15 years one-stop China custom CNC machining parts factory
 185 |
Published by VMT at Mar 02 2025 | Reading Time:About 3 minutes
185 |
Published by VMT at Mar 02 2025 | Reading Time:About 3 minutes
Weld lines in injection molding can be a critical defect, affecting both aesthetic appeal and mechanical strength. These lines occur when two or more molten plastic flows meet but do not fully fuse, creating a visible seam or weakness in the finished product. This defect can result in structural integrity issues, reduced impact resistance, and visual imperfections that lower product quality.
For manufacturers working in CNC machining, CNC lathes, CNC turning centers, and custom CNC machining, ensuring flawless injection-molded parts is essential to maintaining high precision, durability, and customer satisfaction. Understanding what causes weld lines and how to prevent them through mold design, process optimization, and material selection is key to achieving high-quality CNC-machined parts.
A weld line in injection molding is a defect that appears as a visible line or seam on a plastic part. It occurs when two or more molten plastic fronts meet but fail to fully merge, leaving a weak joint. This results in structural vulnerabilities and often affects the surface finish of the part.
Weld lines are particularly problematic in components requiring high mechanical strength, such as automotive, aerospace, and medical device parts. They are often mistaken for flow lines, but flow lines are caused by uneven cooling and resin flow, whereas weld lines result from incomplete fusion of polymer streams.
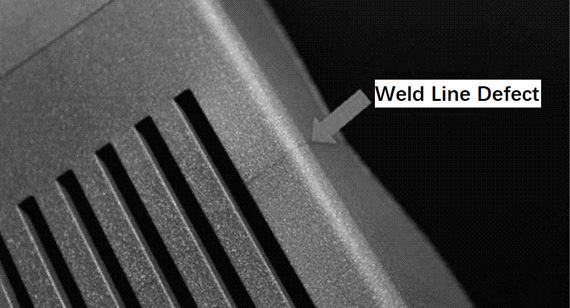
Weld lines form due to incomplete molecular bonding when separate plastic flow fronts meet. The primary reasons include:
✔ Low mold temperature, preventing proper fusion.
✔ Inadequate injection pressure, causing flow hesitation.
✔ Poor gate location, leading to improper flow paths.
✔ High cooling rate, solidifying the polymer before full integration.
Addressing these factors helps minimize weld lines, ensuring stronger, defect-free injection-molded parts.
Weld lines manifest as thin, visible seams in injection-molded parts, often found near:
These defects can lead to:
✔ Cracking under stress in load-bearing applications.
✔ Reduced cosmetic appeal due to uneven surface finishes.
✔ Weakened impact resistance, compromising part durability.
Understanding where and why weld lines form allows manufacturers to implement effective countermeasures.
Weld lines in injection molding are a common defect that occurs when two or more molten plastic flows meet but fail to fuse properly. These lines create weak points in the final part, reducing structural integrity, durability, and surface aesthetics.
For manufacturers in CNC machining, CNC turning centers, and CNC prototype machining, avoiding weld lines is essential to producing high-quality, defect-free plastic components. The primary causes of weld lines include pressure variations, improper temperature settings, mold design flaws, injection speed issues, material impurities, and excessive mold release agents. Understanding these factors helps optimize molding conditions and improve final part quality.

1. Pressure: Inconsistent or Low Injection Pressure
How Injection Pressure Affects Weld Line Formation
✔ Low injection pressure prevents the plastic from fully bonding, leading to weak weld lines.
✔ Uneven pressure distribution creates incomplete fusion, increasing the risk of defects.
✔ Improper holding pressure allows premature solidification, reducing molecular bonding at weld seams.
Solution:
Maintaining optimal injection pressure reduces weld lines, ensuring stronger, more durable plastic parts.
2. Temperature: Improper Melt and Mold Temperature
How Temperature Influences Weld Lines
✔ Low melt temperature prevents polymer chains from fully bonding, leading to weak weld lines.
✔ Cold mold surfaces cause premature solidification, reducing flow continuity.
✔ Uneven heating creates inconsistent plastic flow, increasing defect risk.
Solution:
Ensuring proper temperature settings helps achieve better fusion between plastic fronts, minimizing weld line defects.
3. Mold Design: Poor Flow Paths and Gating Placement
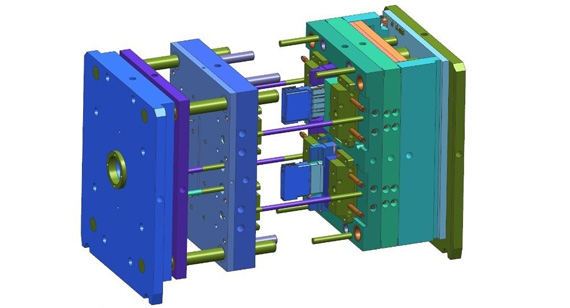
How Mold Design Affects Weld Lines
✔ Incorrect gate placement causes uneven plastic flow, leading to multiple weld fronts.
✔ Sharp corners and abrupt transitions create disruptions in flow paths.
✔ Inadequate venting traps air, preventing proper fusion.
Solution:
A well-designed mold ensures uniform plastic flow, reducing weld lines and improving part quality.
4. Speed: Incorrect Injection and Flow Rate
How Injection Speed Influences Weld Line Formation
✔ Slow injection speeds allow the material to cool too early, preventing proper bonding.
✔ Fast speeds cause air entrapment and turbulence, disrupting weld fusion.
✔ Inconsistent speed control leads to variable material viscosity, affecting part quality.
Solution:
Correcting speed-related defects improves weld line strength and surface finish in plastic injection molding.
5. Impurities: Material Contamination and Additives
How Material Impurities Contribute to Weld Lines
✔ Contaminated plastic resin disrupts flow consistency, leading to weak weld areas.
✔ Recycled or mixed materials introduce uneven melt characteristics, affecting bonding.
✔ Excessive fillers alter polymer properties, reducing fusion capability.
Solution:
Maintaining clean, high-quality plastic resins significantly reduces weld lines, improving final part strength.
6. Excessive Release Agent: Barrier to Proper Fusion
How Mold Release Agents Affect Weld Line Formation
✔ Too much release agent creates a non-stick surface, preventing plastic bonding.
✔ Residue buildup disrupts material adhesion, increasing defects.
✔ Uneven application leads to inconsistent part strength and surface finish.
Solution:
By controlling release agent usage, manufacturers can prevent weak weld lines, ensuring stronger and more reliable injection-molded parts.
Conclusion
Weld lines in injection molding result from insufficient pressure, improper temperatures, flawed mold design, incorrect injection speeds, material contamination, and excessive mold release agents. Addressing these six key factors ensures better material fusion, stronger plastic parts, and improved surface quality.
For CNC machining, CNC turned parts, and custom CNC machining, ensuring high-quality, defect-free plastic components is critical to maintaining structural integrity and customer satisfaction. By implementing process optimizations and design improvements, manufacturers can eliminate weld lines and enhance product performance.
Key Takeaways: How to Reduce Weld Lines in Injection Molding
✔ Increase injection pressure and optimize holding time.
✔ Maintain proper melt and mold temperature for better fusion.
✔ Redesign mold flow paths and gate locations.
✔ Adjust injection speed to avoid turbulence and premature cooling.
✔ Use high-quality resins and minimize impurities.
✔ Limit mold release agent application to prevent adhesion issues.
Implementing these strategies ensures flawless plastic parts, making CNC machining services and CNC prototype machining more efficient and reliable.
Weld lines in injection molding are more than just a cosmetic issue—they are structural weak points that can compromise the strength, durability, and overall quality of a plastic part. These defects occur when two or more plastic melt flows meet but fail to bond completely, leaving a visible line or seam.
For industries that rely on CNC machining, CNC turning centers, and CNC prototype machining, weld lines can reduce product lifespan, impact mechanical performance, and create rejection rates that lead to higher production costs. Understanding why weld lines should be avoided ensures higher-quality injection-molded components for automotive, aerospace, medical, and consumer product manufacturing.
Fragility: Weakening the Structural Integrity of Parts
How Weld Lines Reduce Mechanical Strength
✔ Incomplete molecular bonding at the weld line reduces tensile strength.
✔ Parts are more likely to crack under mechanical stress or impact.
✔ Load-bearing components fail faster due to weak weld seams.
Industries Most Affected by Weld Line Fragility
Real-World Impact
If a plastic automotive component with a weld line is subjected to vibrations, heat, and external forces, the weakened area can crack, leading to premature part failure. Similarly, in medical applications, an implant or surgical tool with weld line weaknesses may break under stress, posing a significant risk to patient safety.
Solution: How to Strengthen Weld Lines
Avoiding weld lines ensures reliable, structurally sound plastic parts that meet industry standards and safety regulations.
Deform the Surface Appearance: Compromising Aesthetic and Functional Quality
How Weld Lines Affect Surface Finish
✔ Visible seams and inconsistencies lower product quality.
✔ Surface irregularities affect coatings, painting, and finishing.
✔ High-end consumer products require flawless appearances.
Industries Where Surface Appearance Matters Most
Real-World Impact
A smartphone casing with a visible weld line can appear low-quality, reducing consumer trust in the brand. Similarly, an automotive dashboard with noticeable weld marks affects customer perception of premium quality.
Solution: How to Improve Surface Appearance
Eliminating weld lines ensures a smooth, polished finish, making products more visually appealing and marketable.
Conclusion: Why Avoiding Weld Lines is Essential for High-Quality Manufacturing
Weld lines are not just an aesthetic issue; they weaken structural integrity, reduce durability, and lower the perceived quality of a product. By addressing pressure, temperature, mold design, and material selection, manufacturers can eliminate weld lines and ensure stronger, high-performance plastic parts.
For CNC machining services, CNC turning factories, and prototype machining, ensuring flawless injection-molded parts improves reliability, customer satisfaction, and overall production efficiency.
Weld lines in plastic injection molding compromise both aesthetic quality and structural integrity. These defects form when two molten plastic flows meet but do not completely bond, creating weak points and visible marks on the final product.
For industries like automotive, medical, aerospace, and electronics, avoiding weld lines is crucial to producing high-quality, durable, and visually appealing components. By modifying part design, mold design, molding conditions, and plastic processing parameters, manufacturers can significantly reduce or eliminate weld lines in injection-molded parts.
1. Change the Part Design
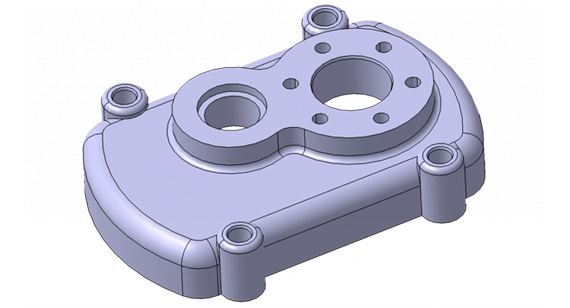
How Part Design Influences Weld Lines
✔ Sharp edges and abrupt transitions disrupt material flow, leading to multiple weld fronts.
✔ Thin-walled areas cool too quickly, preventing proper molecular bonding.
✔ Inserts and holes interrupt melt flow, causing weak weld seams.
Best Practices for Part Design Optimization
✅ Increase Wall Thickness – Ensures better material flow and fusion.
✅ Eliminate Sharp Edges – Rounded edges create smoother plastic flow.
✅ Reposition Inserts & Holes – Placing features away from weld-prone areas reduces seam formation.
✅ Use Uniform Thickness – Prevents uneven cooling and material separation.
By optimizing part design, manufacturers can improve plastic flow paths and reduce the likelihood of weld lines.
2. Change the Mold Design
The injection mold design directly affects how the plastic flows, fills, and bonds during molding. By optimizing gating, runner types, and venting, manufacturers can control the movement of molten plastic, minimizing weld lines.
Three Key Mold Design Modifications to Reduce Weld Lines
1. Gating: Controlling Plastic Entry Points
How Gating Affects Weld Lines
✔ Poor gate placement causes multiple melt fronts, leading to weak weld seams.
✔ Uneven plastic entry results in incomplete material fusion.
✔ Incorrect gate size affects pressure distribution, leading to visible marks.
Best Practices for Gate Optimization
✅ Move the gate to a location that allows continuous flow without interruptions.
✅ Use multiple gates strategically to create a balanced flow path.
✅ Select an appropriate gate size to ensure adequate pressure and flow rate.
Proper gate placement can significantly reduce weak joints and visible weld lines in molded parts.
2. Runner Type: Controlling Plastic Flow Paths
How Runner Systems Impact Weld Lines
✔ Cold runners cause early solidification, increasing weld line formation.
✔ Improperly sized runners create uneven material flow, leading to defects.
✔ Poorly balanced runner designs generate multiple flow fronts, causing weld lines.
Best Practices for Runner System Design
✅ Use hot runners to maintain a consistent melt temperature.
✅ Balance runner size and shape to distribute plastic evenly.
✅ Minimize runner length to reduce cooling time before fusion occurs.
A well-designed runner system ensures better material flow, stronger welds, and fewer visible marks.
3. Venting: Eliminating Trapped Air for Better Fusion
How Venting Affects Weld Lines
✔ Trapped air prevents proper plastic bonding, creating weak weld lines.
✔ Poor venting leads to air bubbles, resulting in structural weaknesses.
✔ Over-pressurized cavities cause inconsistent flow, increasing seam visibility.
Best Practices for Mold Venting
✅ Incorporate vents in critical areas to remove trapped air.
✅ Use vacuum venting systems for high-precision molding.
✅ Ensure vents are properly sized to allow air escape without material leakage.
Effective venting systems ensure complete plastic fusion, reducing the risk of weld line formation.
3. Adjusting Molding Conditions
Why Molding Conditions Affect Weld Lines
✔ Low injection speed and pressure lead to incomplete fusion.
✔ Improper temperature settings result in premature cooling and weak bonds.
✔ Rapid cooling causes uneven flow, increasing weld line defects.
Best Practices for Molding Condition Optimization
✅ Increase injection speed and pressure to improve plastic fusion.
✅ Adjust holding pressure to ensure better weld strength.
✅ Extend cooling time to allow proper material bonding.
Fine-tuning molding conditions enhances part quality, weld strength, and surface finish.
4. Plastic Processing: Key Factors Affecting Weld Lines
There Are Two Key Plastic Processing Aspects That Influence Weld Line Formation:
1. Plastic Melt & Mold Temperature
✔ Low melt temperature causes incomplete material bonding.
✔ Cold mold surfaces solidify plastic too early, preventing proper fusion.
Best Practices for Temperature Optimization
✅ Increase melt temperature to enhance molecular diffusion.
✅ Raise mold temperature to delay premature cooling.
✅ Use uniform heating to maintain flow consistency.
2. Injection Speed & Pressure
✔ Slow speeds cause early cooling, preventing complete fusion.
✔ Low pressure results in weak, visible weld seams.
Best Practices for Speed & Pressure Optimization
✅ Increase speed to maintain continuous material flow.
✅ Use higher pressure to eliminate gaps between plastic flows.
✅ Balance cycle times to ensure proper cooling and bonding.
Optimizing plastic processing parameters ensures seamless part formation with minimal weld defects.
Conclusion: Eliminating Weld Lines for High-Quality Injection-Molded Parts
Weld lines in plastic injection molding weaken parts and reduce visual appeal. By modifying part design, mold design, molding conditions, and plastic processing parameters, manufacturers can:
✔ Enhance structural integrity by ensuring complete material fusion.
✔ Improve surface appearance for flawless, high-quality components.
✔ Increase production efficiency by reducing part rejection rates.
For industries requiring CNC machining, CNC turned parts, and CNC prototype machining, eliminating weld lines ensures reliable, defect-free production.
Implementing these best practices results in stronger, more durable, and visually perfect plastic injection-molded parts.
Weld lines in injection molding are a common defect that weakens CNC machined parts. By optimizing pressure, temperature, mold design, and material properties, manufacturers can significantly reduce weld line defects.
For industries like automotive, aerospace, and CNC prototype machining, achieving flawless, high-strength components is crucial. Implementing proper injection molding techniques ensures high-quality CNC-turned parts with minimal defects.
What is the difference between a weld line and a flow line?
A weld line forms when two molten plastic flows meet but do not fully fuse, leading to a visible seam that weakens the part. A flow line, on the other hand, is a cosmetic defect that appears as streaks or patterns due to uneven material flow or cooling rates. Weld lines are a structural issue, whereas flow lines mainly affect surface aesthetics.
What is a weld line called?
A weld line is also known as a:
✔ Knit line – Often used interchangeably in the industry.
✔ Seam line – Refers to the visible join between two plastic flows.
✔ Bond line – Describes the area where the plastic should fuse but does not completely.
What is the difference between a weld line and a parting line?
A weld line is a material defect that forms due to incomplete bonding of molten plastic flows. A parting line, however, is a mold design feature where the two halves of the mold meet, forming a visible but non-structural seam.
What is the difference between a weld line and a meld line?
✔ Weld Line – Forms when two flow fronts meet at a shallow angle and fail to fully fuse, leading to weak mechanical strength.
✔ Meld Line – Occurs when two plastic flows meet at a higher temperature and merge better, resulting in a stronger bond with less structural weakness.
While both are visible seams, meld lines generally maintain better mechanical integrity than weld lines.
What is the difference between a knit line and a weld line?
✔ Knit Line – A broader term that includes both weld lines and meld lines, referring to any meeting point of plastic flows.
✔ Weld Line – A weaker type of knit line, occurring when the plastic does not fully fuse.
How to reduce weld lines in injection molding?
To minimize weld lines, manufacturers should:
✔ Optimize gate placement to ensure even material flow.
✔ Increase mold and melt temperature to enhance fusion.
✔ Adjust injection speed and pressure for better flow dynamics.
✔ Use venting to eliminate trapped air, which can prevent proper bonding.
✔ Modify part design to reduce interruptions in the plastic flow path.
These strategies help ensure stronger weld areas and improved surface finish.
What is the root cause of a weld line?
✔ Low mold or melt temperature, preventing proper fusion.
✔ Poor gate placement, leading to multiple flow fronts.
✔ Insufficient injection pressure, causing incomplete bonding.
✔ Air entrapment, preventing direct contact of the plastic flows.
By addressing these root causes, manufacturers can eliminate weak weld lines and improve part strength.
What is the angle of a weld line?
Weld lines typically form at an angle where two melt fronts converge. The sharper the angle, the weaker the weld line. Ideally, flow fronts should meet at angles greater than 135° to enhance bonding and reduce seam visibility.
How to improve weld line strength?
✔ Increase mold and melt temperatures to improve polymer diffusion.
✔ Adjust holding pressure to ensure full molecular bonding.
✔ Enhance material selection, using resins with better flow properties.
✔ Modify gate location to reduce weld line formation.
Stronger weld lines lead to more durable injection-molded parts, ideal for high-stress applications in CNC machining, aerospace, and automotive industries.
How to reduce sink marks in injection molding?
✔ Increase holding pressure to allow more material to fill voids.
✔ Use uniform wall thickness to promote even cooling.
✔ Optimize mold temperature to prevent localized shrinkage.
✔ Slow down cooling rates to allow gradual material contraction.
These adjustments help ensure smooth, defect-free surfaces, reducing the need for post-processing.
What does a good welding line look like?
✔ Minimal visibility with a uniform surface finish.
✔ No structural weaknesses or cracks in high-stress areas.
✔ Smooth transition between plastic flows, without discoloration or rough textures.
A well-formed weld line should be indistinguishable from the surrounding material, maintaining both strength and aesthetics.
What causes flow lines in injection molding?
✔ Uneven cooling rates cause streaks and flow marks.
✔ Inconsistent melt flow speed creates visual defects.
✔ Improper mold design can cause turbulence and inconsistent filling.
Flow lines can be minimized by optimizing material flow, temperature control, and injection parameters.
Final Thoughts
Avoiding weld lines and flow defects is essential for producing high-quality plastic components. By optimizing injection molding conditions, improving mold design, and adjusting processing parameters, manufacturers can enhance part strength, visual appeal, and overall performance.
For industries requiring CNC machining, CNC turned parts, and CNC prototype machining, ensuring flawless plastic molding improves product quality and customer satisfaction.
