of industries, including aerospace, automotive, marine, and manufacturing. Plastic welding allows manufacturers to create custom CNC machining parts that are durable, reliable, and cost-effective. Unlike traditional adhesive bonding or mechanical fastening, plastic welding creates permanent, seamless joins that improve the integrity and functionality of plastic components.

Step 1: Set Up Your Workspace and Clean the Plastic
Before starting the welding process, it’s essential to clean the plastic pieces that need to be joined. Any dirt, oil, or contaminants on the plastic can affect the quality of the weld. Setting up a clean workspace will help ensure that the plastic is free from contaminants that could interfere with the welding process. Additionally, ensuring that your equipment is in good working order is essential for safety and precision.
Step 2: Join the Plastic
Once the workspace is set up and the plastic is cleaned, it’s time to apply heat, pressure, or both, depending on the type of welding method used. The plastic pieces are then held together using a welding tool or press, which provides the force necessary for the materials to bond. Proper alignment of the pieces is essential to create a strong, lasting weld.
Step 3: Complete the Weld
After applying the necessary heat or pressure, the weld is allowed to cool and solidify. Depending on the method used, the cooling time will vary. It’s crucial to allow the weld to fully solidify before moving on to the next phase of production to ensure the bond is strong and secure.
Plastic welding is an essential process in various industries such as automotive, medical, and manufacturing. It is used to join plastic components through heat, pressure, or both, forming a strong and permanent bond. Choosing the appropriate welding method depends on factors like material type, part size, and the specific needs of the project. Here are 10 different methods for welding plastics, along with their advantages and disadvantages.
Plastic welding is a versatile and efficient process for joining plastic parts. With various methods available, each offering unique benefits, it’s important to understand the specific applications and limitations of each welding technique. Whether you are working with thin or thick materials, understanding these techniques will help ensure that you achieve the best results. In this guide, we explore 10 common plastic welding methods, detailing how they work, their advantages, and their drawbacks.
Ultrasonic Welding
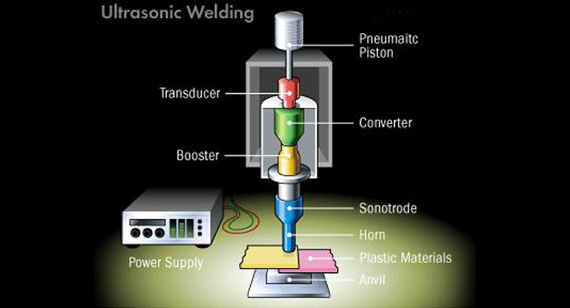
What is Ultrasonic Welding?
Ultrasonic welding uses high-frequency sound waves to generate heat at the interface of two plastic parts. The ultrasonic vibrations cause the material to melt, and pressure is applied to join the parts together. It is widely used for thermoplastics such as polypropylene and polyethylene.
Advantages of Ultrasonic Welding
Disadvantages of Ultrasonic Welding
Laser Welding

What is Laser Welding?
Laser welding uses a focused laser beam to melt and join plastic parts. The precise energy from the laser beam melts the plastic, allowing the parts to fuse together. Laser welding is especially effective for joining clear plastics and is commonly used in the medical and automotive industries.
Advantages of Laser Welding
Disadvantages of Laser Welding
Friction Welding
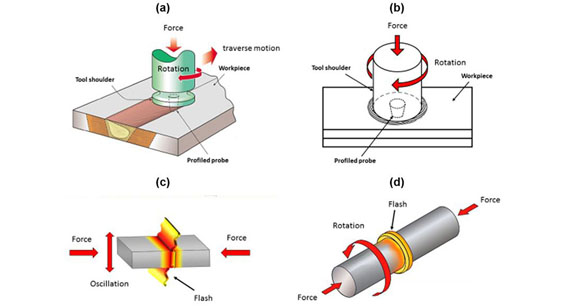
What is Friction Welding?
Friction welding involves generating heat by rubbing two plastic parts together at high speed. The friction creates heat at the interface, which melts the plastic, allowing it to fuse. There are two primary types of friction welding: Continuous Induction Friction Welding and Inertia Friction Welding.
Advantages of Friction Welding
Disadvantages of Friction Welding
High Frequency Welding
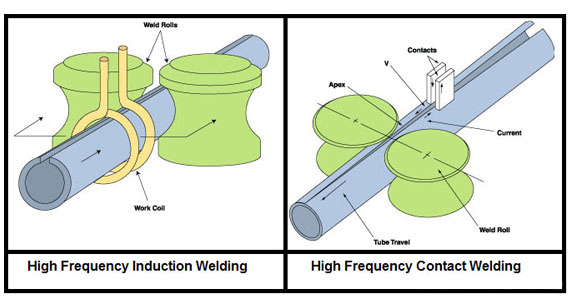
What is High Frequency Welding?
High-frequency welding uses electromagnetic waves to generate heat within the plastic material. These waves cause the plastic to heat up and melt at the interface, allowing the parts to be fused together. It is mainly used for PVC and other thermoplastics.
Advantages of High Frequency Welding
Disadvantages of High Frequency Welding
Vibration Welding
What is Vibration Welding?
Vibration welding uses high-frequency vibrations applied to the plastic parts while pressure is applied. The vibrations generate heat through friction, causing the plastic to melt and join. There are two types of vibration welding: Linear Vibration Welding and Orbital Vibration Welding.
Advantages of Vibration Welding
Disadvantages of Vibration Welding
Hot Plate Welding
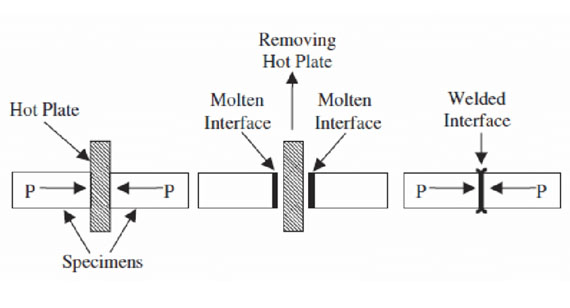
What is Hot Plate Welding?
Hot plate welding involves heating the surfaces of two plastic parts using a heated plate. Once the plastic parts are soft enough, they are pressed together to form a strong bond. It is widely used for larger, thicker plastic parts, especially in automotive and industrial applications.
Advantages of Hot Plate Welding
Disadvantages of Hot Plate Welding
Hot Gas Welding
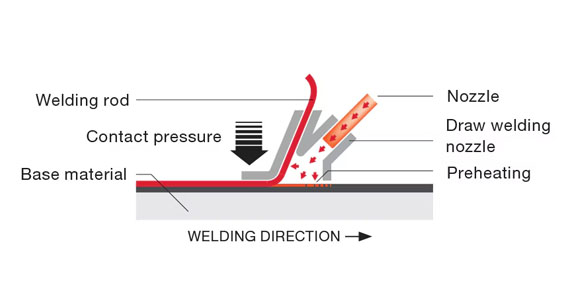
What is Hot Gas Welding?
Hot gas welding uses a stream of hot air or gas to melt the plastic parts and join them together. A welding rod is often used to feed additional material into the weld pool to help complete the bond. This method is commonly used for repairs or joining smaller parts.
Advantages of Hot Gas Welding
Disadvantages of Hot Gas Welding
Spin Welding
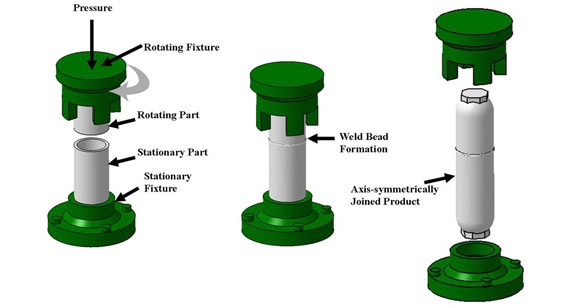
What is Spin Welding?
Spin welding involves rotating one plastic part at high speed while applying pressure to the part being joined. The friction created by the rotation generates heat at the contact interface, which melts the plastic and fuses the parts together.
Advantages of Spin Welding
Disadvantages of Spin Welding
Contact Welding
What is Contact Welding?
Contact welding involves using a heated tool or plate to apply heat to two plastic parts, causing the plastic to melt and bond. This process is simple and effective for smaller applications where precision is less critical.
Advantages of Contact Welding
Disadvantages of Contact Welding
Automatic Welding

What is Automatic Welding?
Automatic welding refers to a welding process where the operation is controlled by machines or robotic systems, rather than manual labor. The system uses pre-programmed instructions to execute tasks, such as applying heat to join materials like metals and plastics. In automatic welding, the welder or robot arm controls the welding equipment, adjusting parameters like speed, power, and duration of the weld to achieve optimal results. The precision of the automatic system ensures a consistent and uniform weld across multiple parts or products, making it ideal for mass production.
This method can be used for various types of welding, including MIG (Metal Inert Gas) welding, TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) welding, and arc welding. The machine or robotic arm operates the welding gun, feeding the welding wire, and adjusting the weld parameters automatically as needed. Automatic welding systems are particularly effective in high-volume industries where high consistency and speed are required.
Advantages of Automatic Welding
Disadvantages of Automatic Welding
Conclusion
Plastic welding is an essential method for joining plastic parts across various industries, each of the 10 methods discussed offers unique advantages and limitations. The best welding method depends on the materials, project requirements, and production volume. Whether you're working with small parts requiring high precision or large plastic components needing strong bonds, understanding these welding methods will help you choose the most efficient and cost-effective option for your needs. By selecting the right technique, you can ensure a strong, durable, and reliable connection between plastic components for your project.
Plastic welding is a reliable and effective method for joining plastic components, offering significant advantages over adhesives and mechanical fasteners. By utilizing heat, pressure, or a combination of both, plastic welding creates seamless, strong, and permanent bonds between plastic materials. This method is widely used across industries, including automotive, aerospace, medical, and consumer goods manufacturing. Below, we explore the primary benefits of plastic welding and why it is a preferred choice for many applications.
Plastic welding provides manufacturers with a durable, cost-effective, and environmentally friendly method of joining plastic parts. Unlike adhesives, which may degrade over time, or mechanical fasteners, which add weight and bulk, plastic welding ensures a permanent, lightweight connection. The process is adaptable to different joint shapes and materials, making it a highly flexible and practical solution for various applications. Whether in CNC machining, prototyping, or mass production, plastic welding delivers superior performance while reducing the need for extra consumables and maintenance.
Additional Consumables
One of the most significant advantages of plastic welding is that it typically does not require additional consumables like adhesives, screws, or rivets. Traditional joining methods often rely on extra materials that increase costs, production time, and complexity. In contrast, plastic welding relies solely on the plastic materials being fused together, sometimes with the addition of a compatible welding rod, if necessary.
By eliminating the need for adhesives and fasteners, plastic welding reduces material waste and streamlines the assembly process. This makes it an efficient and sustainable option for high-volume manufacturing and precision applications, ensuring cost savings while maintaining strong, durable joints.
Compatible with Any Joint Shape
Plastic welding is highly adaptable to a wide variety of joint shapes, making it a superior option for complex and intricate designs. Unlike mechanical fasteners that require pre-drilled holes or adhesives that struggle with uneven surfaces, plastic welding seamlessly joins curved, angular, and non-standard joint configurations.
Manufacturers working with CNC-machined plastic parts, custom prototypes, or intricate industrial components benefit greatly from this flexibility. Plastic welding techniques such as ultrasonic and laser welding can accommodate even the most challenging geometries, ensuring strong bonds without compromising design integrity.
No Ventilation Required
Unlike traditional metal welding, which produces hazardous fumes and requires proper ventilation systems, plastic welding is generally a cleaner and safer process. While some plastic materials may emit minimal fumes when heated, most welding techniques—such as ultrasonic, vibration, and hot plate welding—do not require extensive ventilation or fume extraction systems.
This makes plastic welding more suitable for controlled environments like cleanrooms, medical device manufacturing, and electronic assembly, where maintaining air quality is critical. The reduced need for ventilation also lowers operational costs and simplifies the setup process, making plastic welding a more accessible solution for various industries.
Affordable Choice
Plastic welding is a cost-effective method that reduces production expenses in several ways:
These cost advantages make plastic welding an economical choice for mass production and large-scale manufacturing, ensuring high-quality results at a reduced cost.
Highly Flexible Welding Option
Plastic welding is compatible with a broad range of materials, making it an incredibly versatile joining method. It works well with common thermoplastics such as:
Different plastic welding techniques, such as ultrasonic welding, friction welding, and hot gas welding, can be selected based on material properties and application requirements. This adaptability ensures that manufacturers can use plastic welding across various industries, from medical devices to automotive components, without being limited by material constraints.
Lighter than Using Mechanical Fasteners
In applications where weight reduction is a priority—such as automotive, aerospace, and portable electronic devices—plastic welding offers a significant advantage. Unlike screws, rivets, and other mechanical fasteners, which add weight and bulk to a product, plastic welding creates a seamless, integrated bond without the need for additional hardware.
Reducing the weight of assembled plastic components enhances overall performance, improves energy efficiency, and lowers transportation costs. This is particularly beneficial for industries focused on fuel efficiency, lightweight construction, and miniaturization.
Welds Are Permanent
A key advantage of plastic welding is the creation of permanent and durable bonds. Unlike adhesives, which can degrade over time due to temperature fluctuations, moisture exposure, or chemical interactions, welded plastic joints provide long-lasting strength.
Plastic welding creates a molecular bond between the materials, ensuring a high-strength, impact-resistant connection that can withstand mechanical stress, vibrations, and harsh environmental conditions. This permanence is critical in industries where reliability is paramount, such as:
Because the welds are structurally integrated into the material, they do not loosen or weaken over time, making plastic welding an ideal solution for long-term durability.
To achieve the best results in plastic welding, follow these essential tips:
Select the Right Welding Method:
Different welding techniques work better with specific plastic materials. For example, ultrasonic welding is ideal for small, delicate parts, while hot plate welding is better suited for larger plastic components.
Ensure Proper Surface Preparation:
Clean the plastic surfaces before welding to remove dust, oils, or contaminants. Any impurities can weaken the bond and affect weld quality.
Control Heat and Pressure Settings:
Applying the correct heat and pressure ensures a strong weld. Too much heat can degrade the plastic, while insufficient heat may result in weak bonds. Always fine-tune welding parameters based on material properties.
Check Material Compatibility:
Some plastics weld better than others, and not all thermoplastics are compatible with every welding method. Ensure that the plastics being joined have similar melting points and chemical compositions.
Use Proper Fixturing:
Secure the plastic components firmly in place to maintain precise alignment during welding. Poor positioning can lead to weak or misaligned welds.
Perform Weld Testing:
Before final production, conduct tests on sample materials to verify weld strength, appearance, and durability. This helps identify any necessary adjustments in welding settings.
Monitor for Defects:
Common plastic welding defects include poor fusion, air bubbles, or surface irregularities. Inspect welds carefully and make corrections as needed to achieve optimal results.
Conclusion
Plastic welding is a highly efficient, cost-effective, and reliable method for joining plastic components. Its numerous benefits—including reduced material costs, permanent bonds, compatibility with various joint shapes, and lightweight assembly—make it an excellent choice for manufacturers across multiple industries. By selecting the right welding technique and following best practices, manufacturers can achieve strong, durable, and high-quality plastic welds that stand the test of time.
Whether you’re working with CNC machining parts, custom prototypes, or high-volume production, plastic welding provides a seamless, permanent solution that enhances product performance while reducing costs. With the right tools, materials, and expertise, plastic welding can revolutionize the way plastic components are assembled, ensuring long-term success and reliability.
Plastic welding is a specialized process that involves joining plastic components by applying heat, pressure, or both. While the process may seem straightforward, several factors must be considered to ensure strong, durable, and high-quality welds. Unlike metal welding, plastic welding requires precise control of heat, tools, and materials to achieve optimal results. Understanding the key considerations, such as selecting the right welding rods, welding guns, and welding tools, will help prevent defects and improve the efficiency of plastic welding operations. In this guide, we will explore the essential factors to consider when welding plastics, followed by an overview of different types of plastic welds and their applications.

Heat Considerations in Plastic Welding
Why is Heat Control Important?
Heat is one of the most critical factors in plastic welding. If the temperature is too low, the plastic won’t melt properly, resulting in a weak bond. On the other hand, excessive heat can cause degradation, burning, or warping of the material. To ensure a strong, high-quality weld, it’s essential to control the heat according to the type of plastic being welded.
Key Factors in Heat Control:
Plastic Type: Different plastics have different melting points. For example:
Welding Technique: Each welding method requires specific heat settings. Ultrasonic welding and hot gas welding use different temperature ranges and heat application methods.
Preheating: In some cases, preheating the plastic parts before welding can help achieve a more uniform and consistent bond.
Heat Source Control: Ensure that the heat gun or welding tool is calibrated correctly to avoid overheating or underheating.
Welding Rods for Plastic Welding
What Are Welding Rods?
Welding rods are filler materials used in hot gas welding and hot plate welding to reinforce the weld joint. The rod must be made of the same material as the plastic being welded to ensure a strong bond.
Choosing the Right Welding Rod
Material Compatibility:
Rod Diameter:
Rod Shape:
Proper Storage of Welding Rods
Welding rods should be stored in a dry, cool place to prevent contamination and moisture absorption, which can weaken the weld.
Welding Guns for Plastic Welding
What is a Welding Gun?
A plastic welding gun is a tool used to generate the necessary heat and airflow to melt plastic materials for welding. There are different types of welding guns, depending on the welding method used.
Types of Welding Guns
Hot Air Welding Gun:
Extrusion Welding Gun:
Ultrasonic Welding Gun:
Selecting the Right Welding Gun
Welding Tools for Plastic Welding
Beyond welding guns, several essential tools help improve the efficiency and quality of plastic welding:
Welding Nozzles
Clamps and Fixtures
Wire Brushes
Temperature Controllers
Different welding techniques result in different weld types, each with varying strength and application suitability. Below are the six most common plastic welds.
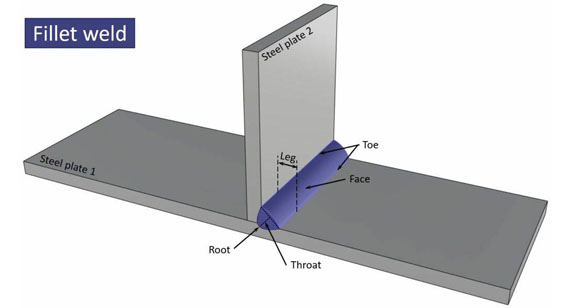
1. Fillet Welds
2. Inside Fillet Joints
3. Flat Fillet Appearances
4. X-Joints
5. V-Joints
6. Lap Joints
Plastic welding plays a significant role in industries that require durable, high-quality, and cost-effective solutions for joining plastic parts. Here are some of the common applications where plastic welding techniques are utilized:
Aerospace: Lightweight, strong plastic components are often welded for use in aerospace applications. Methods like laser welding and friction welding are used to produce parts that need to withstand high stress and harsh conditions.
Agriculture: In agricultural applications, plastic welding is used to create tanks, containers, and protective covers. The ability to weld plastics without the need for mechanical fasteners makes it ideal for agricultural machinery and products.
Automotive: Plastic parts such as bumpers, dashboards, and interior components are welded together to create strong, durable joints. High-volume techniques such as ultrasonic welding and vibration welding are commonly employed in automotive manufacturing.
Marine and Ocean: Plastic welding is used to manufacture watertight seals for marine and ocean equipment. Methods like high-frequency welding are used to ensure strong, leak-proof joints for plastic boat parts, tanks, and pipes.
Creating Plastic Parts
Conclusion
Plastic welding is a versatile and essential process used in numerous industries. By carefully considering heat settings, welding rods, tools, and welding guns, manufacturers can ensure strong, reliable welds. Understanding the different weld types and their applications allows engineers and fabricators to choose the best method for their specific needs. Whether in aerospace, automotive, agriculture, or marine applications, plastic welding provides durable, high-quality results that meet industrial demands.
Why Are Plastics So Widely Used?
Plastics are widely used due to their lightweight, durability, corrosion resistance, and cost-effectiveness. They are easy to manufacture, mold into various shapes, and provide excellent insulation properties. Plastics are also resistant to chemicals and moisture, making them suitable for automotive, medical, aerospace, and consumer goods industries. Their adaptability and recyclability further enhance their appeal in modern manufacturing.
Can Different Plastics Be Welded Together?
Yes, but only if the plastics are chemically compatible. Welding different plastics together requires materials with similar melting points and molecular structures. Thermoplastics like polyethylene (PE) and polypropylene (PP) can typically be welded together, but attempting to weld dissimilar plastics, such as ABS and PVC, may result in weak or failed joints.
Is the Weld Strong?
Yes, properly executed plastic welds can be as strong as or stronger than the original plastic material. The strength of the weld depends on factors such as:
What Types of Welds Are Used for Plastics?
The six most common types of plastic welds include:
Each weld type is chosen based on the material, application, and strength requirements.
Is Plastic Welding Worth It?
Yes, plastic welding is a cost-effective, durable, and efficient method for joining plastic components. It eliminates the need for adhesives and mechanical fasteners, reducing overall material and labor costs. Additionally, plastic welding ensures a permanent, lightweight, and structurally sound bond, making it ideal for industrial applications like automotive parts, medical devices, and consumer electronics.
Will JB Weld Plastic Become Hard?
Yes, JB Weld PlasticWeld is a two-part epoxy putty designed to bond and repair plastic materials. It cures into a hard, durable surface that can be sanded, painted, or drilled. However, unlike plastic welding, JB Weld does not fuse plastic at a molecular level—it adheres to the surface and may not be as strong as a welded joint.
Can You Weld Cracked Plastic?
Yes, cracked plastic can be welded using techniques like hot gas welding, ultrasonic welding, or friction welding. The success of the repair depends on:
Plastic welding can fully restore strength and durability, making it superior to adhesives or temporary fixes.
What Is the Most Effective Way to Repair Broken Plastic?
The best repair method depends on the type of plastic and the extent of the damage:
For load-bearing applications, plastic welding is the most effective solution.
Is Plastic Welding Stronger Than Glue?
Yes, plastic welding is generally stronger than glue because it fuses the plastic at a molecular level, forming a permanent bond. In contrast, glue adheres only to the surface, making it susceptible to peeling or breaking under stress. Welded joints provide:
Plastic welding is preferred for industrial, automotive, and structural applications requiring superior durability.
Can Plastics Be Welded Together?
Yes, plastics can be welded together, but they must be compatible thermoplastics with similar melting points. Welding incompatible plastics can result in weak bonds or material degradation. Some common welding techniques for plastics include:
For best results, always use welding rods made from the same type of plastic as the material being welded.
How Strong Are Plastic Welds?
Plastic welds can be as strong or stronger than the original material when done correctly. Factors influencing weld strength include:
When high-stress resistance is needed, techniques like hot plate welding and spin welding provide the most durable bonds.
Can You Weld Plastics with Heat?
Yes, heat is the primary method used in plastic welding. Different welding techniques use heat to melt plastic and create a strong bond:
Proper heat control is essential to prevent burning, warping, or weak welds.
What Is the Best Way to Join Plastics Together?
The best joining method depends on the application:
For structural integrity, longevity, and high strength, plastic welding is the preferred choice.
Which Is Better, JB Weld or Epoxy?
Both JB Weld and epoxy adhesives are used for plastic repair, but they have key differences:
Plastic welding, however, is stronger than both, as it physically fuses the plastic rather than just adhering to the surface.
How Strong Is JB Weld Plastic?
JB Weld PlasticWeld is strong but not as durable as plastic welding. It offers a tensile strength of up to 3500 PSI, making it useful for minor repairs. However, it may crack under high stress, whereas welded plastic joints maintain their integrity under load-bearing conditions.
Will Magnets Stick to JB Weld?
No, JB Weld is not magnetic. It is a non-metallic adhesive that does not contain iron, nickel, or cobalt, which are necessary for magnetism. However, if applied to a metal surface, magnets will still stick to the underlying material.
What Happens If You Weld on a Magnet?
Welding on a magnet can cause issues such as:
To avoid these issues, remove the magnet or use a demagnetizing tool before welding.
Conclusion
Plastic welding is a strong, reliable, and efficient method for joining plastics, outperforming adhesives and mechanical fasteners in durability. Whether you’re repairing cracked plastic, manufacturing custom CNC parts, or working in aerospace or automotive industries, understanding the best welding techniques, material compatibility, and proper heat control will ensure long-lasting, high-quality welds.
